Context:
- This article is based on the news “Why the Indian Army is embracing AI” Which was published in the Indian Express. The Indian Army has been deploying Artificial Intelligence (AI) surveillance systems along its borders with Pakistan and China.
| Relevancy for Prelims: AI in Defence, Border Security and Surveillance, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), RADAR, AGNI-D surveillance software, and WARDEC.
Relevancy for Mains: What is Ai and Role of AI in Defence sector, and What significance and concerns are related to the AI in defence sector. |
Ai in Defence: Advancing Border Security & Surveillance
- A total of 140 AI-based surveillance systems have been deployed for this purpose.
- These systems include high-resolution cameras, sensors, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) feeds, and radar feeds.
- The data collected from these various sources is processed and analyzed using artificial intelligence technology.
- The primary goal of these systems is to detect intrusions at the borders and classify potential targets for more effective border security.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- AI is the simulation of human intelligence by computers. It relates to the ability to learn, rationalize and undertake appropriate actions to achieve a specific goal.
Increasing Deployment of AI in Defence sector
- AI-Based Real-Time Monitoring: The Indian Army is using AI-based real-time monitoring software for generating intelligence in counter-terrorist operations.
- High-Tech Military Simulators: The military is also adopting high-tech military simulator technologies to train recruits, with the potential for broader implementation in future training programs.
- AI Technologies Launch: Defense Minister launched 75 newly-developed AI technologies during the “AI in Defense” symposium, showcasing robotics, automation tools, and intelligence surveillance.
- Defense AI Dialogue with the United States: The United States and India have agreed to launch a Defense Artificial Intelligence Dialogue and expand joint cyber training efforts.
- AGNI-D Surveillance Software: An AI-based surveillance software called AGNI-D was unveiled at Aero India for surveillance and security in the eastern Ladakh sector, near the China border.
- Features of AGNI-D: AGNI-D can recognize movement, weapons, vehicles, tanks, and missiles in real-time and recorded video footage.
- WARDEC: The Army Training Command and Rashtriya Raksha University are collaborating to establish a ‘Wargame Research and Development Centre’ in New Delhi, known as ‘WARDEC’.
-
- This center will be India’s first simulation-based training facility using AI and virtual reality for metaverse-enabled gameplay.
- It aims to train soldiers and test strategies for various scenarios, including warfare, counter-terrorism, and counter-insurgency operations.
|
Also read: Security Challenges and their management in Border Areas
What is the significance of AI in Defence?
- Game-Changer in Various Fields: AI is seen as a game-changer in logistics, information operations, and intelligence collection.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: AI can significantly improve military logistics and supply chain management, enhancing efficiency.
- AI-Based Border Surveillance: India employs 140 AI-based surveillance systems at its borders with Pakistan and China, reducing human involvement and enhancing security by detecting intrusions and classifying targets.
- AI-Powered Drones: AI-equipped drones excel in day and night reconnaissance missions, capturing images and extracting data from remote locations. They also detect enemy drones, offering cost-effective threat mitigation.
- Lethal Autonomous Weapon Systems (LAWS): LAWS autonomously detect, select, and engage hostile targets, multiplying force effectiveness while requiring minimal personnel.
- Autonomous Combat Vehicles and Robots: These technologies enhance soldier protection and performance, aiding in monitoring casualty evacuation,
- Positioning in Intelligent Warfare: India aims to position itself at the forefront of intelligent warfare strategies, recognizing the importance of AI in various military applications, including border control, comprehensive surveillance, and AI-equipped drones for reconnaissance missions.
- Data Management and Enhanced ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) Capabilities:
- AI can process vast amounts of military data, providing actionable intelligence.
- Supports on-field warfighters with credible intelligence.
- Example: Project Maven in the United States uses AI for data analysis in counter-insurgency operations.
- AI aids physical ISR in harsh terrains and weather conditions, reducing risks to human soldiers.
- Cybersecurity
- AI is used for both ISR activities and as a weapon system (offensive or defensive).
- Trained AI systems are more efficient in identifying and responding to cyber threats.
