In Budget 2024, the Union Finance Minister announced plans to develop Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs) as part of India’s push to expand its nuclear energy capabilities.
- The government plans to partner with the private sector to set up Bharat Small Reactors and conduct research and development on small modular reactors and newer nuclear technologies.
About Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs)
BSRs represent a significant shift in India’s nuclear energy strategy, aiming to make nuclear power more accessible and versatile. Nuclear energy is the fifth-largest source of electricity for India which contributes about 3% of the total electricity generation in India.
- Refers: BSRs are compact nuclear reactors designed to generate electricity on a smaller scale compared to traditional large nuclear power plants.
- Based On: The BSRs will be based on India’s tried and tested 220-megawatt pressurised Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) technology, of which 16 units are already operational in the country.
- Design: The design of BSMRs is ongoing at the Bhabha Atomic Research Center in Mumbai.
- Need For: The government will need to create new policies and legal frameworks to enable private sector participation in nuclear energy generation.
- It will also be crucial to address safety concerns, manage nuclear waste effectively, and ensure that the development of BSRs aligns with the country’s broader energy and environmental goals.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Significance of Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs)
This marks a historic shift in India’s nuclear policy, as the Atomic Energy Act of 1962 previously did not permit private sector participation in nuclear energy generation. It is expected to open up new avenues for financing and accelerate the growth of nuclear power in India.
- Flexibility: BSRs offer several advantages over conventional large-scale nuclear plants. They are more flexible in terms of siting, can be deployed faster, and are potentially more cost-effective.
- Serve Captive Power Units: These reactors could be particularly useful for providing power to remote areas or serving as captive power units for large industries like cement and steel.
- Alignment with Global Trends: The development of BSRs aligns with global trends in nuclear energy, where small modular reactors (SMRs) are gaining attention. However, BSRs are distinct from SMRs.
- While SMRs are an entirely new concept involving factory-made, easily assembled reactors, BSRs are based on India’s existing PHWR technology.
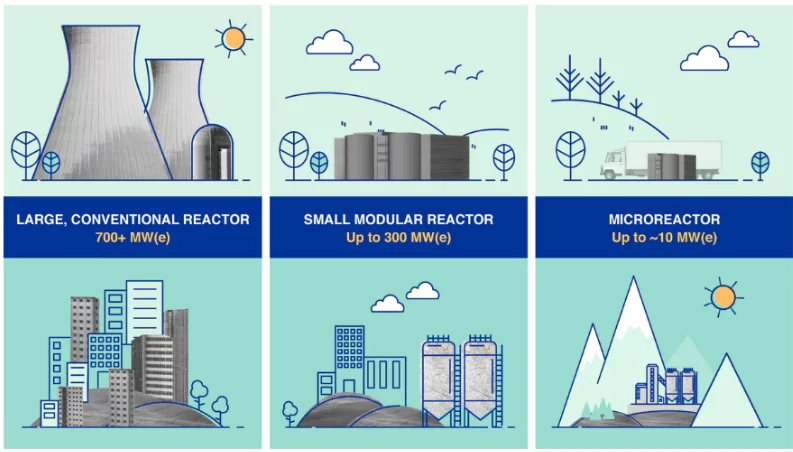
About Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
SMRs are miniaturised versions of large nuclear power plants. They promise to be safer by virtue of having fewer operating parts and more safety features.
- Purpose: A reactor with output lower than 300 MW is considered ‘small’. The purpose of this exercise is to turn this “proven” reactor into a small nuclear power facility.
- Need: SMRs have emerged as an option to complement existing power generation facilities, including nuclear ones.
- Capacity: SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit.
- Availability: There are more than 80 SMR designs and concepts globally. Most of them are in various developmental stages.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
![]() 27 Jul 2024
27 Jul 2024
