High temperatures and reduced salinity in Sambhar lake may have created conditions conducive to avian botulism, resulting in the mass deaths of migratory birds in Rajasthan.
- At least 600 migratory bird deaths were reported by the Centre for Avian Research Institute earlier this month.
About Avian Botulism
- Avian botulism is a neuro-muscular disease caused by Botulinum, a natural toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
- Habitat of Bacteria: Clostridium botulinum is commonly found in soil, rivers, and seawater, and affects both humans and animals.
- Growth Conditions: The bacteria thrive in anaerobic (oxygen-free) environments and do not grow in acidic conditions.
 Impact on Birds: It affects the nervous system, causing paralysis in the legs and wings of birds.
Impact on Birds: It affects the nervous system, causing paralysis in the legs and wings of birds.- Prevalence in Wetlands: Bacterial spores are prevalent in wetland sediments and are found in wetland-dwelling invertebrates like insects, mollusks, and crustaceans, as well as healthy vertebrates, including birds.
- Trigger Conditions: Outbreaks often occur when temperatures exceed 21°C and during drought conditions.
- Management and Challenges
- Treatment Limitations: Avian botulism cannot be treated; prompt removal and proper disposal of affected birds are essential to prevent the spread.
- Past Incidents: A similar outbreak in Sambhar Lake in 2019 caused the deaths of nearly 18,000 birds.
- Predictability: Outbreaks are difficult to forecast as they depend on specific environmental conditions, such as shifts in salinity coinciding with the arrival of migratory birds.
- Vulnerability of Migratory Birds
- Susceptibility: Migratory birds arriving after long flights are often weakened, making them more prone to diseases like botulism.
- Role of Carcasses: Decaying bird carcasses attract maggots, which can contaminate water sources and infect other birds and animals.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
About Sambhar Lake
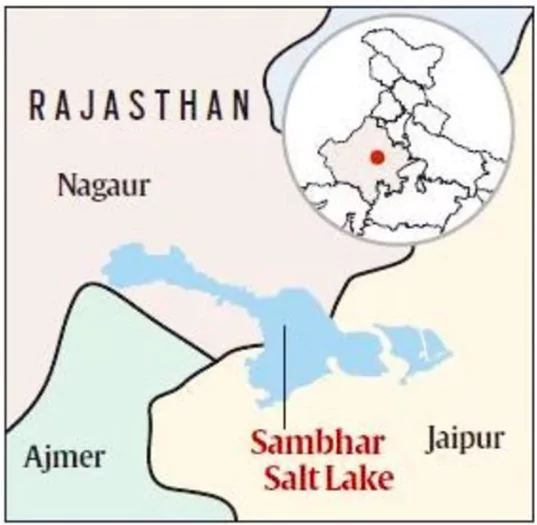
- Location: Situated about 80 km southwest of Jaipur, Rajasthan.
- Geographical Significance: It is India’s largest inland salt lake and represents a depression in the Aravalli Range.
- Fauna: Flamingoes, pelicans and the waterfowls are commonly sighted at the Sambhar Lake.
- Environmental Importance
- Ramsar Site: Declared a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention in 1990.
- Water Sources: Receives water from six rivers: Samaod, Khari, Mantha, Khandela, Medtha, and Roopangarh.
- Vegetation: Features xerophytic vegetation, which is adapted to dry conditions.
Central Avian Research Institute (CARI)
- Location: Based in Izzatnagar, near Bareilly, Uttar Pradesh.
- Establishment: Founded in 1979 under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Functions
- Conducts research in poultry science, focusing on areas like avian genetics, breeding, nutrition, feed technology, physiology, and reproduction.
- Aims to enhance the Indian poultry industry through scientific advancements.
![]() 19 Nov 2024
19 Nov 2024

 Impact on Birds: It affects the nervous system, causing paralysis in the legs and wings of birds.
Impact on Birds: It affects the nervous system, causing paralysis in the legs and wings of birds.