- Essential in combating evolving and sophisticated cyber threats that surpass human capabilities.
What are the concerns related to the AI in defence?
- Budget Constraints: India’s current AI investment in the military is seen as inadequate compared to its strategic rival, China.
- According to the Delhi Policy Group, a security think tank, the Indian military allocates approximately US$50 million annually for AI spending. China invests more than 30 times as much in AI technology.
- Over-Reliance on Surveillance Systems: There is a concern that overreliance on even advanced surveillance systems may not be foolproof, as demonstrated by the recent surprise attack on Israel. anticipating and preventing unexpected threats.
- Complexity of Counter-Terrorism: Counter-terrorism and counter-insurgency operations often involve complex and nuanced situations that AI systems do not interpret easily. Human intelligence is crucial in understanding the subtleties of human behavior and decision-making in such contexts.
- Misidentification of Targets: AI systems may make mistakes in identifying targets, potentially leading to unintended attacks on non-combatants or friendly forces, resulting in unacceptable collateral damage.Ex, U.S. drone surveillance footage has misidentified civilians as terrorist targets in the August 2021 strike in Afghanistan.
- Data and Privacy: Balancing personal data protection with AI’s benefits poses challenges and trade-offs between privacy and prosperity.
- Ethical Dilemma: There is a moral question regarding whether AI systems should have the authority to autonomously select and engage targets without human intervention, especially in situations where human lives are at stake.
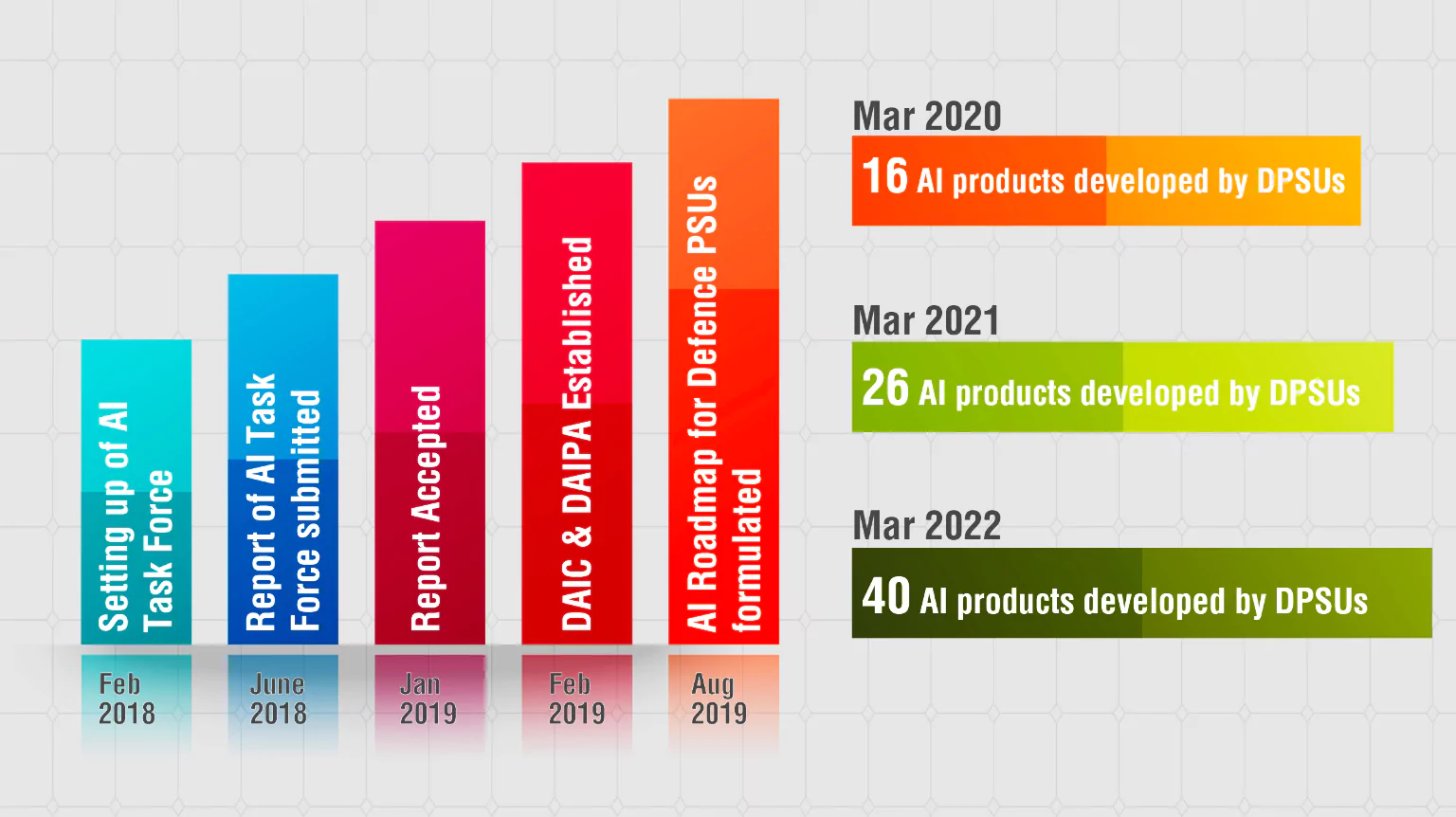
Task Force For Implementation of AI
- In March 2018, the Ministry of Defence (MoD) established a Task Force under Sh. N Chandrasekaran, Chairman of Tata Sons.
Key Recommendations
- Integration of AI strategy with defence strategy.
- Establishment of the Defense AI Council (DAIC) and Defense AI Project Agency (DAIPA).
- Development of a Data Management Framework and appointment of a Data Management Officer.
- Scaling up Data Centers and creating a facilitated network of Test Beds.
- Collaboration with industry and start-ups for AI development and IP management.
- Implementation of AI training courses across Defence training centers and institutes.
- Earmarking an AI budget from the annual Defense Budget with a Rs 1,000 crore corpus for five years to support AI activities.
