![]() 13 May 2025
13 May 2025
English
हिन्दी

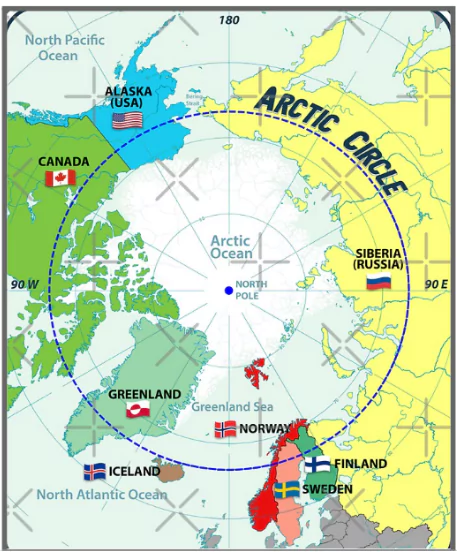
Denmark assumed the rotating chairmanship of the Arctic Council, taking over from Norway.
| Aspect | Details |
| Established | 1996 |
| Nature | Intergovernmental forum — does not deal with military/security issues |
| Mandate | Promotes cooperation on environmental protection, sustainable development, and Indigenous rights in the Arctic region |
| Member Countries | 8 Nations: Russia, US, Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden |
| Permanent Participants | 6 Indigenous organizations representing Arctic peoples |
| Observers | States and Non-States organizations can be Observer (Total 38)
India has been an Observer since 2013. |
| Recent Tensions | Post-2022, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, 7 members paused cooperation with Russia, previously the largest Arctic player and former Council chair. |
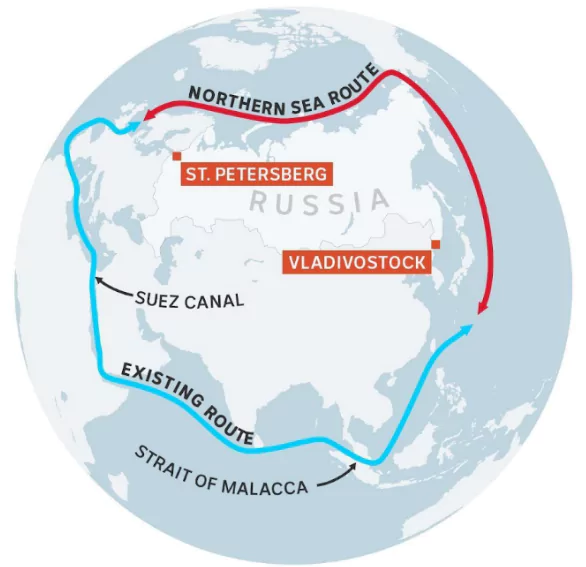
PWOnlyIAS Extra Edge: The Arctic Ocean
|
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>