The Bhopal Gas Leak tragedy is one of the biggest industrial disasters of all time, took place on the night of December 2 and 3, 1984. Know more about Bhopal Gas leak tragedy and its causes here.

The Bhopal Gas Leak Tragedy, often regarded as the world’s worst industrial disaster, occurred on the night of December 2-3, 1984, in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh. A catastrophic leak of methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas from the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) pesticide plant exposed over 500,000 people to the toxic substance. This disaster led to immediate and long-term devastation, causing thousands of deaths, severe health complications, and environmental damage. The tragedy highlighted critical lapses in industrial safety, regulatory oversight, and emergency preparedness, serving as a grim reminder of the need for stringent safety protocols in industrial operations.
The Bhopal Gas Leak is often considered the worst industrial disaster in history, which not only resulted in deaths but also chronic diseases.
National Pollution Control Day is observed annually on December 2 in India to honor the lives lost in the Bhopal Gas Tragedy of 1984 and to raise awareness about the importance of pollution control. On December 2, 2024, the Bhopal gas leak tragedy will mark the 40th anniversary. The day serves as a reminder to implement stricter environmental regulations, promote sustainable practices, and encourage individuals and industries to adopt eco-friendly measures. It emphasizes the need to reduce air, water, and soil pollution for a healthier and safer environment for future generations.
There were many root causes of the Bhopal Gas Leak disaster. Some of the root cause of the Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster:
Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) was an Indian subsidiary of the American multinational Union Carbide Corporation (UCC). Established in 1934, UCIL operates in various industrial sectors, including chemicals, metals, and agricultural products. Its pesticide manufacturing plant in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, became the site of the Bhopal Gas Tragedy in 1984, one of the world’s deadliest industrial disasters.
UCIL manufactured pesticides and related products, with methyl isocyanate (MIC) being a key ingredient in producing Sevin, a pesticide. The Bhopal plant was set up in 1969 to meet the growing agricultural demand in India. However, the plant faced issues such as financial losses, safety oversights, and reduced production, which led to cost-cutting measures, ultimately contributing to the disaster.
| Particulars | Key Facts About Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) |
|---|---|
| Established | 1934 |
| Parent Company | Union Carbide Corporation (UCC), USA |
| Industry | Chemicals, metals, and agriculture |
| Bhopal Plant | Established in 1969 to manufacture pesticides like Sevin |
| Key Chemical | Methyl Isocyanate (MIC), a highly toxic ingredient used in pesticide production |
| Bhopal Gas Tragedy | Occurred on December 2-3, 1984, due to a massive leak of MIC gas |
| Casualties | Over 3,000 immediate deaths; long-term effects on more than 500,000 people |
| Headquarters in India | Mumbai, Maharashtra |
| Current Status | UCIL was taken over by Eveready Industries India Limited in 1994 and is no longer operational in its original capacity. |
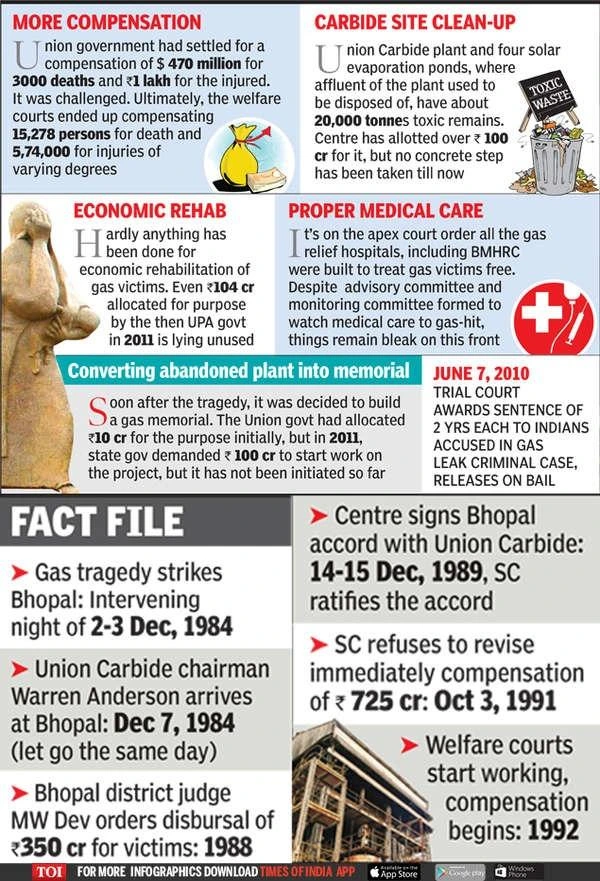
Source; TOI
The Bhopal Gas Leak disaster remains to be one of the biggest industrial disasters of all time. The lives of people affected have never been the same.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
The disaster was caused on December 3, 1984 in the city of Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
The Union Carbide Company, which was a major pesticide manufacturer, was involved in the disaster.
The disaster occurred when 40 tons of toxic methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas leaked out of the Union Carbide factory.
The Union Carbide factory contained three underground tanks that were used to store liquid Methyl Isocyanate (MIC). On 2nd December, water accidentally entered one of the underground tanks holding MIC, triggering an instant exothermic reaction caused by the presence of contaminants, high ambient temperatures, and various other factors.
Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, Public Liability Insurance Act of 1991, and Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster (Processing of Claims) Act in 1985.
The gas that leaked during the Bhopal Gas Tragedy was Methyl Isocyanate (MIC), a highly toxic chemical used in pesticide production.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>