The first science result from the Aditya-L1 mission is out. Aditya L1 mission has achieved its first scientific milestone by using its primary payload, the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), to precisely estimate the onset time of a coronal mass ejection from the Sun on July 16.
Key Observations of the Aditya L1 mission
- Close-range CME Observation: VELC’s unique spectroscopic data allows scientists to study CMEs near the Sun’s surface, which is usually challenging with visible-light observations alone.
- Thermodynamic Insights: VELC helps scientists understand the thermodynamic properties of CMEs close to their source regions on the Sun, offering valuable insights into solar eruptions.
- Solar Cycle Monitoring: The Sun is currently approaching the peak of its solar cycle (Cycle No. 25), suggesting an increase in CME activity.
- VELC’s continuous monitoring can yield extensive scientific data about these eruptions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME)
- Definition: A Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) is a massive release of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona into space.
- Cause: CMEs are caused by the sudden reconfiguration of the Sun’s magnetic fields, which leads to an explosive release of energy.
-
- Frequency: CMEs are more frequent during the peak of the Sun’s 11-year solar cycle.
- Characteristics: They consist of billions of tons of charged particles (plasma) that travel at speeds of hundreds to thousands of kilometers per second.
- Impact on Earth:
- Satellite Disruption: CMEs can damage satellite electronics and impact GPS and communication systems.
- Geomagnetic Storms: When CMEs interact with Earth’s magnetic field, they can cause geomagnetic storms, potentially disrupting power grids and radio communications.
- Auroras: CMEs can intensify auroras, creating spectacular light displays near the poles.
|
About Aditya L1 Mission
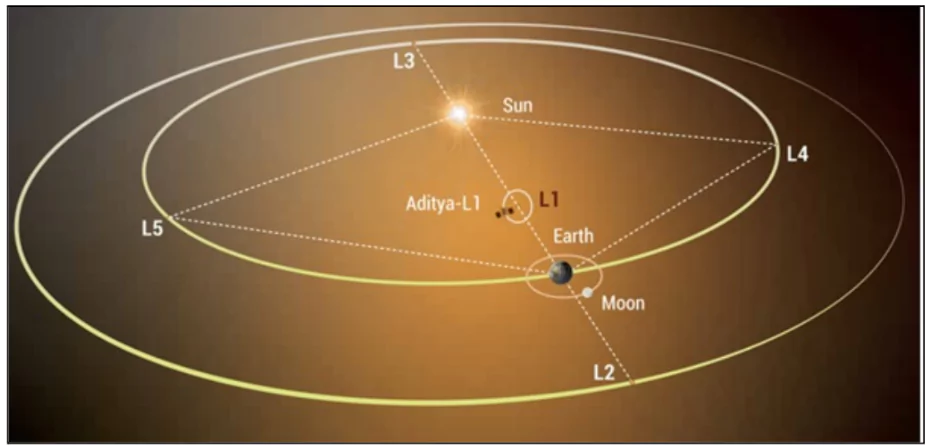
- Launch Date: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched the Aditya-L1 mission on September 2, 2023, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- Mission Goal: Aditya-L1 is India’s first dedicated scientific mission to study the Sun.
- Payload: The mission’s primary payload, the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), was developed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAp), Bengaluru.
- Current Orbit: Aditya-L1 was placed in a halo orbit around the Earth-Sun Lagrange point (L1) on January 6, 2024.
- Mission Lifespan: Aditya-L1 is designed to operate for five years, continuously observing and gathering data on solar phenomena.
![]() 4 Nov 2024
4 Nov 2024

