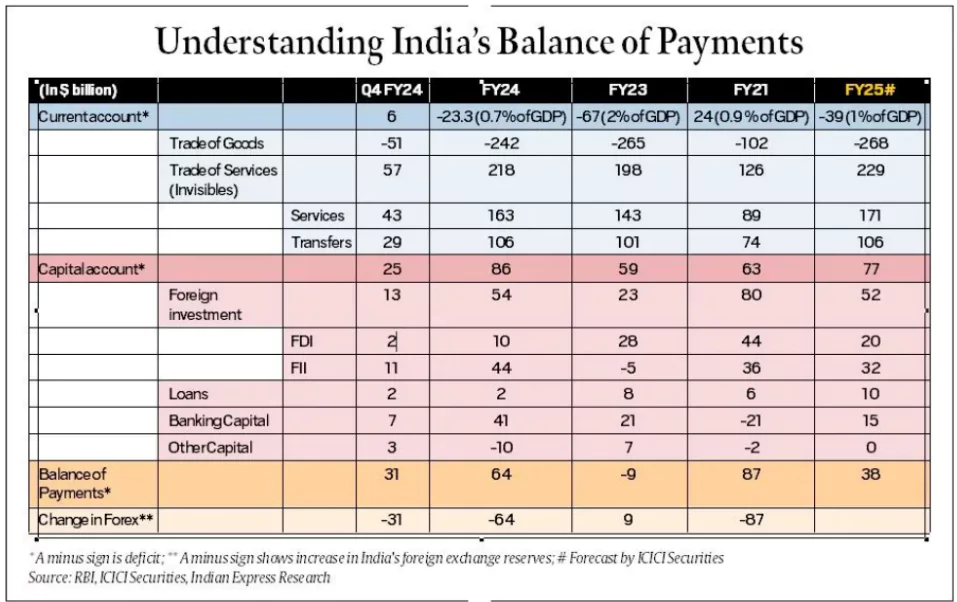
India’s current account balance showed a surplus of $5.7 billion or 0.6% of GDP during the fourth quarter (Jan-Mar) of 2024 (Q4FY24), marking a return to surplus after 10 quarters.
Balance of Payments (BoP)
- About: The Balance of Payments (BoP) summarizes all transactions completed by a country’s individuals, companies, and government bodies with entities outside the country over a specified period.
- It illustrates the total outflows and inflows of money, denominated in currencies like US Dollars or Indian Rupees.
- Types of Transactions in Balance of Payments
- Trade (export or import) of goods or services.
- Investments (such as an Indian buying land in the US or an American firm investing in Indian stock exchanges).
- Exchange of loans between India and other countries, among others.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Components of the Balance of Payments (BoP):
- Current Account: This includes transactions related to current consumption. It is further divided into:
- Trade Balance: Reflects the export and import of physical goods.
- Invisibles Trade: Involves trade in services such as banking, IT, and tourism.
- Recent Data: According to the data, India had a trade deficit (imports exceeding exports) but a surplus in invisibles trade. However, due to the larger trade deficit compared to the surplus in invisibles trade, India’s overall current account is in deficit, known as the Current Account Deficit (CAD).
- Capital Account: The capital account comprises transactions that are not for current consumption but for investment purposes.
- This includes net foreign investments (both foreign direct investment and foreign portfolio investments), as well as loans or borrowed funds between countries.
- According to the table, India recorded a capital account surplus of $90 billion from April to December 2021, in contrast to a current account deficit of $26.6 billion.
- Balance of Payments (BoP): Each of these accounts—current and capital—can individually show either a surplus or deficit.
- A surplus indicates that more money is entering the country than leaving it, while a deficit (indicated with a (-) sign) means more money is leaving the country than entering it.
- The BoP always balances by definition, meaning that any deficit in one account must be offset by a surplus in the other account.
- Difference between Balance of trade and Balance of payments: The balance of trade represents the difference between a country’s exports and imports of goods, focusing solely on visible items.
- In contrast, the current account of the balance of payments includes goods, services, and unilateral transfers such as remittances and donations. The balance of trade forms a component of the current account.
- Purpose of Bop: A country’s BOP is vital for the following reasons:
- The BOP of a country reveals its financial and economic status.
- A BOP statement can be used to determine whether the country’s currency value is appreciating or depreciating.
- The BOP statement helps the government to decide on fiscal and trade policies.
- It provides important information to analyse and understand the economic dealings with other countries.
Balancing of Balance of Payments (BoP)
- Managing BoP Imbalances: To balance the BoP, the RBI deducts these dollars, holding them (-) while adding them as assets to its foreign currency reserves.
- Impact on Foreign Reserves and Money Supply: The increased forex reserves can increase the money supply in the Indian economy, potentially leading to higher inflation, as the RBI also increases liabilities by printing an equivalent amount ($63.5 billion) of domestic currency.
- Impact of RBI Non-Intervention: Without RBI intervention, increased rupee demand relative to the dollar would have appreciated the rupee.
- Consequently, Indian exports would have become more expensive for the US and other countries, reducing demand.
- Simultaneously, cheaper foreign goods would have increased Indian imports. This scenario would widen the trade deficit or current account deficit to a degree where the BoP would self-balance.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Considerations Against Constant Surplus
- Challenges of Pursuing a Current Account Surplus: Striving for a current account surplus isn’t always advantageous for economies, particularly for developing ones like India. During the FY 2020-21 COVID-19 lockdowns, for instance, a surplus may suggest underutilized economic capacity due to halted economic activities.
- Healthy Current Account Deficit: A current account deficit ranging from 1.5% to 2% of GDP is generally regarded as healthy for India. It indicates strong domestic demand and essential imports of capital goods to enhance production capacity.
- Facilitating Economic Growth: This deficit supports sustainable economic growth by enabling investments in productive assets, essential for enhancing future export capacities.
![]() 8 Jul 2024
8 Jul 2024
