Context
CEO of OpenAI expressed a commitment towards the development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
About Turing test
- According to the Turing test, if a machine can engage in a conversation with a human without being detected as a machine, it exhibits human intelligence.
- Alan Turing is considered to be the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence.
|
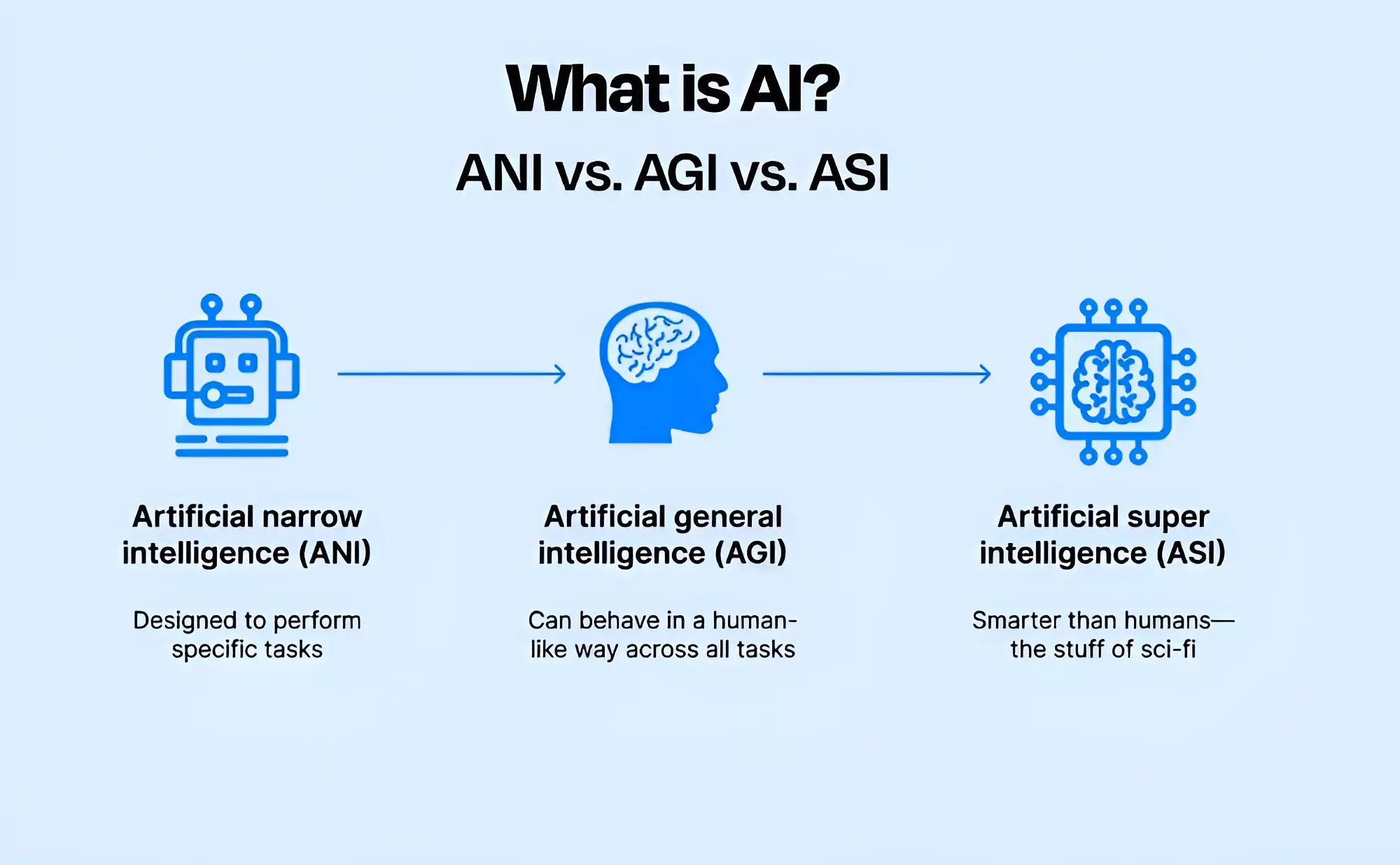
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
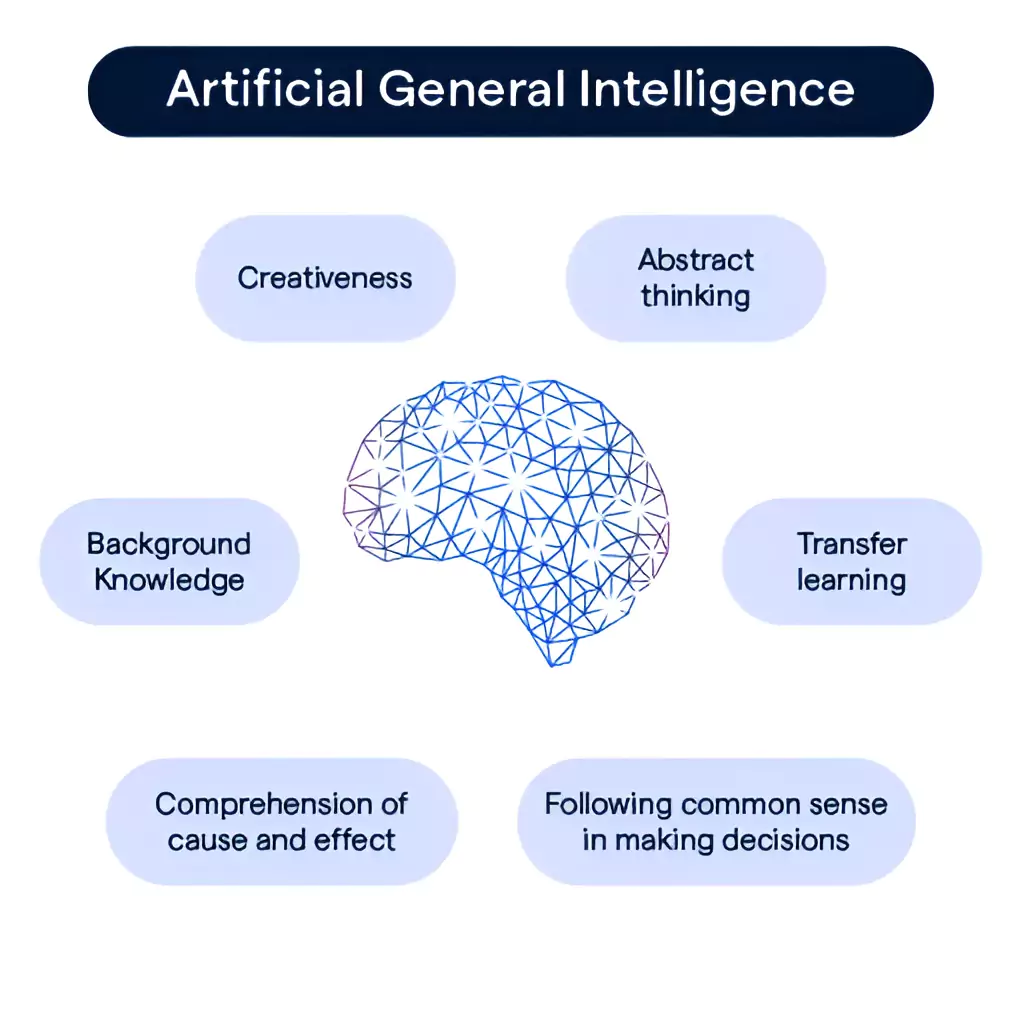
In ‘Computing Machinery and Intelligence’ (1950), Alan Turing introduced the Turing test, a benchmark for machine intelligence. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to a machine or a software that can perform any intellectual task that a human can do. This includes reasoning, common sense, abstract thinking, background knowledge, transfer learning, ability to differentiate between cause and effect, etc.
- Objective: To emulate human cognitive abilities such that it allows it to do unfamiliar tasks, learn from new experiences, and apply its knowledge in new ways.
 With AGI, researchers aim to build a software or computer that can do everything that a human computer does.
With AGI, researchers aim to build a software or computer that can do everything that a human computer does.- It will work like a super-intelligent robot capable of comprehending everything humans say, acquiring new knowledge akin to human learning, and generating solutions for complex problems.
- Difference between AGI and Artificial Intelligence/Narrow AI: Narrow AI is designed to perform specific tasks such as image recognition, translation, but it remains limited to its set parameters.
- On the other hand, AGI envisions a broader, more generalized form of intelligence, not confined to any particular task (like humans).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Significance of Artificial General Intelligence
- Healthcare: It can redefine diagnostics, treatment planning, and personalized medicine by integrating and analyzing vast datasets, far beyond the capabilities of humans.
