Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the setting up of 12 industrial smart cities under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP).
Other Projects Approved by CCEA
In addition to 12 industrial smart cities, the CCEA also approved the following projects:
- Railway Projects: The CCEA approved three railway projects and two new railway lines, multi-tracking projects with a total estimated cost of Rs 6,456 crore.
- Coverage: These three railway projects covering 7 Districts in 4 states- Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Chhattisgarh.
- These will increase the existing network of Indian Railways by about 300 kms.
- Significance: These will improve logistical efficiency by connecting the unconnected areas, increase the existing line capacity and enhance the transportation networks, resulting in streamlined supply chains and accelerated economic growth.
- Hydropower Projects: The Union Cabinet approved equity support of Rs 4,136 crore to northeast states for developing hydropower projects, totalling 15,000 Mw capacity over the next eight years with a view to meeting the country’s climate commitment.
- Equity Participation: The money will be used to support equity participation by the northeastern states through joint ventures between their entities and Central public sector developers of the hydroelectric projects.
- Equity participation refers to the ownership of shares in a company or property.
- The Central assistance is envisaged to be spent by April 2032.
- The scheme will have gross budgetary support of 10% for the northeastern region from the power ministry’s total outlay.
- Significance: It will encourage participation by state governments, spreading the risk and avoid time and cost over-runs due to delays in land acquisition and local issues.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
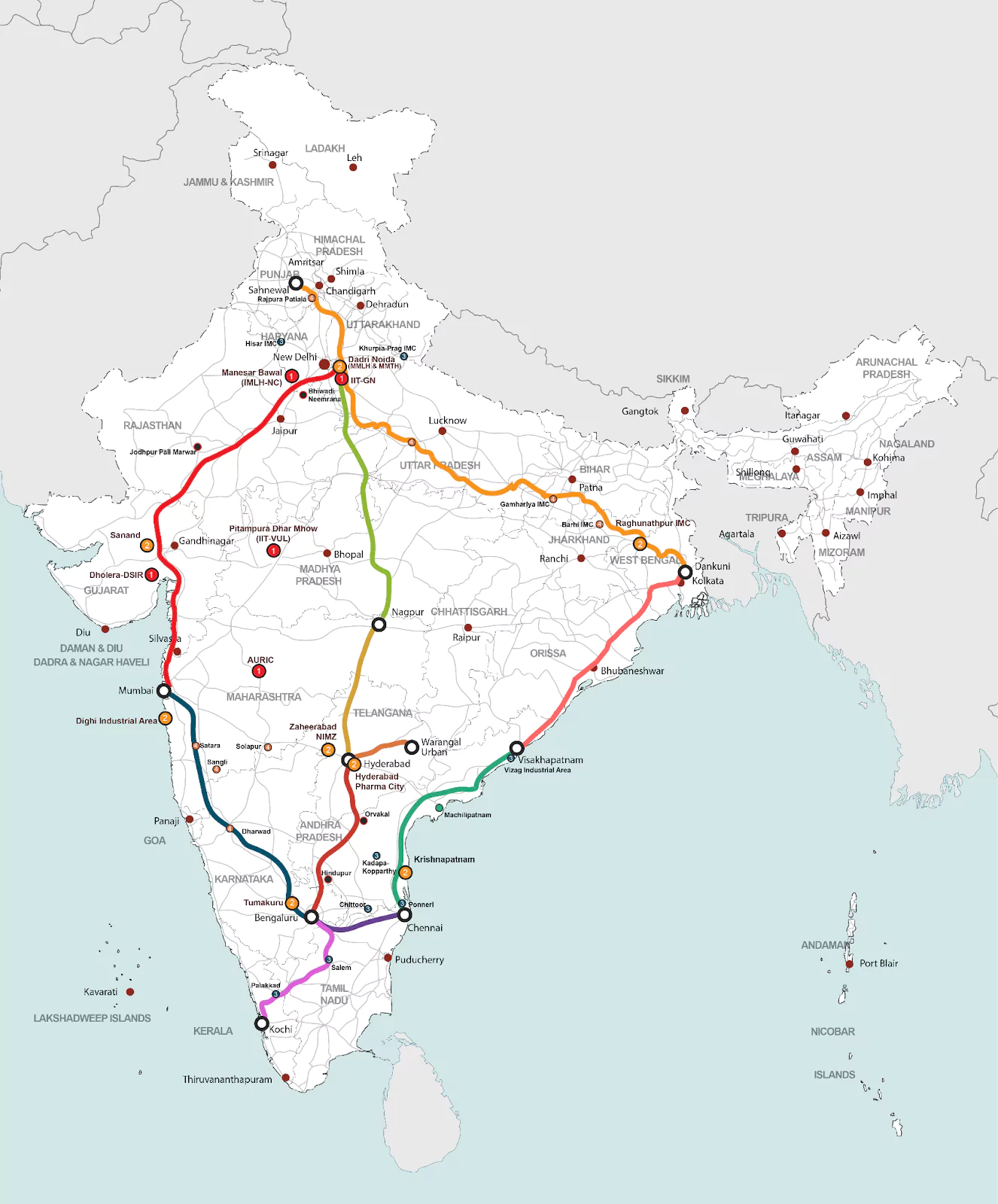
About the Industrial Parks Projects
To transform the industrial landscape of the country, the move is set to create a robust network of industrial nodes and cities that will significantly boost economic growth and global competitiveness.

