Recently, World Bank Released Annual International Debt Report (IDR) 2024
About Annual International Debt Report
- It provides detailed information on external debt for low- and middle-income countries
| low- and middle-income countries: Criteria
The classification of countries is based on the Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
- Low-Income Countries : GNI per capita: $1,145 or less
- Lower Middle-Income Countries: GNI per capita: Between $1,146 and $4,515
- Upper Middle-Income Countries: GNI per capita: Between $4,516 and $14,005
- High-Income Countries: GNI per capita: More than $14,005
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Key Contributions of the IDR
- Data Insights: Tracks borrowing patterns and new lending methods.
- Debt Relief Impact: Assesses the outcomes of initiatives to reduce debt burdens.
- Transparency Promotion: Encourages accurate debt recording and reporting.
Key Findings of the International Debt Report 2024
The report highlights trends and developments in external debt for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) over the past decade (2013–2023), with a focus on 2023.
- Trends in External Debt Stock (2013–2023)
- The total external debt stock of LMICs grew by 2.4% in 2023, reaching US$8.8 trillion.
- The increase in long-term debt was largely due to higher borrowing from multilateral creditors.
- Trends in External Debt Flows (2013–2023)
- Net debt flows (disbursements minus repayments) turned positive in 2023, totaling US$220.7 billion.
- This was a significant recovery (fivefold increase) compared to 2022 but remained lower than the levels seen between 2017 and 2021.
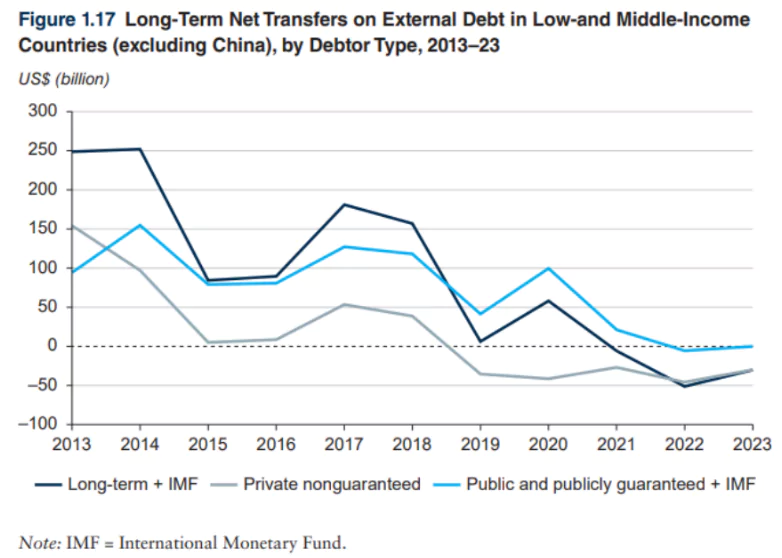
- Trends in Net Transfers on External Debt (2013–2023)
- Higher interest payments negatively impacted net debt transfers.
- Net debt transfers reflect the difference between the amounts borrowed (new disbursements) and the amounts repaid (interest and principal).
What is the debt-to-GNI ratio?
- It is a metric that compares a nation’s total external debt to its gross national income.
- A high ratio shows a high level of external debt relative to its income.
|
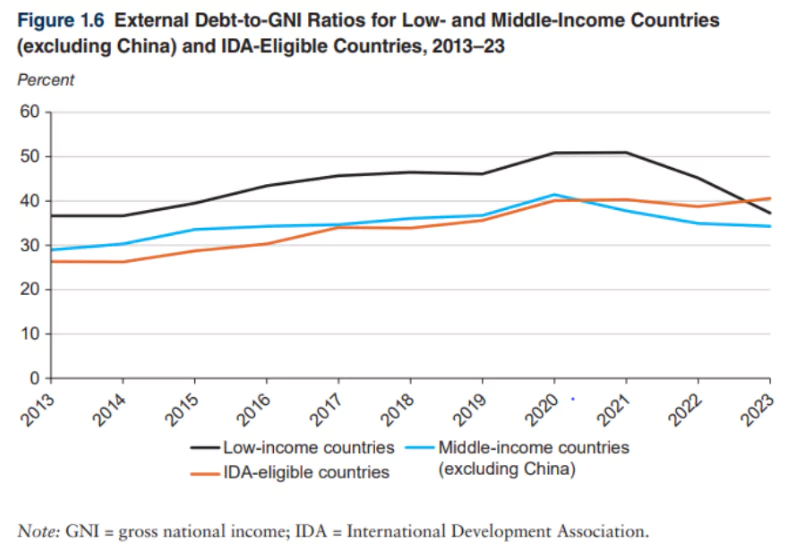
- Debt Ratios and Debt Resolutions
- The debt-to-GNI ratio for LMICs (excluding China) slightly decreased by 0.8 percentage points, standing at 34.4% in 2023.
- This ratio has been on a declining trend since reaching a two-decade high of 41.8% in 2020.
 Debt Servicing Burdens (2013–2023)
Debt Servicing Burdens (2013–2023)
- LMICs faced record-high debt servicing costs of US$1.4 trillion in 2023 (principal and interest payments).
- For LMICs excluding China, debt servicing costs increased by 19.7%, reaching US$971.1 billion—almost double the amount recorded a decade ago.
- Role of Multilateral Lenders
- Multilateral lenders, such as the World Bank, IMF, and regional development banks, became the primary source of financial support for LMICs during the pandemic and beyond.
- Their support included emergency relief and balance-of-payments assistance.
- Borrowing from private creditors fell due to:
- Adverse market conditions.
- Reduced investments in emerging markets.
- A shift towards concessional loans from official creditors in IDA-eligible countries.
- Growth in Debt Stock from Official Lenders
- Long-term debt stock owed to the World Bank and IMF by LMICs has grown by 63.1% since the pandemic, compared to marginal growth in private lending.
- LMICs (excluding China) owed US$421.8 billion to the World Bank’s lending arms in 2023, accounting for 34% of all multilateral creditors’ debt.
- Rising Interest Rates and Costs
- Interest rates on new loans increased significantly in 2023:
- Official creditors: Rates rose by 2.1 percentage points to 4.09%.
- Private creditors: Rates increased by 1.37 percentage points to 6.0%, the highest since 2008.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
What is external debt?
- External debt is the money a country borrows from foreign sources like other governments, banks, or international organizations. It is divided into two types:
- Short-term debt: Needs to be repaid in a year or less.
- Long-term debt: Has a longer repayment period.
- Main Features of External Debt
-
- Types of External Debt:
- Public Debt: Borrowed by the government.
- Private Debt: Borrowed by private companies.
- Multilateral Debt: Loans from organizations like the World Bank and IMF.
- Bilateral Debt: Loans from one country to another.
- Commercial Loans: Borrowed from banks or investors.
- Why Countries Borrow:
- To build roads, schools, and hospitals.
- To manage financial crises.
- To cover gaps in government budgets.
- How Debt is Repaid:
- Countries pay back the principal amount and interest.
- Sometimes, they take new loans to repay old ones.
|
![]() 7 Dec 2024
7 Dec 2024


 Debt Servicing Burdens (2013–2023)
Debt Servicing Burdens (2013–2023)
