Recently, The second edition of the “All-India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey 2021-22” by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development was released.
All-India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey 2021-22
- Agriculture remains central to India’s economy, supporting the livelihoods of the majority of its population.
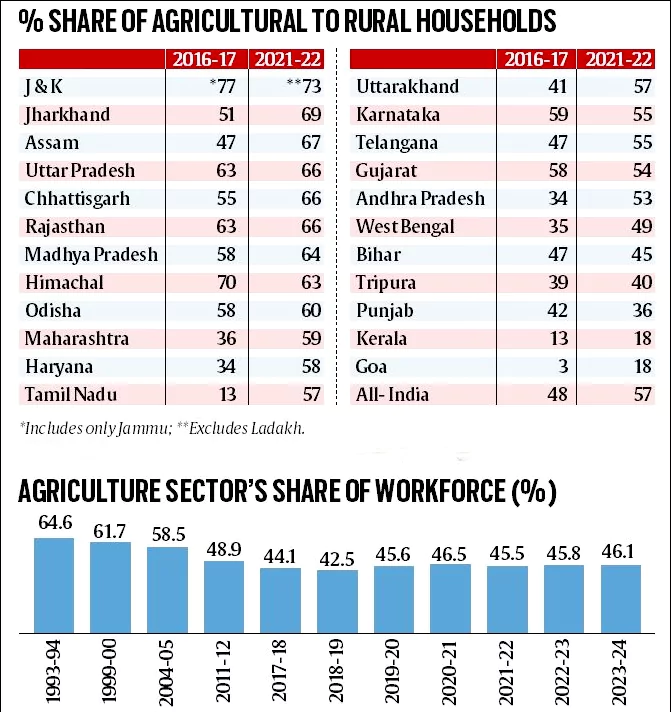
- 57% of rural households rely on agriculture for their livelihood.
- This dependence is higher among agricultural households compared to non-agricultural ones.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is Financial Inclusion?
It is a method of providing banking and financial services to individuals.
- Objective: It aims to provide basic financial services to everybody in the society regardless of their income or savings.
- It also ensures that marginalized people make the best use of their money and get education related to finance.
- Introduction in India: In India, It was first introduced by RBI in 2005.
Key Findings from NABARD Survey (2021-22)
- Rising Agricultural Dependence: 57% of rural households were identified as “agricultural,” up from 48% in 2016-17.
- Definition of Agricultural Households: An agricultural household is one that:
- Earned more than Rs 6,500 from farming activities (including crops, livestock, aquaculture, etc.)
- Had at least one self-employed member in these activities during the reference year (July 2021 to June 2022).
-
Income Trends in Rural Households
- Higher Income for Agricultural Households:
- Agricultural households had an average monthly income of Rs 13,661 in 2021-22, higher than Rs 11,438 for non-agricultural households.
- In 2016-17, agricultural households also earned more (Rs 8,931) compared to non-agricultural households (Rs 7,269).
- Sources of Income for Agricultural Households
- Only about a third of agricultural household income comes from cultivation.
- Two-thirds of income comes from wage labor, government or private services, and other enterprises.
-
Increase in Income from Farming Activities
- Contribution of Farming: The share of income from farming (cultivation and animal husbandry) rose across land size categories:
 For households with less than 0.01 hectare: from 23.5% to 26.8%
For households with less than 0.01 hectare: from 23.5% to 26.8%- For households with 0.41-1 hectare: from 38.2% to 42.2%
- For households with 1.01-2 hectares: from 52.5% to 63.9%
- For households with over 2 hectares: from 58.2% to 71.4%
- Diversification of Income Sources
- 56% of agricultural households rely on three or more income sources, while 66% of non-agricultural households depend on a single source.
- Households with four or more income sources earn almost four times more than those with just one income source.
- This income diversification reflects the resilience of small farmers amidst declining cultivation income.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
-
Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic
- Covid-19 Influence on Agriculture: The pandemic may have contributed to the increase in reliance on agriculture, as farming activities were exempt from lockdown restrictions.
- Good Monsoon Years: Four consecutive good monsoons from 2019 helped improve farming incomes.
