Context
End to End encryption has fundamentally shifted the landscape of data privacy and control, impacting various stakeholders profoundly.
What is encryption?
- Encryption involves changing information that can be consumed into a form that is not consumable, following specific sets of rules.
- There are different kinds of such rules (See Image).
- For example, (with particular settings) the Data Encryption Standard (DES) encrypts the words “ice cream” to AdNgzrrtxcpeUzzAdN7dwA== with the key “kite”. If the key is “motorcycle, ” the encrypted text becomes 8nR+8aZxL89fAwru/+VyXw==.
- The key is some data using which a computer can ‘unlock’ (decrypt) some ‘locked’ (encrypted) text, knowing the rules used to ‘lock’ it.
What is End to End Encryption?
- End to End Encryption is a secure communication method. E2E is encryption that refers to particular locations between which information moves.
- It encrypts data between two devices (sender and receiver). It prevents unauthorized access during transfer, excluding third-party access such as cloud service providers, internet service providers (ISPs), and cybercriminals.
- There are two important forms of encryption: Encryption-in-Transit and E2E encryption.
- Encryption-in-transit means it is encrypted before a message is relayed from the server to the actor (or vice versa). This scheme is used to prevent an actor from being able to read the message’s contents by intercepting the relay.
- In End to End Encryption, the message is encrypted both in transit and at rest – i.e. when being relayed from the sender’s phone to the server (or vice versa) and when it is sitting inside the server. It is only decrypted when a receiver receives the message.
Can End to End Encryption Be Cracked?
- End to End Encryption promises to keep messages confidential.
- A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack can crack this encryption.
- In this scenario, an attacker intercepts the encryption key through device hacking.
Prevention of MITM Attacks:
- Users can safeguard against MITM attacks by verifying fingerprints in a separate channel, ensuring the integrity of the encryption process.
|
Mechanism of End to End Encryption
- The encryption keys (for scrambling and unscrambling messages) are not stored with the service provider but directly on the user’s devices (endpoints).
- Messages are transformed into an unreadable format using a special algorithm during transmission.
- This “scrambled” data is unreadable without the decryption key.
How is information encrypted?
- There are many Encryption methods that vary based on the level of secrecy and protection.
- There are major differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption
Hash functions
- This function is responsible for encrypting a message.
- It has various properties
- Message Concealment: The hash function encrypts input messages into digests, ensuring that given the digest, the original message content remains confidential.
- Consistent Digest Length: Regardless of the length of the input message, the hash function produces a fixed-length digest, preventing inference about the original message length from the digest.
- Unique Digests: Different messages result in distinct digests, preventing the generation of identical encrypted outputs for varied input data.
Example Of Hash Function:
- DES Algorithm, Feistel Function, etc.
|
-
- Symmetric encryption: Symmetric encryption utilizes a single key for encryption and decryption, exemplified by DES and Triple DES.
- Symmetric encryption is suitable when the sender and recipient are the same, as in encrypting a computer’s hard drive or setting a WiFi password.
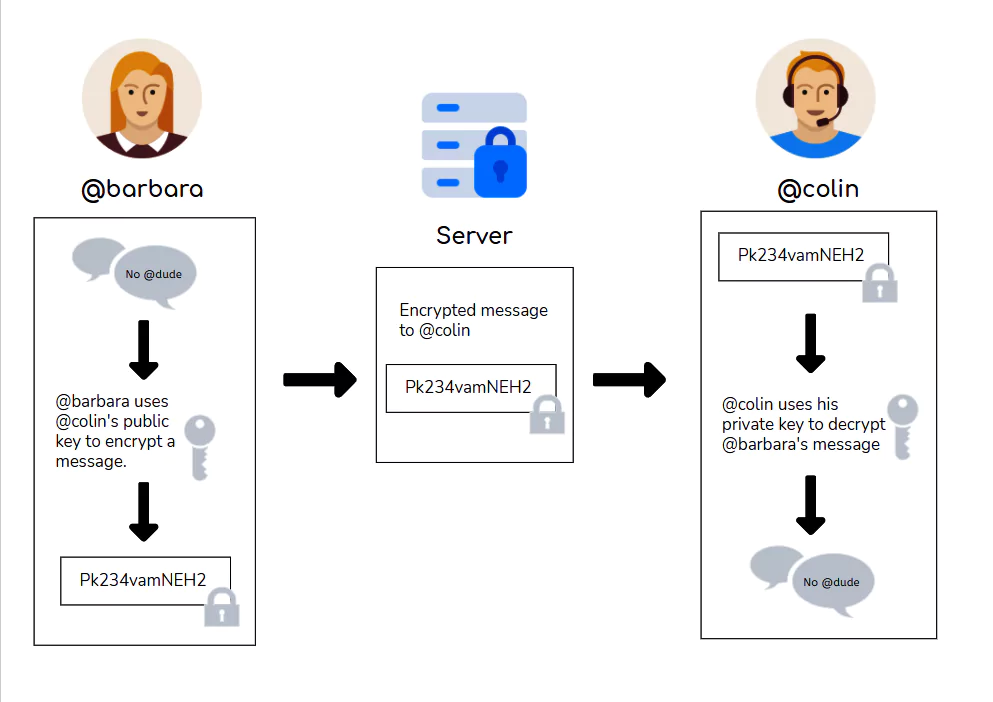
- Asymmetric encryption
- Asymmetric encryption involves separate keys for encryption and decryption.
- The public key encrypts the message, while a corresponding private key decrypts it.
- This encryption is very useful when the recipient and sender are different.
- The longer the key, the higher the level of protection it provides and vice-versa.
- For Example The messaging app WhatsApp uses the Curve25519 algorithm to create public keys for messages.
- Curve25519 uses the principles of elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC).
- ECC’s advantage is that it can provide the same level of security as another asymmetric encryption algorithm but with a shorter key.
- Distinct symmetric and asymmetric schemes utilize various hash functions for message encryption.
Benefits
- Secure Communication:
- End to end encryption relies on public key cryptography that stores private keys on the devices involved.
- Messages are only readable by those accessing these private keys on the endpoint devices.
- Protection from Unwanted Access:
- E2EE safeguards user data from unauthorized parties like service providers, cloud storage providers, and companies dealing with encrypted data.
- Tamper-Resistance:
- Decryption keys in End to End Encryption are not sent separately; they are already with the recipient.
- If a message is tampered with during transit, it can’t be deciphered by the recipient, ensuring the tampered content remains unreadable.
- Other Benefits:
- E2E encryption empowers activists and journalists in oppressive regimes to communicate securely, safeguarding sensitive information from government surveillance and censorship.
Drawbacks
- Communication Endpoint Complexity:
- Some End to End Encryption implementations permit re-encryption of data during transmission.
- It is crucial to identify and delineate the communication endpoints precisely.
- Compromise at these endpoints may lead to the exposure of encrypted data.
- Excessive Privacy Concerns:
- Service providers’ inability to grant law enforcement access to the encrypted content raises privacy issues.
- The rise of End to End Encryption has sparked debates about balancing user privacy with content moderation responsibilities. Companies grapple with finding ways to combat illegal activity while upholding user privacy rights and complying with regulations.
- Limited Metadata Protection:
- While messages are indecipherable during transit, details like the date and recipient remain visible.
- This exposed metadata can offer valuable information to unauthorized individuals.
Conclusion
End to End Encryption is a powerful tool with significant implications for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. It raises broader questions about individual autonomy, government overreach, and the ethical responsibilities of technology companies in the digital age.
Also Read: Cyber Security And Rising Incidence Of Cyber Crime
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 24 Jan 2024
24 Jan 2024

