Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi chaired a roundtable with Indian AI start-ups ahead of the India AI Impact Summit 2026.
- The interaction highlights India’s strategic intent to position India as a global hub for ethical, inclusive and indigenous artificial intelligence innovation.
- A total of 12 Indian AI start-ups, qualified under the Foundation Model Pillar, participated in the roundtable ahead of the Summit scheduled next month in India.
- The Foundation Model Pillar, a key component under the IndiaAI Mission aims to develop indigenous, large-scale AI models that can be adapted across many tasks such as language, healthcare, science, governance, and agriculture.
| India’s AI Start-Up Ecosystem: India has about 1.8 lakh startups, and around 89% of newly launched startups last year used AI in products or services. |
Key outcomes of the Roundtable Meet
- Observations by AI Start-Ups
- Shift in Global AI Centre: Start-ups noted that the centre of gravity of AI innovation and deployment is beginning to shift towards India.
- Rapid Sectoral Growth: The AI sector in India was highlighted as witnessing rapid growth with vast future potential.
- Prime Minister’s Vision for AI:
- AI for Societal Transformation: The Prime Minister underlined the importance of artificial intelligence in transforming society and reiterated India’s role as a global technology leader through the upcoming Summit.
- Start-Ups as Nation Builders: He emphasised that start-ups and AI entrepreneurs are the co-architects of India’s future, reflecting India’s capacity for innovation and large-scale implementation.
- Made in India, Made for the World: The Prime Minister urged the development of a distinct Indian AI model that embodies the spirit of “Made in India, Made for the World.”
- Ethics and Trust: The Prime Minister stressed that Indian AI models must be ethical, unbiased, transparent, and grounded in data privacy principles.
- Inclusive and Affordable AI: He highlighted India’s potential to lead globally in affordable AI, inclusive AI, and frugal innovation.
- Promotion of Local Content: Indian AI models should promote local and indigenous content, including regional languages, to reflect India’s cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Assurance of Support: The Prime Minister assured full government support for the success and global scalability of Indian AI models.
About the India AI Impact Summit 2026
- Host: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Venue: New Delhi, February 2026
- Theme: Democratizing AI, Bridging the AI Divide
- The AI Impact Summit will be the fourth in the series, following:
- Bletchley Park Summit (UK, 2023)
- Seoul Summit (South Korea, 2024)
- AI Action Summit (Paris, France, 2025)
- Key Themes of Paris AI Action Summit 2025: Public Interest AI , Future of Work, Innovation & Culture, Trust in AI, Global AI Governance.
- Aim: It aims Tto promote responsible, inclusive, and development-focused AI cooperation, with a strong emphasis on the Global South.
- Builds upon existing global efforts such as the G20 AI Principles, UN and GPAI resolutions, the African Declaration on AI, and the Hamburg Declaration on Responsible AI.
- Conceptual Framework:
- The India AI Impact Summit is structured around three core ‘Sutras’—a Sanskrit term denoting guiding principles that connect knowledge with action.
- These pillars outline how artificial intelligence can be leveraged through multilateral cooperation for shared global benefit.
- People: Promotes human-centric, inclusive, culturally sensitive, and trustworthy AI.
- Planet: Advocates responsible AI aligned with climate action, sustainability, and lower energy use.
- Progress: Focuses on AI-driven equitable growth in health, education, governance, agriculture, and public services.
- Operational Framework: Seven Chakras
- The Sutras are translated into action through Seven Chakras, which represent priority domains for international cooperation and tangible AI outcomes.
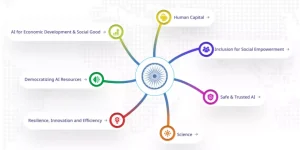
|
Why need for AI Start-ups in India/ Role of Indian AI Start-Ups
- Technological Self-Reliance:
- AI start-ups are essential for achieving technological sovereignty by reducing India’s dependence on foreign AI platforms and proprietary models.
- Indigenous AI solutions help safeguard national data, strategic autonomy and digital security.
- Leveraging India’s Demographic and Data Advantage
- India’s large population generates vast and diverse datasets that can be effectively harnessed by domestic AI start-ups.
- Local start-ups are better positioned to develop context-specific AI solutions suited to India’s socio-economic realities.
- Promotion of Indian Languages and Culture
- Indian AI start-ups play a crucial role in developing multilingual and Indian language AI models.
- Language-inclusive AI ensures digital inclusion and prevents exclusion of non-English-speaking populations.
- Inclusive and Affordable Innovation
- AI start-ups promote frugal and affordable innovation, making advanced technology accessible to a wider population.