|
Also read: Hamas Attack on Israel: Lessons For India to Learn
Way Forward
- Human Accountability: Defining the extent of human involvement and responsibility in AI-driven military operations is crucial. Clear lines of accountability need to be established for any mishaps or wrongdoing.
- Doctrinal Variations: The extent of AI system autonomy may vary among different military doctrines, but there is a general consensus that fully unpredictable autonomous systems may not be preferred in military operations.
- The US, for example, recently updated its policy directive on autonomy in weapon systems, allowing them to use lethal force, but with the caveat that such autonomous systems must be explicitly designed to allow commanders to “exercise appropriate levels of human judgment over the use of force”.
- Set-up Processes and Practices: Establish processes and practices that facilitate collaboration with research labs, academia, startups, and the private sector.
- The Indian Army has been closely collaborating with Academia, the Indian Industry and DRDO for the realization of complex AI-based projects.
- For this, an AI Lab has been established at the Military College of Telecommunication Engineering wherein AI projects have undergone extensive in-house testing.
- Role of Private Sector: Recognize the private sector’s pivotal role in making AI accessible and efficient for military purposes. Foster an ecosystem that promotes the flow of both capital and skills, which is essential for AI innovation.
- Robust Hardware and Enabling Data Banks: Invest in robust hardware and establish data banks to support AI operations. Critical infrastructure availability is crucial for AI’s success in both civilian and military applications.
Conclusion:
Deploying AI in defence, the Indian Army has integrated 140 AI-based surveillance systems along its borders with Pakistan and China, utilizing high-resolution cameras, sensors, UAV feeds, and radar feeds. These systems analyze data to detect intrusions, classify targets, and bolster border security, showcasing AI’s transformative role in real-time monitoring, military simulators, and intelligence surveillance.
| Prelims Question (2020)
With the print state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
1. Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
2. Create meaningful short stories and songs
3. Disease diagnosis
4. Text-to-Speech Conversion
5. Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (d) |
![]() 21 Oct 2023
21 Oct 2023


