Recently, India hosted the 2nd BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) Foreign Ministers’ Retreat.
- It focused on providing an “informal platform to discuss ways and means of cooperating and accelerating action in security, connectivity, trade, and investment within the Bay of Bengal.
Crucial Insights on the Recent Retreat
The retreat was held in preparation for the sixth summit meeting, scheduled for September, in which the BIMSTEC leaders will meet in person for the first time in the post-pandemic era.
- They are also expected to sign the BIMSTEC Agreement on Maritime Transport Cooperation to improve regional connectivity, a foundational aim of this grouping.
- About Parts of the Retreat: The retreat was divided into following two parts:
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| First Segment |
- Assessment: Participants assessed the current state of regional cooperation within BIMSTEC, building on a presentation by India on the implementation of key outcomes of the 1st Retreat.
|
- Sharing of Multiple Ideas: Multiple ideas were shared by the member states including the establishment of Centers of Excellence in member states, focusing on Agriculture, Disaster Management, and Maritime Transport.
|
- Support Announced by India: For cancer research, treatment, and issuance of e-visas for patients of all BIMSTEC states, while Sri Lanka proposed the inclusion of kidney disease.
|
- Need Felt: For involving the private sector in trade and promoting young entrepreneurs was also highlighted and also for the importance of connectivity, cyber-security, and countering the trafficking of narcotics and illegal arms.
|
| Second Segment |
- A Segment of Expectations and Proposals: Expectations of each country from the forthcoming summit were discussed and these proposals will be presented to the heads of state before the September summit.
|
- Sri Lanka: It underscored the need to map mineral resources found in abundance in the BIMSTEC countries and create opportunities for the vertical integration of stages of production within specific sectors in the economies of the countries, enabling them to diversify their production structure.
|
- Bangladesh: It highlighted the need for cooperation in the Blue Economy and urged member states to ban fishing during the breeding season to address the problem of depleting catch in the Bay.
|
- Bhutan: It expounded on the need for collaboration in tourism and cultural exchanges.
|
- Nepal: It highlighted its ‘whole of the region’ approach to leverage synergies among member states and transform BIMSTEC into a results-oriented regional forum.
|
- Thailand: It underscored the need for cooperation in non-traditional security domains.
|
- Myanmar: It added the need to combat online scamming to the list.
|
| Bilateral Merits: |
- While the retreat was a multilateral milestone for India, it had its bilateral merits too.
|
- Myanmar: With Myanmar, India shared its concerns over the flow of displaced persons, narcotics, and arms across the border and urged for the return of unlawfully detained Indians.
|
- Bangladesh: With Bangladesh, India requested to ensure the smooth supply of daily essentials and send a technical team for the Teesta project.
|
- Access to the Sea: Strengthening ties with Bangladesh and Myanmar accords India the advantage of providing its landlocked north-eastern region with access to the sea.
- Improved ties with Myanmar and Thailand will also lend India the opportunity to have a more profound presence in the Indo-Pacific, as it holds the ASEAN (Association of South-East Asian Nations), in which these two countries are members, to be of central importance in its vision of the Indo-Pacific.
|
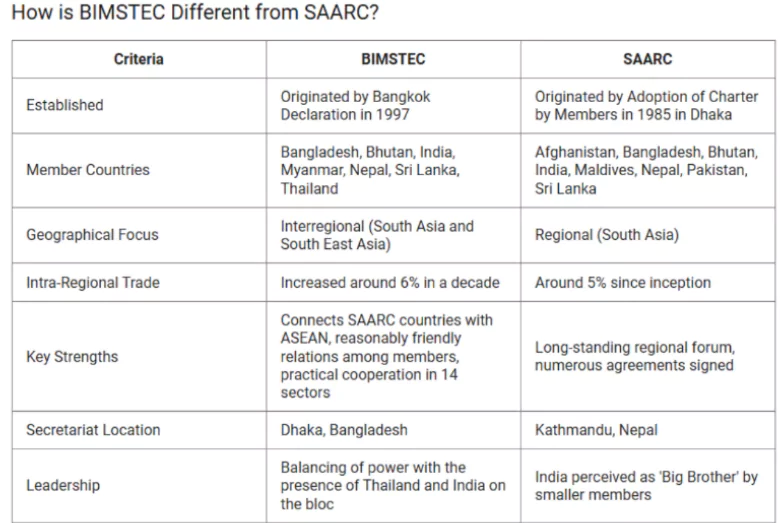
About BIMSTEC
BIMSTEC is a regional organisation of seven Member States lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal, cooperating across seven diverse sectors.