- Target: The Committee cleared an outlay of ₹28,602 crore to set up 12 industrial parks across 10 States and along 6 major industrial corridors, in line with an announcement in the Union Budget.
- Time Frame: These will be completed in three years.
- Aim: To set up robust infrastructure to drive “balanced” regional development.
- Coverage Regions: Khurpia (Uttrakhand), Rajpura-Patiala (Punjab), Dighi (Maharashtra), Palakkad (Kerala), Agra and Prayagraj (Uttar Pradesh), Gaya (Bihar), Zaheerabad (Telangana), Orvakal and Kopparthy (Andhra Pradesh) and Jodhpur-Pali (Rajasthan).
- The name of one city has not been revealed as the Model Code of Conduct is in force in poll-bound states.
- Included Corridors: The CCEA nod covers the development of one industrial park each along the corridors coming up between Vizag and Chennai, Hyderabad and Bengaluru, Hyderabad and Nagpur, and Chennai and Bengaluru.
- Coverage Parks: These include two parks of about 2,600 acres in Kopparthy and Orvakal in Andhra Pradesh, a 3,245 acre facility in Telangana’s Zaheerabad and a 1,710 acre park in Palakkad, Kerala.
- Existing Projects: In addition to these new sanctions, the NICDP has already seen the completion of four projects, with another four currently under implementation.
- Infrastructure Completed: Dholera (Gujarat), Auric (Maharashtra), Vikram Udyogpuri (Madhya Pradesh) and Krishnapatnam (Andhra Pradesh)
- Infrastructure under Implementation: Tumakuru (Karnataka), Krishnapatnam (Andhra Pradesh), Nangal Chaudhary (Haryana) and Dadri-Greater Noida (Uttar Pradesh)
About Industrial Parks
An industrial park is an area specifically zoned and planned for industrial development.
- Examples: Dholera SEZ, Gujarat; Adani Mundra Special Economic Zone etc.
- Significance of Industrial Parks:
- Productivity and Competitiveness: Industrial parks create job opportunities and encourage shared use of infrastructure, boosting productivity and competitiveness.
- Growth and Development: They attract Foreign Direct Investment and stimulate growth in manufacturing activities.
- Some of the benefits of industrial parks include integrated infrastructure, cost savings, and localised environmental controls.
- Overall, they contribute to regional economic development by stimulating local industries and creating a conducive environment for business expansion.
Key Highlights of the Recently Announced 12 Industrial Parks
These cities will be similar to a ‘necklace of industrial cities’ on the backbone of Golden Quadrilateral and will be contributed by both the union and the state government.
- Strategic Investments: NICDP is designed to foster a vibrant industrial ecosystem by facilitating investments from both large anchor industries and Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Smart Cities and Modern Infrastructure: The new industrial cities will be developed as greenfield smart cities of global standards, built “ahead of demand” on the ‘plug-n-play’ and ‘walk-to-work’ concepts.
 Plug-n-Play Concept: It implies that the necessary infrastructure will be readily available, making it easier for businesses to set up operations quickly.
Plug-n-Play Concept: It implies that the necessary infrastructure will be readily available, making it easier for businesses to set up operations quickly.- Walk-to-Work Concept: It emphasises creating residential areas close to workplaces, thereby reducing commute times and enhancing the quality of life for residents.
- Area Approach on PM GatiShakti: Aligned with the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, the projects will feature multi-modal connectivity infrastructure, ensuring seamless movement of people, goods, and services.
- Vision for a ‘Viksit Bharat’: By positioning India as a strong player in the Global Value Chains (GVC), the NICDP will provide developed land parcels ready for immediate allotment, making it easier for domestic and international investors to set up manufacturing units in India.
- Commitment to Sustainable Development: The projects under the NICDP are designed with a focus on sustainability, incorporating ICT-enabled utilities and green technologies to minimise environmental impact.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Significance of the Recently Announced 12 Industrial Parks
The continued progress highlights the government’s commitment to transforming India’s industrial sector and fostering a vibrant, sustainable, and inclusive economic environment.
- Growth: These projects represent a significant leap forward in India’s quest to enhance its manufacturing capabilities and economic growth by equipping cities with advanced infrastructure and efficient industrial operations.
- Development: These greenfield industrial “smart cities” can attract potential investments of ₹1.5 lakh crore, creating a potential 1 million direct and up to 3 million indirect jobs.