- Finance and business: AGI could automate various processes and enhance the overall decision-making, offering real-time analytics and market predictions with accuracy.
- Education: AGI could transform adaptive learning systems that work towards the unique needs of students. This could potentially democratize access to personalized education worldwide.
- Economy: AGI will lead to a lot of productivity and economic value promising unprecedented problem-solving capabilities and creative expression.
Concerns Related to Artificial General Intelligence
- Environmental Implications: The immense computational power needed raises environmental concerns, stemming from both energy consumption and the generation of electronic waste.
- Job Losses: AGI could lead to a significant loss of employment, and widespread socio-economic disparity, where power would be concentrated in the hands of those who control the AGI.
- Security Concerns: It could introduce new security vulnerabilities creating challenges for the governments in the absence of adequate regulations.
- Loss of Human Skills: If humans become too much dependent on AGI, it might lead to the loss of basic human skills and capabilities.
- AGI Autonomy: Its capabilities could surpass those of human beings, rendering its actions challenging to comprehend and forecast.
- This could potentially result in a scenario where it attains an excessive level of autonomy, to the extent that humans lose control and take actions detrimental to human welfare.
Conclusion
Stringent regulations are needed to ensure that the development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is in line with human values and safety standards
Also Read: New Delhi AI Declaration
![]() 6 May 2024
6 May 2024
 With AGI, researchers aim to build a software or computer that can do everything that a human computer does.
With AGI, researchers aim to build a software or computer that can do everything that a human computer does.