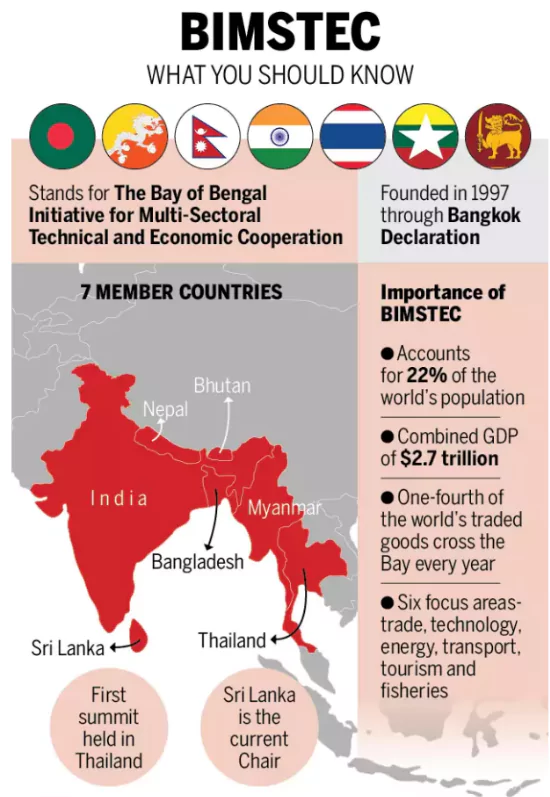
- Formation: It was founded as BIST-EC, in June 1997, with the adoption of the Bangkok Declaration, with Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka and Thailand as members.
- It became BIMST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation) with the entry of Myanmar in late 1997. And eventually, it was named in its current form, when Nepal and Bhutan became members in 2004.
- Secretariat: Dhaka, Bangladesh
- Membership: It has a total of seven member countries:
- Five from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka
- Two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand
- Founding Principles: Principle of Sovereign Equality, Territorial Integrity, Political Independence, Non-interference in Internal Affairs and Peaceful Coexistence and Mutual Benefit.
- Aim: BIMSTEC aims to counter the onslaught of globalisation by accelerating regional growth through mutual cooperation by utilising regional resources and geographical advantages.
- It was not about creating a new region for cooperation but to revive the connectivity and common interests of the members of the Bay of Bengal region.
- The Bay of Bengal region was one of the world’s most integrated regions until the early twentieth century, but after the 1940s, when members of the region became independent and pursued separate goals and alliance systems, “the region’s sense of community has almost completely eroded”.
 Distinctive Features of BIMSTEC:
Distinctive Features of BIMSTEC:
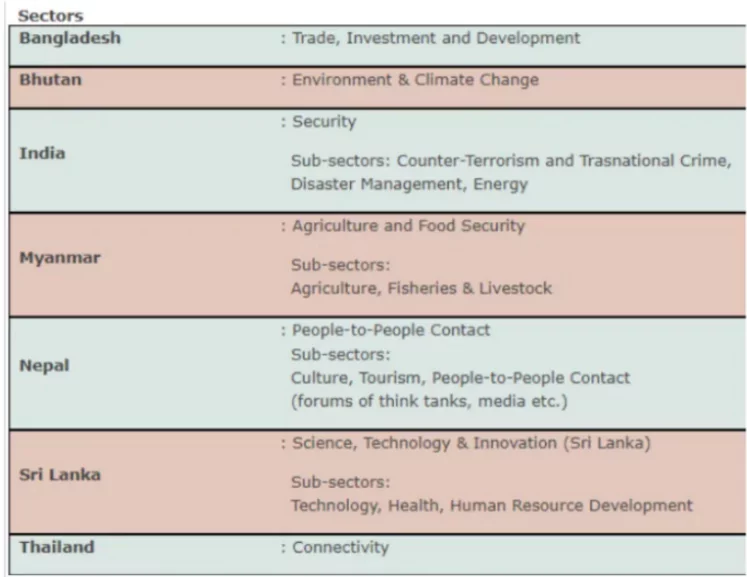
- Division of Responsibilities: Goals and areas of cooperation are divided among member states.
- Example: India has previously been responsible for sectors such as transportation, tourism, and counter-terrorism within BIMSTEC.
- Sector-Driven Organisation: Unlike many other regional groupings, BIMSTEC is a sector-driven cooperative organisation. Six areas of focus under BIMSTEC are —trade, technology, energy, transport, tourism and fisheries.
- Priority Areas: BIMSTEC has identified 14 priority areas: Trade & Investment, Transport & Communication, Energy, Tourism, Technology, Fisheries, Agriculture, Public Health, Poverty Alleviation, Counter-Terrorism & Transnational Crime, Environment & Disaster Management, People-to-People Contact, Cultural Cooperation.
