Recently, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi participated in the G-7 Outreach Summit. The 51st G7 Summit was held in Kananaskis, Canada.
- India has been invited to attend the G7 Summit outreach sessions twelve times.
- 2003 (France), 2005 (UK), 2006 (Russia), 2007 (Germany), 2008 (Japan), 2009 (Italy), and more recently every year since 2019, including the 2025 summit in Canada.
- This is Prime Minister Modi’s first visit to Canada since 2015, following an official invitation from Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney.
- Indian PM also held a bilateral meeting with the Prime Minister of Canada on the sidelines of the G7 Summit.
Key Highlights of the Bilateral Meeting Between India and Canada
- Reaffirmation of India-Canada Relations: Both leaders emphasized the importance of shared democratic values, rule of law, and commitment to sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Restoration of Diplomatic Ties: India, Canada agree to designate new High Commissioners for the 1st time since 2023.
- Trade Relations: Agreed to restart the Early Progress Trade Agreement (EPTA) negotiations, aiming for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- Promotion of Free and Open Indo-Pacific: Both leaders reaffirmed their shared interest in promoting a free and open Indo-Pacific.
|
Major Outcomes and Initiatives
- Kananaskis Wildfire Charter: G7 countries have agreed to cooperate on efforts to manage the impacts of devastating wildfires.
- India endorsed the charter.
- G7 Critical Minerals Action Plan: G7 countries and their allies will form a “critical minerals production alliance” to stockpile and develop materials that are essential for defence systems and advanced technologies.
- AI Governance and Responsible Technology: Recognize the potential of a human-centric approach to artificial intelligence (AI) to grow prosperity, benefit societies and address pressing global challenges.
- G7 pushes for responsible development to address job displacement and ethical concerns.
- G7 Coalition to Prevent and Counter Migrant Smuggling: Reaffirm their commitment to prevent and counter migrant smuggling.
- Under the 2024 G7 Action Plan to Prevent and Counter the Smuggling of Migrants.
- Condemnation of Transnational Repression (TNR): G7 committed to legal and diplomatic measures to protect diaspora communities and uphold democratic freedoms.
- Includes sharing intelligence and strengthening national laws against TNR.
Key Geopolitical Discussions at the 51st G7 Summit (2025)
- Russia-Ukraine War: The ongoing conflict remained a focal point, with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy attending as a guest to urge stronger support. G7 leaders aimed to pressure Russia economically to push for negotiations.
- No joint statement on Ukraine due to U.S. resistance, reflecting internal G7 divisions.
- Individual commitments (e.g., Canada’s aid, UK’s sanctions) were made, but collective action stalled.
- Israel-Iran Conflict: Israel’s airstrikes on Iranian military and nuclear sites, followed by Iran’s retaliatory missile attacks, overshadowed the summit.
- Global Trade and U.S. Tariffs: No formal G7 agreement on trade due to Canada’s decision to avoid a comprehensive communiqué. Bilateral deals (e.g., UK-U.S.) progressed, but broader tensions persisted.
- Indo-Pacific Security and China: G7 members reiterated their commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific, amid concerns over China’s actions in the South and East China Seas.
- No new initiatives were announced, but existing commitments were reaffirmed, aligning with G7’s broader strategy to counter China’s global influence.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Address at the G7 Outreach Session (2025)
- Terrorism and Global Security: Called for a stronger global response against terrorism.
- Advocated for strict actions against countries supporting terrorism and emphasized no double standards in dealing with terrorism.
- Raised critical questions about global complacency towards terrorism:
- Will the world only act when they become a target?
- How can perpetrators and victims of terrorism be equated?
- Will global institutions stay silent on terrorism?
- Energy Security: Emphasized the importance of energy security for future generations.
- Highlighted India’s approach based on availability, accessibility, affordability, and acceptability.
- India has successfully met its Paris climate commitments ahead of time.
- Global South Concerns: Stressed the need for the Global South to be heard and prioritized in global decisions.
- Technology, AI, and Energy Nexus: Noted the growing role of AI in driving efficiency and innovation but also its energy-intensive nature.
