According to the Annual Lightning Report 2024-25, Lightning is responsible for more deaths in India than any other natural disaster.
Annual Lightning Report 2024-25
- Publication: The Report is compiled by the Climate Resilient Observing Systems Promotion Council (CROPC) and India Meteorological Department (IMD).
|
Lightning
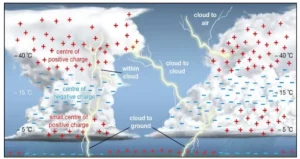
- Lightning is a rapid electrostatic discharge that occurs between clouds or from cloud to ground, usually accompanied by thunderstorms, intense rainfall, winds, and occasionally hail.
- It is a sudden, highly localized phenomenon, often lethal in nature, making it difficult to mitigate compared to slow-onset disasters.
Key Highlights from the Report
- Increase in Lightning Strikes: 400% rise in lightning strikes from 2019 to 2025.
- Emerging Hotspots: New hotspots are emerging, particularly in northern, western, and desert regions such as Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Delhi.
- Shifting Geography of Lightning: Areas such as Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, and Himachal Pradesh have the highest lightning-related fatalities. Rajasthan and Gujarat are also seeing increased lightning activity.
- Fatalities: Over 3,500 lightning fatalities recorded in Madhya Pradesh and Bihar from 2014 to 2025.
- Vulnerability Analysis: The District-Level Vulnerability Analysis highlighted 207 districts with high vulnerability to lightning strikes
- Challenges in Rural and Hilly Areas: Detection capabilities in rural, hilly, and mountainous regions are limited, hindering effective lightning mitigation.
Role of Climate Change and Geography
- Global warming is intensifying thunderstorm activity by increasing atmospheric instability.
- With increased moisture-holding capacity, clouds in such regions tend to generate more extreme rainfall and cloudbursts, which further trigger lightning.
- Geographical Features and Lightning: Rocky formations such as the Western Ghats and Uttarakhand’s limestone hills attract higher levels of atmospheric electricity, contributing to more frequent lightning.
Atmospheric Electricity
- Atmospheric electricity refers to the electrical phenomena that occur in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- It includes the presence of electrical charges in the air, such as in the form of lightning, thunderstorms, and the electrical potential difference between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere.
|
Mitigation and Early Warning Systems
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD), in collaboration with the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), has implemented early warnings through apps such as Mausam, Damini, and Sachet.
- Enhanced lightning forecasting models now provide early warnings using a multi-model ensemble, which improves the chances of timely evacuations and preventive measures.
- Dedicated Agencies and Protocols: NDMA coordinates lightning risk management, while the National Remote Sensing Centre under ISRO contributes with detection services.
- NDMA’s guidelines since 2019 and the Common Alert Protocol (CAP) ensure streamlined alerts across states.
![]() 25 Dec 2025
25 Dec 2025


