India marks 10 years of the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) on 8 April 2025.
About Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) is a flagship Central Sector Scheme aimed at funding the Unfunded micro enterprises and small businesses.
- It was launched in 2015 to provide collateral-free micro credit to small and micro entrepreneurs across India, especially in the non-corporate and non-farm sectors.
MUDRA Card and MUDRA MITRA Mobile Application
About MUDRA Card
- Purpose: It is an innovative credit product that enables hassle-free access to credit for working capital needs.
- Functionality: Acts as a RuPay debit card; It is usable at ATMs, POS machines, and online platforms.
Overdraft Facility: Offers a flexible credit line repayable when surplus cash is available, reducing interest burdens.
About MUDRA MITRA App
- Purpose: Designed to provide comprehensive information about the Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency Ltd. (MUDRA) and its various schemes under PMMY.
- Loan Guidance: It will guide a loan seeker to approach a Banker in availing MUDRA loan under PMMY.
- Resources Access: Provides sample application forms and details on loan categories (Shishu, Kishore, Tarun, Tarun Plus).
|
- Nodal Agency: Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance.
- Implementation Through: PMMY is implemented through MUDRA (Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency), which offers:
- Refinance support to banks, NBFCs, and MFIs,
- Credit guarantee as well as development and
- capacity-building support.
- Loan Categories Under PMMY: PMMY loans are structured into four categories based on business maturity:
- Shishu Category: Loan Limit: Up to ₹50,000; For startups and businesses in their initial stages.
- Kishore Category: Loan Limit: ₹50,000 to ₹5 lakh; For businesses in the growth phase seeking additional capital.
- Tarun Category: Loan Limit: ₹5 lakh to ₹10 lakh; For established businesses aiming to scale up operations.
- Tarun Plus Category (Introduced in Union Budget 2024-25): Loan Limit: ₹10 lakh to ₹20 lakh; For businesses with a good repayment record under the Tarun category, looking for further expansion.
- Eligible Borrowers: The scheme covers a broad base of entrepreneurial entities, including: Individuals, Proprietary concerns, Partnership firms, Private and public limited companies, Other legal entities etc.
- Credit Guarantee Support: The Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU) covers defaults, encouraging financial institutions to lend more.
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU) is the Trust Fund set up by Government of India with the purpose of guaranteeing payment against default in Micro Loans extended to eligible borrowers by Banks/ NBFCs/ MFIs/ Other Financial Intermediaries.
Need for the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana
- Demographic Advantage: India’s demographic dividend needed a platform to turn young aspirations into enterprise.
- Bridging the Credit Gap: Millions of small entrepreneurs lacked access to formal, collateral-free finance.
- Promoting Inclusive Development: Encouraging grassroots entrepreneurship is key to achieving inclusive growth, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Unlocking Entrepreneurial Potential: There existed a strong need to tap into the latent potential of small and micro entrepreneurs who lacked access to formal credit.
- Catalyzing Self-Reliance: A self-employed, self-sustained India aligned with the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Achievements of the Scheme
- Loan Disbursement: Since its launch in April 2015, the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) has sanctioned over 52 crore loans worth ₹32.61 lakh crore.
- Impact on MSME: There has been a massive growth in MSME Lending. MSME credit rose from ₹8.51 lakh crore in FY14 to ₹27.25 lakh crore in FY24.
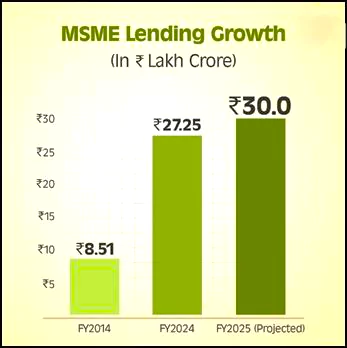 Rising Share in Total Bank Credit: The MSME sector’s share grew from 15.8% in FY14 to nearly 20% in FY24.
Rising Share in Total Bank Credit: The MSME sector’s share grew from 15.8% in FY14 to nearly 20% in FY24.- MSME lending is projected to cross ₹30 lakh crore in FY25.
- Women Empowerment:
- Major Share of Women Beneficiaries: Women constitute 68% of all Mudra beneficiaries, highlighting the scheme’s focus on promoting women-led enterprises.
- Rising Financial Support for Women: From FY16 to FY25, the per woman PMMY disbursement grew at a 13% CAGR, reaching ₹62,679.
- Growth in Savings and Deposits: Per woman incremental deposits rose at a 14% CAGR, touching ₹95,269.
- Inclusive Growth for Weaker Sections:
- Support for Weaker Sections: 50% of Mudra accounts are held by SC, ST, and OBC entrepreneurs.
- Uplifting Minority Communities: 11% of Mudra loan holders belong to minority communities, reflecting the scheme’s commitment to diversity and equity.
- Progressive Lending: From Shishu to Tarun
- Expanding Outreach: Over 52 crore loan accounts have been opened under Mudra Yojana in the last decade, reflecting a surge in grassroots entrepreneurship.
- Shift Towards Growth-Stage Enterprises: The share of Kishor loans (₹50,000–₹5 lakh) rose significantly from 5.9% in FY16 to 44.7% in FY25, showing a transition from micro to small enterprises.
 Scaling Up with Tarun Loans: The Tarun category (₹5 lakh–₹10 lakh) is steadily gaining traction, highlighting Mudra’s role in enabling business expansion, not just initiation.
Scaling Up with Tarun Loans: The Tarun category (₹5 lakh–₹10 lakh) is steadily gaining traction, highlighting Mudra’s role in enabling business expansion, not just initiation.- Lending Lifecycle Support: The scheme supports entrepreneurs across different stages—from starting out (Shishu) to scaling up (Kishor and Tarun).