-
Economic Struggles of Agricultural Households
- Challenges in Agriculture
- 30% of agricultural households faced crop failures due to irregular rainfall, pest attacks, cyclones, and droughts.
- 12% reported losses due to price fluctuations, forcing many to use savings or borrow from informal sources.
- PLFS Data on Employment:
- Agriculture’s share of India’s workforce decreased over the years (from 64.6% in 1993-94 to 42.5% in 2018-19).
- However, post-pandemic, the share rose to 46.5% in 2020-21, showing a reversal of the trend.
- High Expenditure and Debt
- Agricultural households have an average monthly expenditure of Rs 11,710, leaving a small surplus of Rs 1,951.
- Small and marginal farmers spend a higher proportion of their income on food.
- Average debt for agricultural households: Rs 91,231, which is nearly seven times their monthly income.
- Many farmers spend their entire lives repaying these debts.
-
Paradox of Growing Agriculture Dependence in a Growing Economy
- Economic Expansion vs. Agriculture Employment: Despite the economy growing 1.4 times between 2016-17 and 2023-24, there is increasing dependence on agriculture for jobs.
- Lack of Manufacturing Jobs: Manufacturing’s share in employment declined to 11.4% in 2023-24, contributing to surplus labor remaining in agriculture or moving to low-productivity sectors like trade, hotels, and construction.
-
Regional Variations in Agricultural Employment
- States with High Agricultural Employment: Chhattisgarh (63.8%), Madhya Pradesh (61.6%), Uttar Pradesh (55.9%), Bihar (54.2%), and Rajasthan (51.1%).
- States with Low Agricultural Employment: Goa (8.1%), Kerala (27%), Punjab (27.2%), Haryana (27.5%), and Tamil Nadu (28%).
Agriculture Schemes for Welfare of Farmers
There are some of the major Agricultural Schemes in India:
- Agriculture Development Schemes
- Krishi Kalyan Abhiyan: Focuses on improving farmer welfare through various agricultural development activities.
- Soil Health Cards (SHC) Scheme: Provides soil health cards to farmers to help them improve soil fertility and productivity.
- National Bamboo Mission: Promotes the growth and development of bamboo cultivation and industry.
- Green Revolution – Krishonnati Yojana: Enhances agricultural productivity and ensures food security.
- Financial Support and Insurance Schemes
- Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay SanraksHan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA): Ensures remunerative prices for agricultural produce.
- Pradhan Mantri KISAN Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides financial support to farmers for their cultivation needs.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to farmers to protect against crop losses.
- Ayushman Sahakar Scheme: Provides financial assistance for the creation of healthcare infrastructure in rural areas.
- Market Access and Innovation Schemes
- E-NAM (National Agriculture Market): Creates a unified national market for agricultural commodities.
- Yuva Sahakar-Cooperative Enterprise Support and Innovation Scheme: Encourages young entrepreneurs to set up cooperative enterprises.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
- Sustainable Agriculture and Environment Schemes
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY): Aims to improve irrigation coverage and water use efficiency.
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY): Promotes organic farming through participatory guarantee system.
- National Food Security Mission (NFSM): Focuses on increasing production of rice, wheat, pulses, and coarse cereals.
- Mission Amrit Sarovar: Promotes water conservation through the development of water bodies.
- National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM): Supports the development of the beekeeping sector.
- National Mission on Edible Oils (NMEO-OP): Aims to increase the production of edible oils to make India self-reliant.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Promotes sustainable and natural farming practices.
- Education and Skill Development Schemes
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maan-Dhan Yojana (PM-KMY): Provides social security to small and marginal farmers.
- Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyay Unnat Krishi Shiksha Yojana (PDDUUKSY): Focuses on agricultural education and extension activities.
- Livestock and Fishery Development Schemes
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM): Aims to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
- National Scheme of Welfare of Fishermen (NSWF): Ensures the welfare of fishermen through various support measures.
![]() 22 Oct 2024
22 Oct 2024
 For households with less than 0.01 hectare: from 23.5% to 26.8%
For households with less than 0.01 hectare: from 23.5% to 26.8%