Context: Sundar Pichai, CEO of Alphabet and Google, a major figure in big tech, will testify in a landmark antitrust battle over Google's control of search and advertising.

Meta Description: Exploring the impact, concerns, regulatory measures related to Big Tech, including its economic, societal, and political influence globally. This article tried to understand the anti-trust issues, privacy concerns, and job displacement challenges, along with international regulations and the way forward as proposed by the Standing Committee on Finance in India.
Let’s discover the Powerhouses of the Information Technology Industry: Big Tech, the Dominant Players Redefining Technology Landscape.
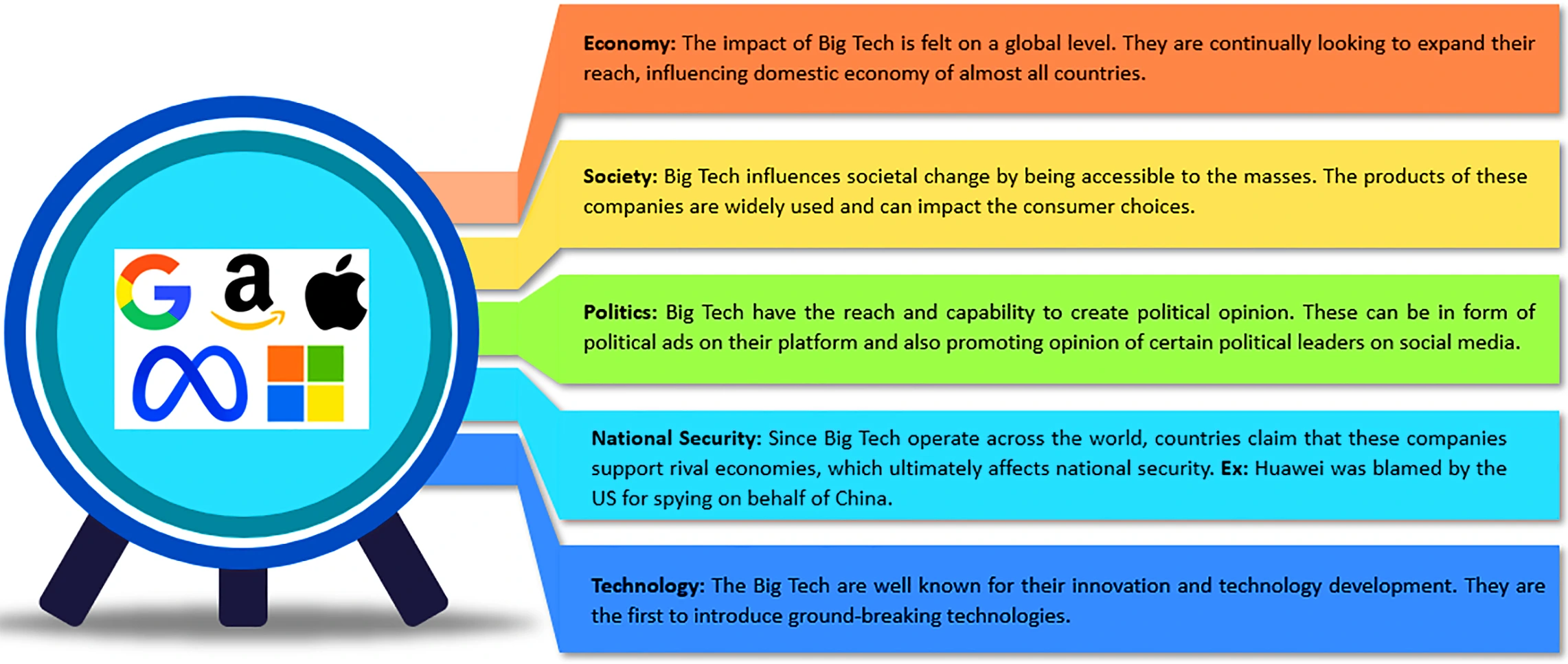
Understanding the Global Impact of Big Tech: How Tech Giants Shape Economies, Societies, and Political Dynamics Worldwide:
Looking at the Controversies: Exploring Challenges Surrounding Big Tech in the Global Arena!
Examining Anti-Competitive Practices: A Deep Dive into Big Tech Companies’ Strategies in India
| Anti-Competitive Practice | Description |
| Anti-Steering Provisions |
|
| Platform Neutrality/ Self Preferencing |
|
| Adjacency/ Building and Tying |
|
| Data Usage (use of non-public data) |
|
| Mergers and Acquisitions |
|
| Pricing/ Deep Discounting |
|
| Exclusive Tie-ups |
|
| Search and Ranking Preferencing |
|
| Restricting Third-Party Applications |
|
| Advertising Policies |
|
India’s Approach to Regulating Big Tech: Strengthening Competition Laws and Safe Harbour Provisions for the Digital Era
Exploring Global Big Tech Regulations: A Comprehensive Overview of Key Legislative Measures Across Continents
| Europe |
|
| USA | The USA (Anti-trust legislation): The US adopted Anti-trust legislation targeting the dominance of Big Tech companies by giving states greater power in competition cases and increasing money for federal regulators. |
| Australia |
|
To ensure a fair, transparent, and contestable digital ecosystem, India needs a Digital Competition Act based on the unique needs of digital markets. On lines of global ex-ante approaches, this Digital Competition Act should:
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Big Tech refers to the most dominant information technology companies, such as Google, Amazon, Apple, Meta (Facebook), and Microsoft, which hold significant influence globally in various aspects like the economy, society, politics, national security, and technology.
Big Tech companies have a global reach and can significantly impact the domestic economies of countries where they operate, influencing job markets, investments, and overall economic growth.
Concerns include anticompetitive behavior, privacy violations, tax avoidance, job displacement, disregard for local laws, dissemination of misinformation, and political influence.
Europe has introduced the Digital Markets Act (DMA) and Digital Services Act (DSA), while the USA has adopted antitrust legislation to address Big Tech dominance.
Recommendations include creating a Digital Competition Act, defining SIDIs, implementing ex-ante regulations, global harmonization, harmonizing with consumer protection laws, ensuring consumer compensation, strengthening the CCI, and setting a code of conduct for SIDIs.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>