Context:
For the year 2024 -25, the interim union budget has allocated Rs 1 crore to encourage the private sector to scale up research and innovation in sunrise industries.
Centre Announces Rs 1 lakh Crore in Interest Free Loans for Private Sector Research
- The funding of Rs 1 crore will be created for fifty years through a loan with no interest.
- In addition to this funding, a new scheme will be launched to increase capabilities of technological advancement in defence application.
- There is no explicit linkage between the corpus (announced in the budget) and the NRF, but it will obviously help the objectives of the National Research Foundation (NRF).
Contribution of Private Sector in R&D
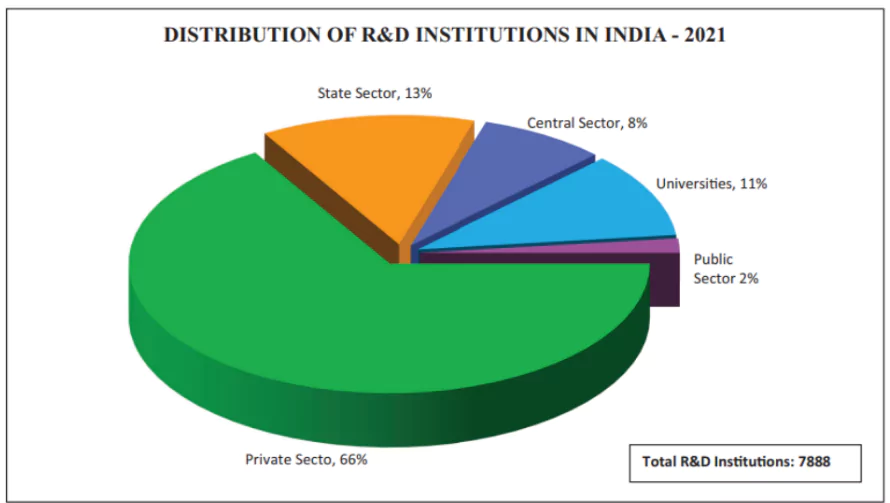
- There are around 7888 R&D institutions in India according to the Directory of R&D Institutions 2021.
- Among these institutions, 66% were in the private sector.
- Though, Private sector is not fully developed, it has shown significant contribution in some specific areas such as
 Information Technology: These companies are focused on developing innovative solutions and are investing in AI, data analytics, etc.
Information Technology: These companies are focused on developing innovative solutions and are investing in AI, data analytics, etc. - Biotechnology: The growth of biotechnology is at a very rapid rate due to its demand in various sectors such as textile, energy, medical, etc.
- In 2023, this sector was valued around 92 billion U.S. dollars.
- Pharmaceuticals: This sector has a larger domain in India due to which these companies are involved in new drug innovation and development. However, investment in this sector is still very low due to low spending on R&D in India.
Challenges of Private Sector in R&D
- Inadequate Funding: It is a major problem in India. India spends around 0.7 % of GDP on R&D which is very low compared to global companies’ contribution.
- Lack of Infrastructure: In addition to the funding, infrastructure is also a major problem in India. There are few quality laboratories and research centers with requisite equipment.
- Migration: Many talented individuals leave India and join international organizations due to which research and development calibr declines.
- The phenomenon of Emigration of the brightest minds to other countries is known as “brain drain”.
- Lack of Proper Training and Education: In India, students don’t get required equipment and training due to which they are incapable of using advanced technologies.
Impact of Interest Free loans For Private Sector Research in India
Advantages Of Interest Free loans For Private Sector Research
-
Financial Relief:
- The availability of interest-free loans will encourage more investment in research and development (R&D) , especially long-term or risky projects.
- More R&D can speed up innovation in areas like healthcare, agriculture, and clean energy.
-
Support for Startups:
- Interest-free loans are great for new companies with good ideas but limited funding options.
- It promotes a lively startup community focused on research and development.
-
Research & Development (R&D) Centres:
- Businesses concentrating on research and development can use the allocated funds to support revolutionary innovations.
-
Education & Skill Development
-
- Efforts focused on cultivating technology talent and skill development are vital in unlocking the potential benefits of this budgetary initiative.
Disadvantages Of Interest Free loans For Private Sector Research
-
Inefficient Resource Allocation
- Picking which projects get money is crucial. Poor decisions could favour big companies over new ones or fund projects with limited success.
-
Distorted Research Priorities
-
- If the loan program focuses too much on specific areas, it might take resources away from other important research.
-
Profit Driven
- Experts argue government decisions as private research is largely profit driven.
National Research Foundation (NRF)
- It is a significant government initiative for funding and mentoring scientific research in higher education.
Key Objectives Of National Research Foundation
- Support and grow research with long-term financing.
- Provide refinancing at low or nil interest rates.
- Democratize funding by connecting Central Government departments, science labs, educational institutions, and industrial bodies.
|
News Source: Downtoearth
![]() 3 Feb 2024
3 Feb 2024
 Information Technology: These companies are focused on developing innovative solutions and are investing in AI, data analytics, etc.
Information Technology: These companies are focused on developing innovative solutions and are investing in AI, data analytics, etc.