- Affordable AI solutions are vital for sectors such as healthcare, education and agriculture, particularly in rural areas.
- Economic Growth and Employment Generation:
- AI start-ups contribute to high-value job creation in areas such as data science, research and engineering.
- They enhance India’s competitiveness in the global digital economy and support the goal of becoming a $5 trillion economy.
- Sectoral Transformation:
-
- In healthcare, AI start-ups improve diagnostics, medical research and disease prediction.
- In industry and manufacturing, AI enhances efficiency through automation, predictive maintenance and simulations.
- In governance, AI can support data-driven decision-making and service delivery.
Initiatives taken by India
- IndiaAI Mission:
- The IndiaAI Mission is a national-level programme approved by the Union Cabinet in March 2024 to strengthen India’s AI innovation ecosystem.
- It seeks to position India as a global leader in Artificial Intelligence (AI) by promoting research, innovation, computing infrastructure, and skilling.
- Implemented by: Digital India Corporation (DIC) under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Foundation Model Development:
- Under the Mission, support is being provided for the development of foundation models, including large language models and multimodal AI systems.
- The initiative aims to reduce dependence on foreign AI platforms and promote technological self-reliance.
- National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence:
- NITI Aayog released the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence, outlining the vision of “AI for All”.
- The core philosophy is to leverage AI to solve pressing societal challenges and improve the quality of life for its citizens.
- The strategy prioritises AI applications in sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, education, smart cities and mobility.
- Digital Public Infrastructure as AI Enabler
- Data-Driven Governance: India’s Digital Public Infrastructure, including Aadhaar, UPI and DigiLocker, provides a robust foundation for AI-based innovation.
- DPI enables large-scale data availability while promoting efficiency and inclusion.
- Kerala: Kerala AI Future Con:
- Ahead of the India AI Impact Summit 2026, the Government of Kerala is organizing a one-day summit titled ‘Kerala AI Future Con’ in January.
- This summit is organized under the India AI Mission, MeitY, and in collaboration with various local partners such as Kerala IT, Startup Mission, and Digital University.
- Tamil Nadu: Deep-Tech Startup Policy
- The Tamil Nadu Government has unveiled a Deep-Technology Startup Policy with a Rs 100 crore outlay during the Umagine TN Technology Summit to support innovation and translate research into commercial projects.
- The policy aims to foster deep-tech innovation, including AI, and supports Tamil Nadu’s shift from an IT services hub to a technology and innovation hub.
Global Initiatives
- Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI):
- GPAI is a multi-stakeholder initiative involving governments, industry, academia and civil society to promote responsible AI innovation.
- It supports AI start-ups through research collaboration, policy guidance and best practices.
- India is a founding member, enhancing its role in shaping global AI governance.
- United Nations Initiatives on AI:
- The United Nations promotes AI innovation through initiatives aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- UN agencies encourage AI start-ups to develop solutions for healthcare, education, climate change and poverty reduction.
- European Union AI Strategy:
- The European Union supports AI start-ups through research funding, AI sandboxes and innovation hubs.
- The EU AI framework aims to balance innovation, consumer protection and ethical safeguards.
- Tech Giant-Led Accelerators:
- Google for Startups Accelerator: AI-First: Global cohort based accelerator with expert guidance to tackle technical challenges.
- AWS Generative AI Accelerator: Supports generative AI startups with up to significant AWS credits and intensive 8-week programme.
- Google.org Accelerator: Generative AI: Open call for impact-focused AI solutions with funding (e.g., share of $30M), pro bono assistance, training, and cloud credits.
- Ignition AI Accelerator: NVIDIA & Tribe collaboration focusing on scaling AI startups, particularly in Asia-Pacific.
- Intel® Liftoff for startups: The program offers a mix of technical mentorship, cloud infrastructure resources, and access to Intel’s market ecosystem
Challenges for AI Start-Ups
- Data-Related Challenges:
- Access to Qquality Ddata: AI models require large, diverse, and labeled datasets, which are costly and often proprietary.
- Competition Commission of India study notes that 68% of AI startups cite access to large, high‑quality datasets as a major barrier
- Privacy & Ccompliance: Adherence to data protection laws (GDPR, DPDP Act, etc.) increases compliance burden.
- High Cost of Technology & Infrastructure:
- AI development requires high computational power, GPUs, cloud services, and continuous model training.
- Dependence on Big Tech platforms may reduce autonomy.
- Limited access to affordable compute infrastructure increases operational costs and restricts innovation.
- Rising costs of AI chips and cloud credits strain early-stage startups.