- This will not only provide livelihood opportunities but also contribute to the socio-economic upliftment of the regions where these projects are being implemented.
- Catalyst for Target: These industrial nodes will act as catalysts for achieving $2 trillion in exports by 2030, reflecting the government’s vision of a self-reliant and globally competitive India.
- To be developed under the NICDP, these industrial nodes will function more like industrial cities, where residential and commercial setups will co-exist.
- Enhancement in Global Value Chains (GVC): Aligning with the vision of Viksit Bharat, these projects will strengthen India’s role in GVC with ready-to-allot land for investors and support the vision of ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’
Challenges in the Implementation of Industrial Park
Following challenges need to be tackled to achieve the best of the potential of Industrial Parks:
- Infrastructure Development: Industrial parks aim to align infrastructure provision with agglomeration economies to boost industrial growth. However, achieving this balance can be challenging.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating bureaucratic procedures and regulatory requirements can delay the establishment and operation of industrial parks.
- Understanding the local political economy is one of the challenges for the implementation of Industrial Parks
- Land Acquisition: Acquiring suitable land for industrial parks can be challenging due to the need to negotiate with landowners, address property disputes, and manage environmental and legal concerns, which can hinder the development process.
- Acquisition of Land for the industry has always been a major issue in India but, the availability of consolidated land parcels with clear title at a strategic location for the development of the Warehouse and Logistics Parks has become a challenge.
- Negative Spillovers: Sometimes, industrial parks generate negative spillover effects. These could include environmental pollution, traffic congestion, or strain on local resources.
- Skill Shortages: Attracting and retaining a skilled workforce may be difficult, impacting the productivity and growth of businesses within the park.
- Underutilisation: Some industrial parks remain underutilised due to various reasons—lack of demand, inadequate marketing, or unfavourable business conditions.
- Impact on Local Communities and Livelihoods: Rapid industrialisation and urbanisation significantly affect local communities, including potential displacement, livelihood changes and environmental degradation.
- These impacts are often not fully considered in the planning and implementation phases of projects.
Way Forward
Following are few suggested measures that need to be adopted:
- Investment in Infrastructure: India needs to prioritise infrastructure projects such as the Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) and the Bharatmala project to improve logistics and connectivity across the country.
- Establishment of Smart Industrial Zones: Establishing Special Economic Zones (SEZs) such as Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT) with integrated infrastructure such as power, water and transport are must to attract manufacturing units.
- Enhancement of Human Skilling: There is a need to expand initiatives like the Skill India Mission to train and certify workers in manufacturing skills, modelled on successful vocational training programs in countries like Germany.
- Adoption of Industry 4.0 Technologies: The time has come to incentivize the adoption of automation, IoT, and digital manufacturing technologies through schemes such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) for electronics manufacturing.
- Focus on Green Manufacturing Initiatives: There is a need to encourage sustainable practices through incentives for eco-friendly technologies and compliance with global environmental standards, similar to Sweden’s carbon-neutral manufacturing goals.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
The approval of 12 new industrial nodes under the NICDP marks a significant milestone in India’s journey towards becoming a global manufacturing powerhouse. With a strategic focus on integrated development, sustainable infrastructure, and seamless connectivity, these projects are set to redefine India’s industrial landscape and drive the nation’s economic growth for years to come.
About National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP)
The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme is Centre’s infrastructure programme to new industrial cities as “Smart Cities”, equipped with new technologies.
- Aim: To develop a series of industrial corridors across the country to promote manufacturing and create job opportunities.
- Function: These corridors are intended to act as a catalyst for the development of manufacturing and service sectors, thereby generating employment opportunities and boosting economic growth.
- Examples: The oldest such corridors are Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) and Western Dedicated Freight Corridor, which are India’s transportation backbone.
- Funding: Government of India, through National Industrial Corridor Development & Implementation Trust (NICDIT), provides funds as equity/debt for the development of world-class trunk infrastructure.
About NICDIT
The NICDIT is a government agency responsible for coordinating and monitoring the development of industrial corridors in India.
- Aim: To establish greenfield smart industrial cities with sustainable, plug-and-play, and ICT-enabled utilities.
About Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs
It coordinates activities requiring high-level policy decisions.
- Task: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs is headed by the PM, reviews economic trends and problems, shaping a consistent and integrated economic policy.
- Deals with pricing of agricultural produce, essential commodities, investment proposals exceeding Rs 1,000 crore, industrial licensing policies, rural development, and the Public Distribution System.
|
![]() 29 Aug 2024
29 Aug 2024



 Plug-n-Play Concept: It implies that the necessary infrastructure will be readily available, making it easier for businesses to set up operations quickly.
Plug-n-Play Concept: It implies that the necessary infrastructure will be readily available, making it easier for businesses to set up operations quickly.