- Emphasized the need for sustainable, clean energy solutions for AI development.
|
About the Group of Seven (G7)
- It is an informal intergovernmental organization of advanced industrialized democracies that meet annually to coordinate global economic policy, security issues, and geopolitical strategies.
- Origin: The G7 was originally formed in 1975 as the G6 (France, West Germany, Italy, Japan, the UK, and the USA) in response to the 1973 oil crisis and ensuing global recession.
- Canada joined in 1976, making it the G7.
- Russia joined to form the G-8 in 1998 but was expelled after the 2014 annexation of Crimea.
- All G7 members are also part of the G20.
- Current Members (2025): United States; United Kingdom; Canada; Germany; France; Italy; Japan.
- Goals of the G7
- Promote global economic stability and sustainable growth
- Coordinate responses to financial crises and trade disputes
- Address global issues like climate change, health pandemics, and food security
- Uphold democratic values, human rights, and rules-based international order
- Counterbalance emerging powers through strategic alliances and policy consensus
- How Does G7 Work?
 The presidency rotates yearly among member countries, which organise the summit and set priorities.
The presidency rotates yearly among member countries, which organise the summit and set priorities.- Leaders meet annually at the summit, while ministers and officials meet regularly throughout the year.
- Other countries and international organisations are sometimes invited as guests to participate in discussions.
- The G7 operates by consensus and does not have binding legal authority, but its influence is significant.
Significance of the G7
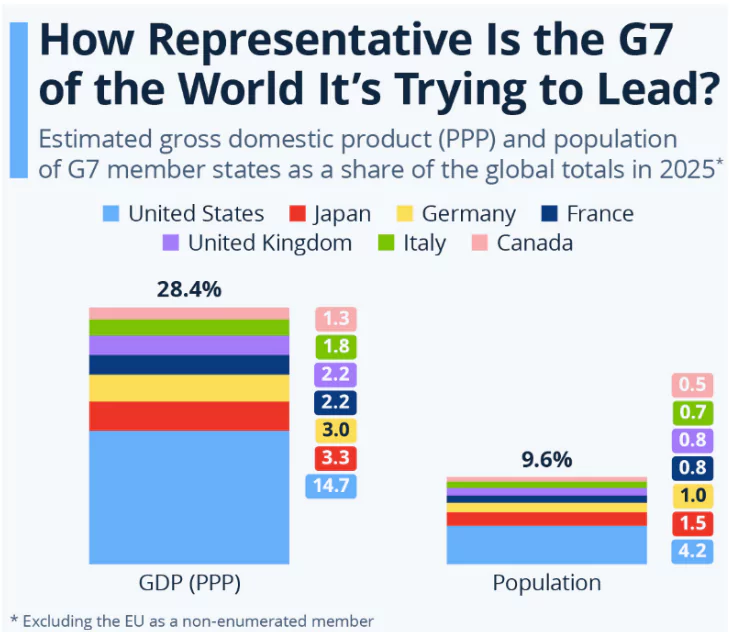
- Coordination of Global Economic Policy: The G7 plays a central role in shaping global economic policy, with its members accounting for around 30% of global GDP.
- The 2024 G7 Summit led to agreements on funding Ukraine through seized Russian assets and on sanctions against Chinese companies supporting Russia’s war efforts.
- Global Security and Geopolitical Stability: The G7 is vital for maintaining global security by coordinating responses to conflicts and geopolitical tensions, especially those involving Russia, Iran, and other powers.
- During the 2025 summit, the G7 called for de-escalation in the Israel-Iran conflict and pledged to safeguard market stability, recognizing the potential threats to energy markets.
- Technological Innovation and Future Growth: The G7 nations play a critical role in advancing technological innovations, particularly in AI, quantum computing, and digital transformation.
- The 2025 G7 Summit emphasized the need for international collaboration on AI and quantum innovations, as well as fostering public-private partnerships to ensure these technologies are safe and sustainable.
- Leadership in Climate Change and Sustainable Development: The G7 countries are at the forefront of global climate action, shaping the international response to climate change through policies and financing.