- Talent Shortage:
- AI start-ups face intense competition for skilled professionals such as data scientists and AI researchers.
- By 2027, AI-related job openings in India could surpass 2.3 million, while the talent pool is expected to grow to around 1.2 million.
- The migration of top talent to global technology firms leads to brain drain and raises hiring costs.
- Regulatory and Compliance Uncertainty
- Evolving regulations on data protection, AI ethics and cross-border data flows create uncertainty for start-ups.
- Compliance costs can disproportionately burden small and early-stage AI enterprises.
- Ethical and Trust Deficit:
- Data bias & representativeness Concerns related to algorithmic bias, lack of transparency and misuse of AI reduce public trust.
- Start-ups must invest additional resources to ensure ethical and explainable AI systems.
- Market Access and Scalability Issues:
- Adoption Barriers: AI start-ups often face difficulties in scaling solutions beyond pilot projects.
- Resistance to adoption by traditional industries and governments slows market expansion.
- Global Competition and Market Dominance:
- Unequal Playing Field: AI start-ups compete with global technology giants that possess superior data, capital and market reach.
- For Instance, AI-Tech giants like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Perplexity are deepening their presence in India.
- Dominance of large firms can stifle innovation and reduce opportunities for smaller players.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks:
- Security Vulnerabilities: AI systems are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, data breaches and model manipulation.
- Inadequate cybersecurity measures can undermine user trust and regulatory compliance.
- Funding Constraints:
- Securing funding is a persistent challenge for AI start-ups, particularly amid economic uncertainty and rising interest rates.
- Venture capitalists are becoming more cautious, preferring businesses with proven models and clear profitability paths.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Policy and Regulatory Framework:
- Predictable Governance: India must develop a clear, stable and adaptive regulatory framework that balances innovation with accountability.
- Regulatory sandboxes can allow AI start-ups to test innovations while ensuring compliance with ethical and legal norms.
- Expanding Access to Compute and Infrastructure:
- Government-supported access to high-performance computing and cloud infrastructure can reduce entry barriers for AI start-ups.
- Shared compute facilities under public-private partnerships can accelerate AI research and development.
- Improving Data Access and Quality:
- Trusted Data Ecosystems: Creation of secure, anonymised and high-quality public datasets can support responsible AI innovation.
- Data-sharing frameworks must ensure privacy, consent and representativeness.
- Building Skilled Human Capital:
- Investment in AI education, research institutions and skilling programmes is essential to address talent shortages.
- Collaboration between academia, industry and start-ups can strengthen applied AI research.
- Ensuring Ethical and Responsible AI:
- AI start-ups should embed ethical principles, transparency and bias mitigation at the design stage.
- Mandatory bias audits and explainable AI systems can enhance public trust.
- Enhancing Access to Finance:
- Long-Term Risk Capital through government-backed funds and venture financing is necessary for research-intensive AI start-ups.
- Incentives for deep-tech investment can reduce financial risks for investors.
- Promoting Indigenous and Inclusive AI:
- AI start-ups should focus on Indian languages, regional needs and local contexts.
- Inclusive AI can bridge digital divides and expand technology benefits to underserved populations.
- Others:
- Innovative Business Models: AI start-ups should explore cost-efficient solutions such as federated learning, open-source tools, and decentralised AI architectures to reduce operational costs, especially in the early stages.
- Policy Advocacy: Engaging with policymakers to shape regulations that promote responsible AI development while ensuring that innovation is not stifled is essential for AI start-ups.
- Investing in Talent Development:
- Developing in-house training programs and partnering with educational institutions will help bridge the talent gap and ensure a steady supply of skilled professionals for the AI sector.
- Fostering entrepreneurial talent through mentorship and expert networks will further support start-ups’ growth.
Role of States
- State governments can promote AI start-ups through state innovation policies, AI hubs and sector-specific pilots.
- Cooperative federalism can enable AI solutions tailored to local governance challenges such as health, agriculture and urban planning.
|
- Role of States:
- State governments can promote AI start-ups through state innovation policies, AI hubs and sector-specific pilots.
- Cooperative federalism can enable AI solutions tailored to local governance challenges such as health, agriculture and urban planning.
Conclusion
The sustainable growth of AI start-ups depends on a holistic ecosystem that integrates innovation, ethics and inclusivity. By strengthening institutional capacity, promoting responsible AI and leveraging its demographic and digital strengths, India can enable AI start-ups to become key drivers of technological leadership, good governance and inclusive national development.
![]() 10 Jan 2026
10 Jan 2026