- ‘Climate Change’ was added as the 14th priority area of cooperation in 2008.
- Among these priority areas, a member country chooses which of the 14 priority areas it is willing to take lead.
- India is the lead country for Transport & Communication, Tourism, Environment & Disaster Management and Counter-Terrorism & Transnational Crime.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
-
Working Mechanism of BIMSTEC:
- Under BIMSTEC, Policy making would be done through two types of meetings:
- Summits, which are supposed to be held every two years.
- Ministerial meetings of Foreign and Commerce Ministers of member countries for deciding on trade and economic affairs, to be held once every year.
- An operational meeting of senior officials to monitor the activities of the grouping is also supposed to be held twice a year.
- BIMSTEC Working Group: BIMSTEC has a coordinating body called the BIMSTEC Working Group, which has a rotating chairman based on which member country chairs the organisation.
- Under this, meetings are to be held monthly at the Dhaka secretariat to review the progress of the regional grouping.
- Business Forum & Economic Forum: It ensures active participation of the private sector.
Significance of BIMSTEC
The group has a combined population of 1.8 billion, or about 22% of the global population and its combined GDP was $4.5 trillion as of 2022, which was about 4.4% of world GDP, per World Bank data. As per UNCTAD, the states had a combined external trade of $1.95 trillion, or about 6% of world trade.
- Bridge between South and South-East Asia: The regional group constitutes a bridge between South and South East Asia and represents a reinforcement of relations among these countries.
- Aligns With India’s Vision: BIMSTEC represents the intersection of
- India’s ‘Neighbourhood First’ outlook, the ‘Act East Policy’, and the SAGAR (Security And Growth for All in the Region) vision.
- Security Cooperation: Shared security challenges such as terrorism and piracy necessitate cooperation among member states.
- India plays a key role in fostering security cooperation through joint exercises, intelligence sharing, and capacity-building initiatives.
- Trade Potential: BIMSTEC is important owing to the land and maritime trade potential of the member countries. There is potential for a Free Trade Agreement within BIMSTEC.
- Disaster Management and Climate Change: The Bay of Bengal region is highly vulnerable to natural disasters and climate change impacts. BIMSTEC offers a framework for regional cooperation in disaster management and climate change mitigation.
- India can lead efforts to enhance regional preparedness and resilience.
- Countering China: BIMSTEC could allow India to push a constructive agenda to counter Chinese investments, and instead follow best practices for connectivity projects based on recognised international norms.
- China has undertaken a massive drive to finance and build infrastructure in South and Southeast Asia through the Belt and Road Initiative in almost all BIMSTEC countries except Bhutan and India. The Chinese projects are widely seen as violating these norms.
- Others:
- Connectivity: Enhancing regional connectivity is its key focus and projects like the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project aim to improve connectivity. Improved connectivity will further boost trade, tourism, and people-to-people exchanges.
- Other examples of connectivity are ASIAN Trilateral Highway, BBIN motor vehicle agreement, etc.
- Energy Cooperation: BIMSTEC also provides a platform for regional energy cooperation as the Bay of Bengal region is rich in natural resources.
- Initiatives like the BIMSTEC Energy Centre and a regional energy grid contribute to energy security and sustainability.
- Multilateral Engagement: It allows India to engage multilaterally with the other countries of the Bay of Bengal region, which are its eastern neighbours and therefore vital for its economic development, security, and foreign policy imperatives.
- India also remains intent on solidifying relations with its eastern neighbours as China’s growing presence in the Bay of Bengal poses a potential threat to regional stability and India’s position as a preferred security partner.
Challenges with BIMSTEC
Following challenges have been faced by BIMSTEC that need to be tackled:
- Sluggish Pace: Lack of efficiency and “sluggish” pace of BIMSTEC’s progress.
- The inconsistency in holding policy making and operational meetings is also a concern.
- The focus of BIMSTEC is very wide, including 14 areas of cooperation like connectivity, public health, agriculture. It is suggested that BIMSTEC should remain committed to small focus areas and cooperate in them efficiently.
- Financial and Human Resources Crunch: BIMSTEC secretariat also suffers from inadequate financial and manpower assistance for its operational activities.
- Initiatives had been undertaken for the creation of a BIMSTEC Development Fund intended to ease the planning, and implementation of projects and programmes under the various cooperation areas, it is yet to be implemented.
- BIMSTEC has a limited budget (approximately US$ 200,000) and delayed implementation of the Development Fund.
