Answer:
|
How to approach the question
- Introduction
- Write about oceanic eddies briefly
- Body
- Write how interplay between physical processes and climatic factors influences the genesis of oceanic eddies.
- Write how interplay between physical processes and climatic factors influences the dissipation of oceanic eddies.
- Write the profound effects of oceanic eddies on marine ecosystems and global climate patterns.
- Conclusion
- Give appropriate conclusion in this regard.
|
Introduction
Oceanic eddies are like underwater tornadoes. They swirl around and can move warm or cold water across the ocean. For example, eddies in the Gulf Stream help carry warm water from the tropics up towards the North Atlantic. They’re important for ocean health and climate.
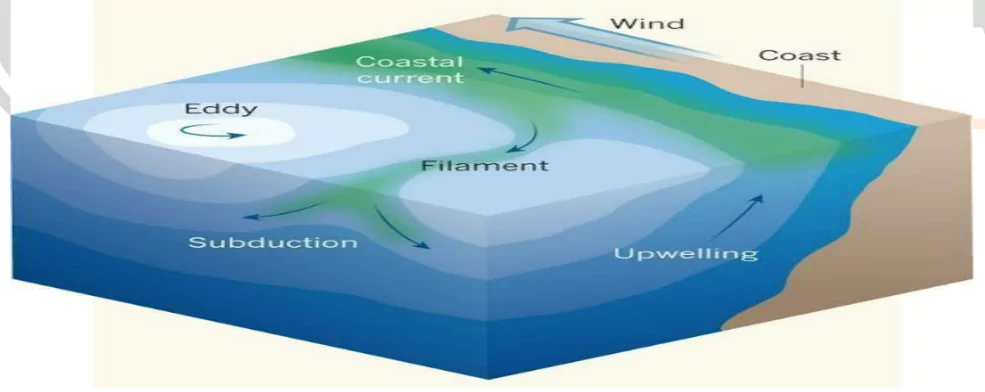
Body
Interplay between physical processes and climatic factors influences the genesis of oceanic eddies
- Ocean Currents: Strong ocean currents, like the Gulf Stream, can create eddies when the flow of water gets disturbed. It’s similar to the swirls you see when a fast-moving river hits a big rock.
- Wind: Wind blowing over the ocean surface can stir the water, creating ripples that can grow into bigger eddies. For example, when winds from a storm blow over the ocean, they can help form eddies.
- Water Density Differences: Eddies can also form when water of different temperatures or salinity (saltiness) meet. Imagine pouring syrup into water; it doesn’t mix well and creates swirls— that’s like an eddy.
- Tides: The regular push and pull of the ocean’s tides can generate eddies. Just as tide changes can cause ripples in a bay or estuary, they can also create larger-scale eddies in the open ocean.
- El Niño or La Niña: These climate patterns change wind and ocean current patterns. These shifts can lead to more or less eddy formation, depending on the conditions.
- Ocean Fronts: These are boundaries where different bodies of water meet—like warm water meeting cold water. This clash can create instabilities that lead to the formation of eddies.
- Atmospheric Pressure Changes: Large-scale changes in atmospheric pressure, such as those caused by moving weather systems, can cause changes in sea surface height, leading to eddy formation.
Interplay between physical processes and climatic factors influences the dissipation of oceanic eddies
- Friction with Seabed: When an eddy encounters shallow waters or an uneven ocean floor, it can slow down due to friction. This process gradually reduces the energy of the eddy, leading to its dissipation.
- Encountering Coastlines: If an eddy moves towards a coast, the coastline can disrupt its circular motion, leading to its eventual disintegration. For instance, eddies in the Gulf Stream often dissipate when they hit the eastern coast of North America.
- Merging with Other Eddies: Sometimes, when two eddies come close, they can merge into one larger eddy. While this new eddy might be bigger, the overall energy is conserved, leading to the original eddies’ dissipation.
- Heat Exchange: Eddies can lose energy through heat exchange with the atmosphere, which can lead to their dissipation. In colder regions, this heat loss can be significant and cause the eddy to break down faster.
- Wind Stress: Strong winds can either aid in eddy formation or contribute to their decay. If winds blow in a direction opposite to the eddy’s spin, they can disrupt its motion and contribute to its dissipation.
- Sea Surface Temperature: Changes in sea surface temperature, often influenced by seasons or larger climate processes, can impact the stability of eddies and influence their dissipation.
- Changes in Water Density: Just as differences in water density can create eddies, changes in these differences (due to warming or cooling, for instance) can destabilize and help dissipate them.
Profound effects of oceanic eddies on marine ecosystems and global climate patterns
- Nutrient Distribution: Oceanic eddies can churn up nutrients from the ocean’s depths and spread them around. This is like giving the ocean a big stir, helping feed small plants and animals living in the water.
- Marine Food Chain: By bringing up these nutrients, eddies help boost the growth of tiny plants called phytoplankton, the base of the ocean’s food chain. This can lead to more fish and other sea creatures in those areas.
- Heat Transport: Eddies help move heat around in the ocean. For example, eddies formed in the Gulf Stream transport warm water and heat from the tropics towards the colder North Atlantic, influencing the region’s climate.
- Carbon Storage: The ocean absorbs a lot of the Earth’s carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas. Eddies can carry this CO2 deep into the ocean, storing it away from the atmosphere and helping to combat climate change.
- Oxygen Supply: When eddies stir up the water, they also bring oxygen down into the deeper ocean. This is crucial for the survival of marine creatures living at depth.
- Climate Buffer: By moving heat and CO2 around, eddies help the ocean act as a buffer against rapid climate change. Without them, Earth’s climate could change much more quickly.
- Marine Migration: Some marine animals, like turtles and seals, use eddies as ‘rest stops’ during long migrations. They’re like underwater pit stops, providing a bounty of food for the journey.
Conclusion
Going ahead, given the complexity and global scale of these processes, the study of oceanic eddies is of paramount importance for improving our understanding and prediction of climate change and its impacts on marine ecosystems.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.



Latest Comments