Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Brief about India’s Seismic vulnerability.
Body
- Discuss about the Vulnerability of India to Earthquake-Related Hazards.
- Examples of Major Disasters Caused by Earthquakes in India
- Salient Features of Major Earthquake Disasters in India
Conclusion
- Conclude your answer with a comprehensive Approach.
|
Introduction:
India is highly vulnerable to earthquake-related hazards due to its location in the seismic zone. The country has a long history of seismic activity, and the northern and north-eastern regions are particularly prone to earthquakes.
Body:
Vulnerability of India to Earthquake-Related Hazards:
India is located in a seismically active region, with several tectonic plates converging in the region. The country is divided into four seismic zones, and most of the northern and northeastern regions fall under zone IV and V, which are considered to be highly active seismic zones. These regions are prone to earthquakes of high magnitude, and the densely populated cities in these areas are highly vulnerable to the impact of earthquakes.
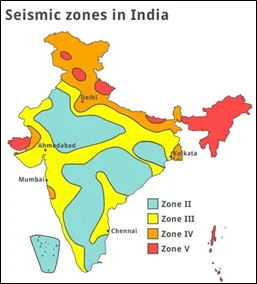
- Examples of Major Disasters Caused by Earthquakes in India:
- Latur Earthquake (1993): The Latur earthquake was a 6.2 magnitude earthquake that struck Maharashtra on September 30, 1993. The earthquake caused significant damage to property and infrastructure in the region and claimed more than 9,000 lives.
- Bhuj Earthquake (2001): The Bhuj earthquake was a 7.7 magnitude earthquake that struck Gujarat on January 26, 2001. The earthquake claimed more than 20,000 lives and caused widespread damage to property and infrastructure in the region.
- Sikkim Earthquake (2011): The Sikkim earthquake was a 6.9 magnitude earthquake that struck Sikkim on September 18, 2011. The earthquake caused widespread damage to property and infrastructure in the region and claimed more than 100 lives.
- Salient Features of Major Earthquake Disasters in India:
- Densely populated cities in affected regions are highly vulnerable.
- Lack of preparedness and inadequate infrastructure.
- Delay in rescue and relief operations.
- Lack of coordination among various agencies.
- Significant loss of life and property damage.
- Need for better risk assessment and early warning systems.
- Importance of land-use planning to reduce vulnerability.
- Need for public awareness campaigns to increase preparedness.
- Importance of adopting a comprehensive approach to earthquake risk reduction.
Conclusion:
The major earthquake disasters in the last three decades have highlighted the need for better preparedness, infrastructure, and coordination among various agencies to mitigate the impact of earthquakes. It is essential to adopt a comprehensive approach to earthquake risk reduction, including risk assessment, early warning systems, land-use planning, and public awareness campaigns.