- The Global Apollo Programme launched at the 2015 G7 summit aims to make clean electricity cheaper than coal power globally, representing a pivotal commitment by G7 countries towards sustainable energy.
- Global Health and Pandemic Preparedness: The G7 is instrumental in coordinating responses to global health crises, such as pandemics, and ensuring equitable health access across nations.
- The G7’s Global Health Initiative helped fund COVID-19 vaccine distribution and continued its efforts to ensure that future health emergencies are met with a unified, global response.
- Diplomatic Influence and International Relations: The G7 wields significant diplomatic influence, shaping global governance frameworks and encouraging multilateral cooperation on global challenges.
- The G7 has expanded its outreach to include emerging powers, like India, recognizing the importance of including diverse perspectives in global policy discussions.
Challenges and Criticism for G7
- Exclusion of Emerging Economies: The G7’s exclusivity limits its representativeness in addressing global issues.
- The G7 excludes China, India, and other emerging economies, which now account for a significant portion of global GDP.
- Ineffectiveness in Addressing Global Conflicts: The G7 has struggled to resolve ongoing geopolitical conflicts, like the Israel-Iran and Russia-Ukraine issues.
- The 2025 summit could not issue a joint statement on Ukraine due to U.S. resistance, highlighting internal divisions.
- The G7’s response to the Israel-Iran conflict was criticized for lacking clear action.
- Weak Consensus on Global Trade Issues: Disagreements on trade policies undermine the G7’s ability to coordinate global economic strategies.
- Trump’s tariffs on G7 members have exacerbated trade tensions, with the U.S. pushing for protectionist measures while others favor multilateral cooperation.
- Declining Influence on Global Economic Governance: The G7’s share of global GDP has decreased, reducing its power in shaping economic policies.
- The G7 now controls about 30% of global GDP, down from 70% in the 1980s.
- Lack of Effective Action on Climate Change: The G7 has faced criticism for not taking stronger action on climate change.
- The failure to mention climate change in the wildfire charter reflected the G7’s reluctance to confront the climate crisis head-on.
- Internal Divisions and Leadership Gaps: The G7 faces growing internal divisions, which undermine its effectiveness and unity.
- The G7 summit in 2025 saw divisions over the Ukraine war and the Israel-Iran conflict, with the U.S. pushing its own agenda, undermining the group’s coherence.
Why is India important for the G7?
- Economic Power and Growth: India is the world’s fourth-largest economy and a key driver of global growth.
- India’s GDP is projected to grow significantly, contributing to global economic stability.
- Large Population Base and Consumer Market: India’s 1.4 billion people make it one of the largest and most influential consumer markets globally.
- Voice of the Global South: India represents the Global South, advocating for the interests of developing nations.
- At the 2025 G7 Summit, India emphasized that the Global South faces the brunt of geopolitical crises, economic instability, and climate change.
- Strategic Position in Global Security: India plays a crucial role in global security and stability, especially in the Indo-Pacific.
- As a member of the Quad (along with the U.S., Japan, and Australia), India is pivotal in countering China’s growing influence in the Indo-Pacific.
- Technological and Digital Leadership: India is a global leader in technology and digital innovation.
- India has a rapidly expanding AI talent pool, driving innovations in sectors like quantum computing, AI, and energy efficiency.
- Renewable Energy and Climate Leadership: India plays a critical role in climate action and renewable energy.
- India is a key proponent of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and has met its Paris climate goals ahead of schedule.
- As of October 2024, India’s renewable energy capacity accounts for 46.3% of its total installed capacity, showcasing its leadership in sustainable energy.
Significance of the G7 for India
- Leveraging Global Platforms for Economic Reforms: The G7 offers India a platform to push for economic reforms and align with global policy frameworks.
- Expanding Multilateral Influence and Partnerships: The G7 acts as a gateway for India to strengthen multilateral relationships outside traditional groupings like BRICS and the G20.
- India’s engagement with G7 members fosters collaboration on socio-economic issues and geopolitical challenges.
- Securing Strategic Economic Interests in Trade Policy: The G7 provides India a platform to secure its trade interests and expand its global market access.
