Context:
A MoU was signed between Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti to implement the Modified Parbati Kalisindh Chambal ERCP Link Project.
- The project envisages integration of the PKC river link project with the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project, under the national perspective plan of interlinking of rivers (ILR) programme of the Government of India.
Modified PKC ERCP Link Project
- It is an inter-state river linking project.
- A Detailed Project Report is being prepared, and based on this, the Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) will be finalised.
- Memorandum of Agreement (MoA): It will consist of aspects like the sharing of water, exchange of water, sharing of costs and benefits, implementation mechanisms, arrangements for management and control of water in the Chambal basin.
-
Benefits PKC ERCP Link Project
-
- Water supply: To provide drinking and industrial water in 13 districts of eastern Rajasthan, and Malwa and Chambal regions of Madhya Pradesh
- Irrigation: providing irrigation in 2.8 lakh ha. area (or more) each in both the states (total of 5.6 lakh ha or more).
|
Parbati Kalisindh Chambal Link Project
- The Parbati Kalisindh Chambal link project is one of the 30 links included in the National Perspectives Plan
- Formulated by: The Ministry of Water Resources and the Central Water Commission in the year 1980.
- Preliminary feasibility report: Of the Kalisindh-Chambal link canal project proposed diversion of water from river Newaj (a tributary of Kalisindh) and Kalisindh to the river Chambal at either the Rana Pratap Sagar dam or the Gandhi Sagar dam.
Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP)
- About: The project aims for intra-basin transfer of water within the Chambal basin, by utilizing surplus monsoon water available in Kalisindh, Parvati, Mej and Chakan sub basins and diverting it into water deficit sub-basins of Banas, Gambhiri, Banganga and Parbati.
- Purpose: To provide drinking and industrial water to 13 districts of eastern Rajasthan i. e. Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Karauli, Sawai-Madhopur, Dausa, Jaipur, Ajmer, Tonk, Bundi, Kota, Baran, and Jhalawar.
- Need: As per The, State Water Resources Department
- Rajasthan with a geographical area of 342.52 lakh hectares accounting 10.4% of the entire country’s land surface holds only 1.16% of India’s surface water and 1.72% of groundwater.
Interlinking of Rivers
- The Government of India formulated a National Perspective Plan (NPP) for interlinking of rivers (ILR) in 1980 with 30 link projects identified.
- Implementing Agency: National Water Development Agency (NWDA)
- Aim: To transfer water from water surplus basins to water-deficit basins
- Components of NPP: Himalayan Rivers Development (14) and Peninsular Rivers Development Component(16)
- The Ken-Betwa Link project (KBLP) is the first ILR project under the NPP
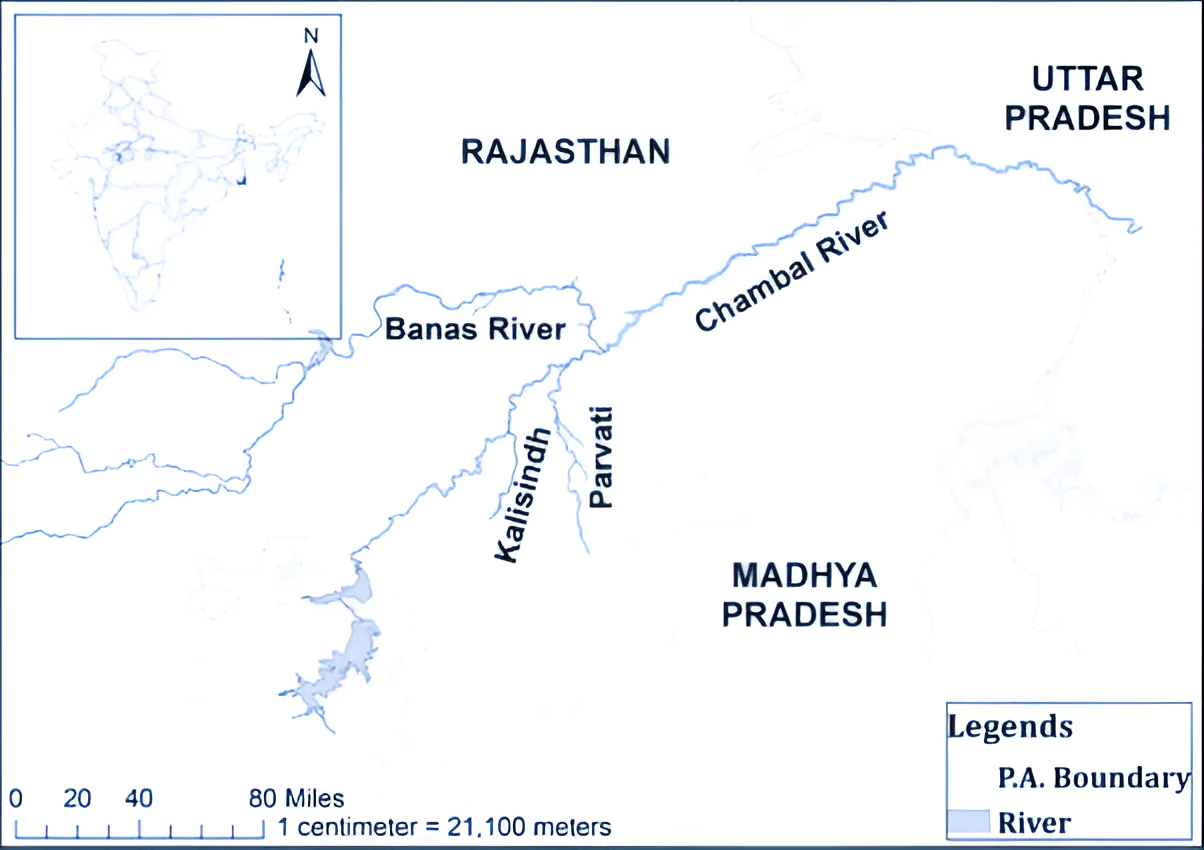
Chambal River
- Origin: From the Bhadakla Falls in Janapav Hills on the northern slopes of the Vindhyan escarpment in Mhow, Madhya Pradesh.
- Drainage Basin States: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh( it joins river Yamuna at jalaun district).
- Tributaries: Shipra, Choti Kalisindh, Sivanna, Retam, Ansar, Kalisindh, Banas, Parbati, Seep, Kuwari, Kuno, Alnia, Mej, Chakan, Parwati, Chamla, Gambhir, Lakhunder, Khan, Bangeri, Kedel and Teelar.
|
Also Read: Interlinking of Rivers—Advantages, Challenges, and Solutions
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 30 Jan 2024
30 Jan 2024