Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction:
Body
- Explain how independent and empowered social audit mechanism is an absolute must in every sphere of public service
- Add examples for clarity.
Conclusion
- Give prospective way ahead
|
Introduction:
Social audit is a process of assessing, monitoring and evaluating the performance of public services and programs by involving citizens and civil society organizations. It is an important tool for promoting transparency, accountability, and good governance.
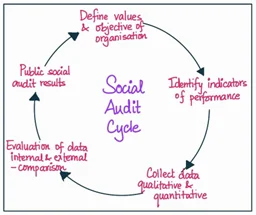
Body:
An independent and empowered social audit mechanism is essential in every sphere of public service, including the judiciary, to ensure performance, accountability and ethical conduct.
- Judiciary:
- Example: In India, the concept of social audit can be extended to the judiciary through mechanisms such as judicial review and transparency in the judicial process. Public scrutiny and evaluation of judicial decisions and the conduct of judges can contribute to accountability and enhance public trust in the judiciary.
- Instances of social audits in the judiciary can include the examination of delays in case disposal, transparency in appointment processes, and ethical conduct of judges.
- Public Services:
- Example: In India, the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) incorporates social audits to ensure transparency, accountability, and public participation in the implementation of the rural employment guarantee scheme.
- Citizens, along with civil society organizations, conduct audits to verify work undertaken, wages paid, and the overall effectiveness of the program.
- Healthcare:
- Example: In India, initiatives like the Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK) have implemented social audits to monitor the provision of maternal and child health services.
- These audits involve the participation of community members, enabling them to assess the availability and accessibility of services, infrastructure, and the conduct of healthcare professionals.
- Education:
- Example: In India, the Right to Education Act (RTE) mandates the involvement of School Management Committees (SMCs) in conducting social audits to monitor the implementation of educational policies.
- SMCs, consisting of parents and community representatives, assess aspects such as teacher attendance, the functioning of mid-day meal programs, and infrastructure facilities.
- Public Infrastructure Projects:
- Example:For instance, the Swachh Bharat Mission (Clean India Mission) in India incorporates social audits to evaluate the progress and impact of sanitation initiatives at the grassroots level.
- These audits involve community members inspecting the construction and usage of toilets, assessing the effectiveness of the program, and identifying any discrepancies or issues.
Conclusion:
An independent and empowered social audit mechanism is essential in every sphere of public service, including the judiciary. It can help ensure that public services are delivered efficiently, transparently and accountability. In the case of the judiciary, social audit can help promote ethical conduct, transparency, and accountability, thereby enhancing public trust in the institution.