- Shaping Global Health Policies and Pandemic Preparedness: The G7 provides India with an opportunity to collaborate on global health and pandemic preparedness, areas where it has demonstrated leadership.
- G7 discussions on global health infrastructure and vaccine equity align with India’s role in ensuring access to medicines and pandemic preparedness.
- G7’s Role in Addressing India’s Security Concerns: The G7 platform allows India to address global security concerns and reinforce its position on issues like terrorism and cybersecurity.
- India benefits by aligning its counter-terrorism strategies with G7 nations and reinforcing the need for global cooperation on cybersecurity.
- Security and Geopolitical Cooperation: The G7 offers India an opportunity to collaborate on global security issues, such as the Indo-Pacific, terrorism, and regional stability.
- The G7’s support for a free and open Indo-Pacific aligns with India’s interests in countering China’s growing influence.
Challenges with India’s engagement with G7 countries
- Conflict of Interests on Global Issues: India’s interests often conflict with those of G7 countries on key global issues like climate change and trade policy.
- India’s emphasis on energy security and sustainable development sometimes clashes with G7 countries’ calls for more stringent environmental regulations.
- Geopolitical Divergence with Western Allies: India’s strategic autonomy often puts it at odds with the G7, particularly with the U.S. and Europe on issues involving Russia and China.
- India’s continued defense and energy ties with Russia (e.g., buying S-400 missiles) have led to tensions with Western allies who favor isolating Russia.
- Pressure on Trade and Economic Policies: India’s growing economy faces pressures from G7 countries on trade liberalization and market access, which may conflict with its domestic policies.
- India often faces calls for greater market access in sectors like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing, which can threaten domestic industries and labor policies.
- Pressure to Align on Security Issues: The G7’s focus on issues like global terrorism and counterterrorism sometimes requires India to align with Western-centric approaches that do not address India’s specific security concerns.
- G7 countries do not fully prioritize India’s concerns with cross-border terrorism from Pakistan or issues like terrorist safe havens.
- Domestic Backlash Against Western Influence: Domestic political resistance in India to greater engagement with the G7 could limit deeper ties.
- The Khalistani issue and other domestic concerns related to foreign interference have led to criticism of G7 countries, especially Canada and the U.K., impacting India’s willingness to engage deeply.
Way Forward for India’s Engagement with the G7
- Strengthen Multilateral Engagement: India should continue engaging with the G7 while also strengthening ties with other multilateral groups like BRICS, G20, and Quad.
- It will help balance global interests and protect India’s strategic autonomy while addressing key challenges.
- Advocate for Global South Issues: India must champion Global South concerns at the G7, focusing on climate action, food security, and economic equality.
- India can push for a more inclusive global policy framework that ensures developing countries are not sidelined.
- Enhance Economic Cooperation: India should deepen economic partnerships with G7 members in sectors like digital trade, critical minerals, and renewable energy.
- Help India secure access to advanced technologies and strengthen supply chains.
- Focus on Sustainable Development: India should work with the G7 on climate change, energy security, and sustainable agriculture.
- Aligns with India’s goals of green energy transition and positions India as a leader in climate action.
- Strengthen Security Cooperation: India should align with G7 countries on counterterrorism, cybersecurity, and regional stability.
- This will enhance India’s global security posture while safeguarding its interests in the Indo-Pacific and beyond.
- Ensure Technological and Digital Sovereignty: India should develop partnerships in AI, quantum tech, and cybersecurity while ensuring data sovereignty and technological independence.
- This will reduce India’s reliance on G7 nations for critical technologies and promote domestic innovation.
Conclusion
The G7 Summit serves as a vital platform for India to strengthen diplomatic relations, advocate for Global South issues, and shape global economic, security, and technological policies. However, India must navigate challenges such as geopolitical divergence and economic pressures to ensure its strategic autonomy and global influence.
![]() 19 Jun 2025
19 Jun 2025


 The presidency rotates yearly among member countries, which organise the summit and set priorities.
The presidency rotates yearly among member countries, which organise the summit and set priorities.