National Consumer Day is observed on the 24th of December annually in India, commemorating the enactment of the Consumer Protection Act in 1986 on this significant date.

On 24th December every year, National Consumer Day is celebrated all over India.
National Consumer Day provides an opportunity for the consumer to get more aware of their rights, and how to dodge or take action against unfair trade practices.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
On 24th December every year, National Consumer Day is celebrated all over India.
The reason behind celebrating National Consumer Day is to spread awareness about consumer rights and responsibilities. In 1986 on this day, the Consumer Protection Act received the assent of the President.
A Consumer is a person or household that acquires goods and services generated within the economy. They obtain goods or services for direct use or possession rather than for exchange, resale or use in production and manufacturing.
Announced under the Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2019, the CCPA handles matters related to the violation of the rights of consumers.
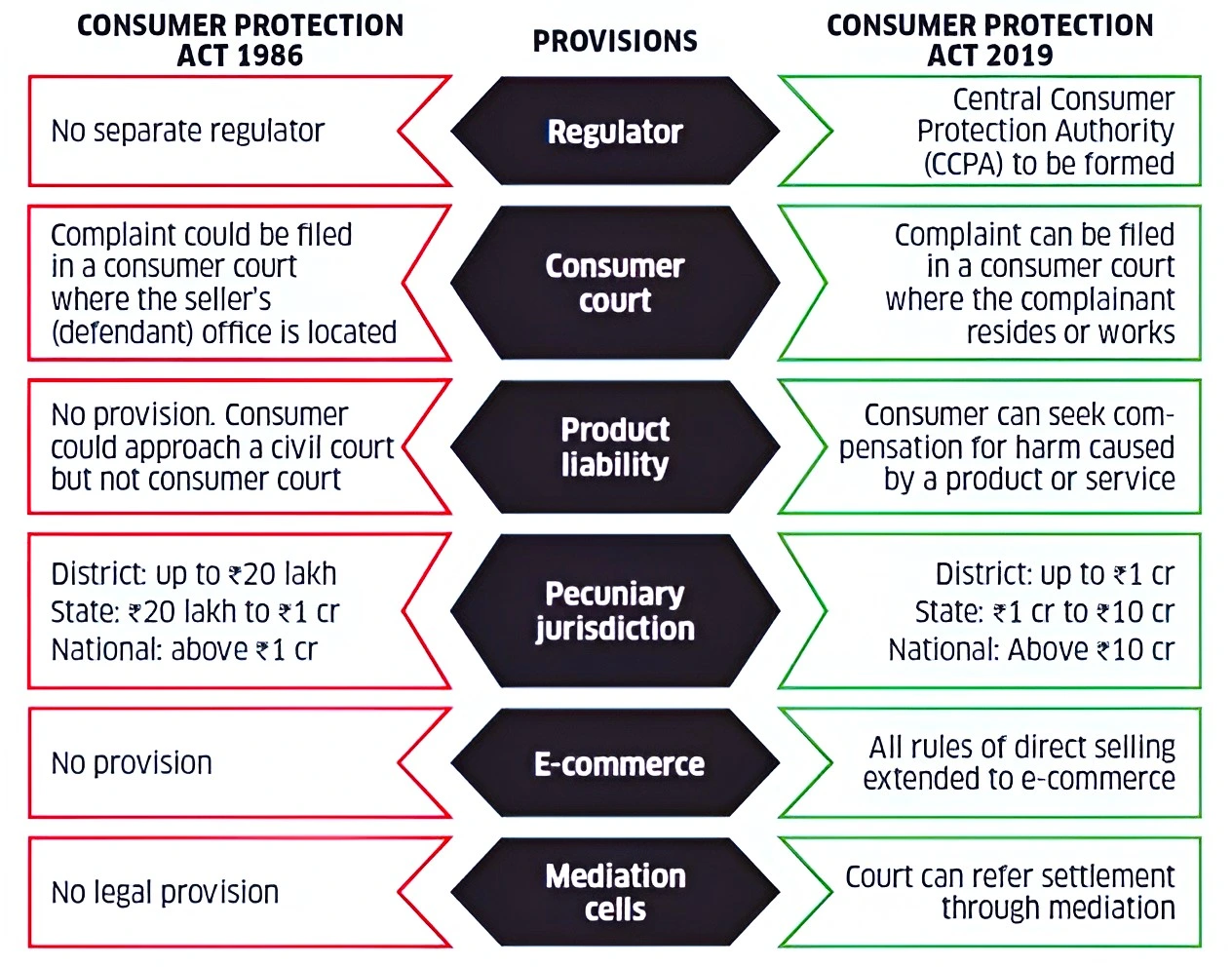
The Consumer Protection Act 1986 safeguards and protects their rights as customers by making grievance redressal mechanisms easy and efficient. The act has been successful in encouraging consumers to speak against insufficiency and flaws in goods and services.
The BIS is India’s National Standards Body that works under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs. Based on the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 2016, it came into effect on 12 October 2017.
The act covers goods and services of all public, private, or cooperative sectors, except the ones exempted by the central government.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>