- Shift in Mindset: From job seekers to job creators, even in rural areas and small towns.
- Bigger Loans, Stronger Businesses
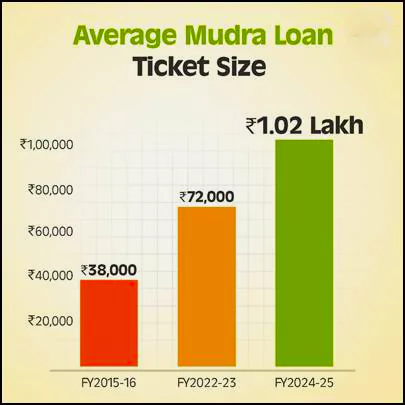
- Rising Average Ticket Size: The average loan amount has shown remarkable growth:
- ₹38,000 in FY16
- ₹72,000 in FY23
- Projected ₹1.02 lakh in FY25.This reflects growing business scale and deeper market integration.
- Boost in Loan Disbursal: Loan disbursement rose by 36% in FY23, signaling renewed entrepreneurial confidence and stronger credit appetite among small businesses.
International Recognition of PMMY
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has consistently acknowledged the impact of the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) in expanding financial access and promoting inclusive entrepreneurship in India.
- 2017: Recognized for enabling women-led businesses and complementing PMJDY by offering collateral-free loans to MSMEs.
- 2019: Praised for supporting micro enterprises in manufacturing, trading, and services through the Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency.
- 2023: Noted significant growth in women-owned MSMEs—now exceeding 2.8 million—due to PMMY’s accessible loan structure.
- 2024: Reaffirmed PMMY’s role in fostering self-employment and formalisation through inclusive credit access.
|
Challenges and Concerns Surrounding Mudra Yojana
- Unequal Distribution: In 2021-22, the top 10 districts received Rs 26,000 crore, about the same as the bottom 318 districts.
- Between 2015 and 2022, the Northeast region has consistently recorded the lowest number of accounts and sanctioned amounts under the scheme, with a noticeable declining trend over the years.
- Absence of a Centralized Customer Database: There is no unified system to collect and manage customer information, hindering efficient verification and formalization of bank accounts.
- Inadequate Credit Access for Weaker Sections: Credit penetration remains poor among weaker sections and underdeveloped regions.
- Need for a Digitized Grievance Redressal Platform: A robust digital platform is required to promptly address queries related to guarantee covers, operational procedures, and technical guidelines.
- Lack of Employment Data: There are no official records on employment generated by Mudra loans. This raises concerns over the effectiveness of the scheme in fostering self-employment or entrepreneurship at scale.
- Growing NPA Concerns
- Official NPA for Mudra: 4% (as of Dec 2017), lower than average PSB NPAs (~10%).
- However, experts estimate that actual NPAs under the scheme may have exceeded ₹14,350 crore within just three years, raising concerns about Mudra loans potentially becoming a growing liability for the banking sector over time.
- Bankers Raise Red Flags: Loans under the Mudra scheme are often pushed without proper business plans or risk assessment due to the absence of collateral, and the pressure to meet disbursal targets has led to violations of sound banking principles.
- Incidents of Fraud and Corruption: In Barmer, Rajasthan, a PNB official fraudulently sanctioned 26 Mudra loans worth ₹62 lakh without proper verification.
- The scheme’s preference for women is often misused through proxy applicants, placing bankers in a dilemma between issuing risky loans or facing complaints.
Way Forward
- Stronger Risk Assessment Mechanisms: There is a need to implement robust credit appraisal systems to ensure loans are granted based on viable business plans and repayment capacity.
- Introduce Enhanced Credit Guarantee Scheme (ECGS): MUDRA should include the Enhanced Credit Guarantee Scheme (ECGS) to encourage banks to lend more to small and micro enterprises. This scheme provides a credit guarantee and reduces the risk for financial institutions.
- Robust Monitoring & Evaluation Framework (RMEF): There is a need to leverage real-time tech to monitor loan disbursement, fund use, and repayment.
- The RMEF will also include beneficiary impact assessments to measure socio-economic outcomes and provide insights for policy enhancements.
- Capacity Building of Borrowers: Offer financial literacy and entrepreneurship training to beneficiaries, especially first-time borrowers and women entrepreneurs.
- Data-Driven Employment Tracking: Establish a framework to track employment generation linked to Mudra loans to evaluate real impact.
- Focus on Medium-Term Scaling Support: Facilitate transition from Shishu to Tarun loans with mentoring, market linkages, and additional working capital support.
- Curb Proxy Loaning Practices: Enforce stricter KYC norms and physical verification to prevent proxy misuse, especially in women-targeted disbursals.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) has fundamentally reshape the landscape of entrepreneurship in India, driving significant progress in financial inclusion.
- To build on MUDRA Yojana’s success, there is a need to strengthen outreach, financial literacy, and monitoring systems.
- A focused and inclusive MUDRA 2.0 can unlock the full potential of India’s micro-entrepreneurs.
![]() 9 Apr 2025
9 Apr 2025

 Rising Share in Total Bank Credit: The MSME sector’s share grew from 15.8% in FY14 to nearly 20% in FY24.
Rising Share in Total Bank Credit: The MSME sector’s share grew from 15.8% in FY14 to nearly 20% in FY24. Scaling Up with Tarun Loans: The Tarun category (₹5 lakh–₹10 lakh) is steadily gaining traction, highlighting Mudra’s role in enabling business expansion, not just initiation.
Scaling Up with Tarun Loans: The Tarun category (₹5 lakh–₹10 lakh) is steadily gaining traction, highlighting Mudra’s role in enabling business expansion, not just initiation.