- Absence of Connected Coastal Ecosystem: BIMSTEC members are yet to build a shared and lucrative coastal shipment ecosystem and also grapple with frequent detention of fishermen who cross territorial borders.
- China Factor: The formation of another sub-regional initiative beside China’s ambitious Belt and Road Initiative, the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar (BCIM) Forum, with the proactive membership of China, has created more doubts about the exclusive potential of BIMSTEC.
- Trade Challenges: India’s percentage of annual trade with BIMSTEC countries as a percentage of its total foreign trade was in the double digits in the 1950s, but was just 4% as of 2020.
- It was also seen that a lot of the time, BIMSTEC member countries do not import goods that are manufactured and exported by other members, instead importing from other non-member countries.
- BIMSTEC members have not adopted a Free Trade Agreement yet, they are involved in multiple bilateral and multilateral free trade, preferential trade and economic cooperation agreements with other countries.
- Others: BIMSTEC countries today face high anti-globalisation measures, the Russia – Ukraine war and new threats, disruption of supply chains, unavailability of emerging and critical technologies, climate change and environmental issues and maritime security issues.
- Bilateral Issues between Member Nations: Bangladesh is facing one of the worst refugee crises of Rohingyas from Myanmar who are fleeing persecution in the state of Rakhine in Myanmar. There is a border conflict between Myanmar and Thailand.
- India and Nepal have border disputes over Kalapani – Limpiyadhura – Lipulekh trijunction between India-Nepal and China and Susta area, West Champaran district, Bihar.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Way Forward
Regional integration is no longer an option but an essential part of a national policy in this age of shared challenges such as trade protectionism, war, climate issues, and energy security, among others. Also, BIMSTEC can draw lessons from ASEAN’s success in multilateral cooperation.
- Trade: It is high time that instead of completing other pillars, BIMSTEC countries implement the goods component of the FTA which has been negotiated already.
- BIMSTEC countries need to re-work for simplification and harmonisation of customs procedures, technical regulations, standards, and SPS measures, in administrative fees and charges, transparency of laws, regulations, and administrative rulings, risk management systems, and digitalization in trade procedures.
- Faster Mobility: BIMSTEC countries may negotiate a BIMSTEC Railway Agreement. Along with it, a regional air transportation agreement in cargo and passenger services will lead to promoting faster mobility of goods and services like tourism, health, and education.
- Attention on Exchange of Energy: The region is going to face many new challenges in the next 25 years including those that are related to climate and biodiversity. BIMSTEC countries should work together on emission reduction, energy efficiency, and renewable energy targets.
- Digital Connectivity: India’s United Payments Interface could be a great lead for other BIMSTEC countries. Digital connectivity is a new hope for BIMSTEC.
- Common Transit System: BIMSTEC Customs Transit System (BCTS) may offer strong catalytic power not only to facilitate trade among BIMSTEC but also to improve the region’s competitiveness.
- BCTS may help BIMSTEC countries with a single vehicle, a single transit, a single bank guarantee, and a single Customs declaration.
- Bay of Bengal countries also need development partners like Japan who can provide investment, technology, and infrastructure.
- Roadmap for Capacity Building: The BIMSTEC Secretariat has been entrusted to come out with Plans of Action for the region in view of the reorganisation of priority areas of cooperation. With increased resources, there is now a need to develop a roadmap for capacity building of the BIMSTEC Secretariat.
- The Secretariat needs to be adequately resourced and has sufficient delegated powers to fulfil its role as a coordinator of activities across BIMSTEC members.
- Others:
- Develop Connectivity Projects: The Indian government should expedite the implementation of connectivity projects, such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand trilateral highway, to facilitate trade and movement. This will not only enhance economic ties but also improve regional stability.
- Deepening Cooperation: BIMSTEC member countries should focus on deepening cooperation in various sectors such as trade, technology, energy, transport, tourism, fisheries, security, counterterrorism, disaster management, and energy.
- Dispute Resolution: BIMSTEC can formulate a dispute-resolution mechanism, which operates on the principles of deliberation and consensus.
Conclusion
This year marks a decade of India’s Act East and Neighbourhood First policies, and the thrust on BIMSTEC is a manifestation of India’s efforts to continue nurturing collaborative growth for national and regional well-being.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Bangkok Vision 2030
Bangkok Vision 2030 would be an overarching kind of document to guide BIMSTEC towards a prosperous, resilient and open region by 2030.
- The goals found in the vision are also in line with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals and Thailand’s bio-circular-green economic model.
|
![]() 29 Jul 2024
29 Jul 2024


 Distinctive Features of BIMSTEC:
Distinctive Features of BIMSTEC:
