Context:
This article is based on the news “A NEW SCHEME OF BIO-MANUFACTURING & BIO-FOUNDRY TO PROVIDE ENVIRONMENT FRIENDLY ALTERNATIVES” which was published in the Indian Express. Recently, the Finance Minister of India proposed a new scheme of Bio manufacturing and Biofoundry in the Interim Budget 2024-25.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Bio Economy in Interim Budget 2024-25
- Transform Manufacturing Paradigm: This scheme will help in transforming contemporary consumptive manufacturing paradigm to the one based on regenerative principles.
- Biotech Sector: The Indian biotechnology sector has witnessed significant growth, and the integration of Bio manufacturing and Biofoundry holds immense promises ranging from pharmaceuticals to sustainable energy.
| Bio Economy: It comprises those parts of the economy that use renewable biological resources from land and sea viz. crops, forests, fish, animals and microorganisms, to produce food, products, textiles and energy etc. |
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Biotechnology
- Biotechnology: It is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells,and molecules for products and services.
- Integration with Bio Manufacturing and Bio Foundry: Biotechnology integrates genetic manipulation, Bio Manufacturing produces biomaterials, and Biofoundry employs automated processes intersecting fields advancing innovation and sustainable solutions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
Status of Biotechnology Industry in India
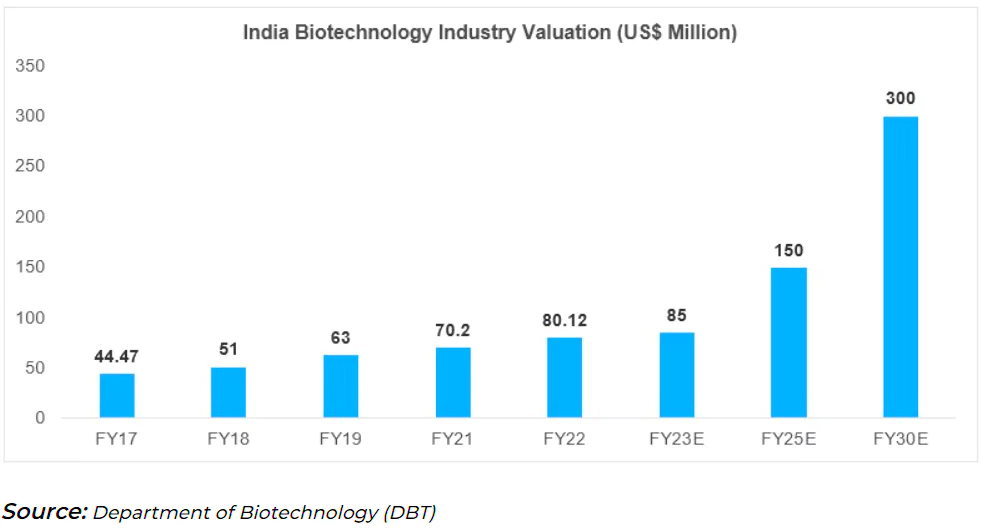
- Global Share: India’s bioeconomy industry accounts for approximately 3% share of the global Biotechnology industry.
- Share in GDP: In 2021-22, the Indian Bioeconomy sector contributed nearly 2.6% share in India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Biotech Startups: The number of biotech start-ups in India has surged from 50 to over 5,300 in the last ten years.
- Biotech start-ups emerging from a robust talent pool are predicted to further double, exceeding more than 10,000 by 2025.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry
Bio Manufacturing
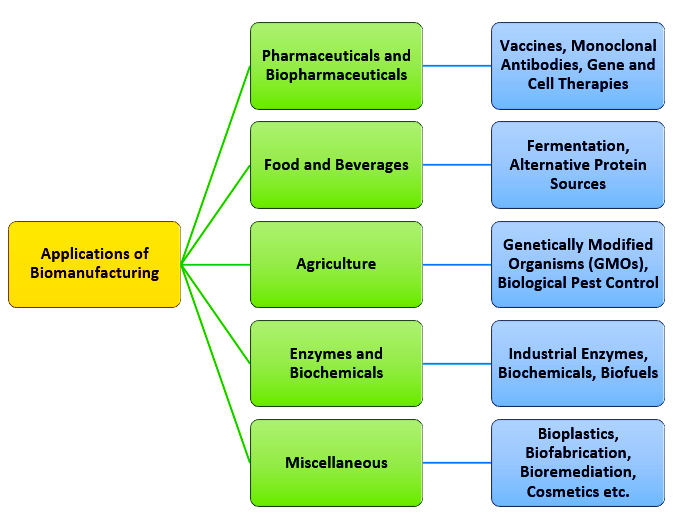
- Bio Manufacturing: It is the use of biological systems that have been engineered, or that are used outside their natural context, to produce a product.
- It uses living systems, particularly microorganisms and cell cultures, to produce molecules and materials on a commercial scale.
- Key Aspects: Includes the selection or engineering of host organisms, optimization of growth conditions, genetic modification for enhanced productivity, and downstream processing to extract and purify the desired product.
- Potential: It has the potential to transform the global industrial system, with up to 60% of physical inputs to the global economy expected to be producible using this technology.
- Uses: Bio Manufacturing is widely used in the production of various products, including pharmaceuticals, biofuels, enzymes, and other chemicals.
- Application of Synthetic Biology: Synthetic biology includes creation of new genomes, biological pathways, or organisms not found in nature and redesign of existing genes, cells, or organisms.
- These capabilities allow for the manufacture of novel products, and also new approaches to existing disciplines such as gene therapy in healthcare.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Biofoundry
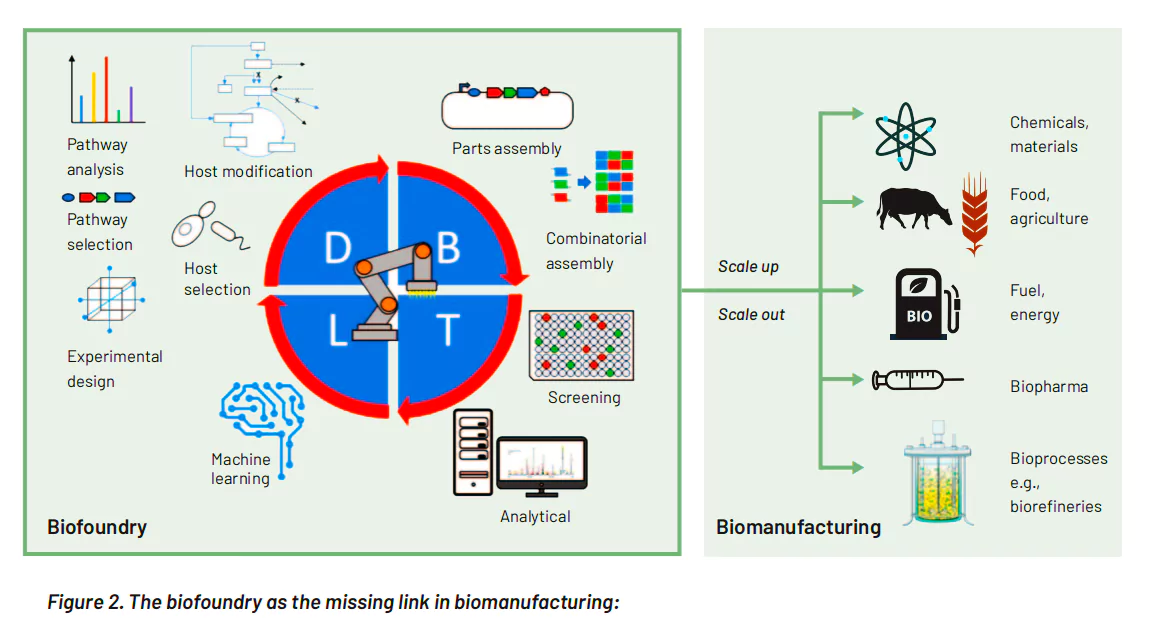
- BioFoundry: Biofoundry is a place where biomanufacturing meets automation. A Biofoundry is a specialized facility or laboratory equipped with automated tools and technologies for the high-throughput design, construction, and testing of biological systems.
 High-throughput (HT) refers to the use of automated equipment to quickly test large numbers of samples for biological activity.
High-throughput (HT) refers to the use of automated equipment to quickly test large numbers of samples for biological activity.
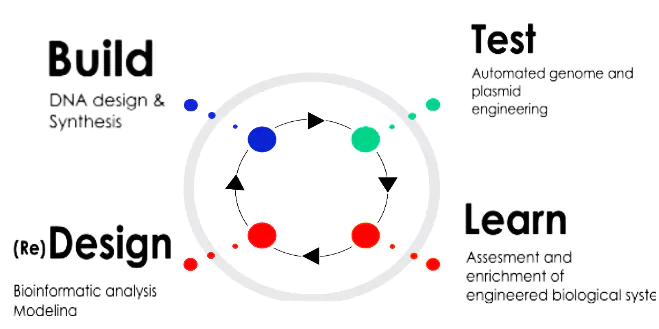
- DBTL Cycle: At the core of biofoundries is the Design-Build-Test-Learn (DBTL) cycle, which involves:
- Computational design of DNA genetic parts.
- Physical assembly of designed DNA parts.
- Prototyping and testing performance of designs in living cells.
- Applying modeling and computational learning tools to inform the design process.
- Goals of Bio-Foundries: Includes accelerating the engineering of biological systems, improving reproducibility, and standardizing the design and construction processes.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
Significance of Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry in India
- Economic Growth: They can catalyze economic growth by providing sustainable alternatives to traditional manufacturing methods. India is regarded as one of the leading destinations for bio innovation and biomanufacturing and is thus recognized as a sunrise sector and a critical component of India’s mission of becoming a US$ 5 trillion economy by 2024.
- According to the Science & Technology Minister, India is poised to be among the top 5 global Bio Manufacturing hubs by 2025.
- In 2014, India’s bioeconomy stood at about $10 billion,and reached $80 billion in 2023 and is expected to touch $300 billion by 2030.
- India as the Global Biomanufacturing Gub: With its infrastructure, pharmaceutical manufacturing expertise, and the available workforce, India aims to become a leading bio manufacturing hub with plans to increase fermentation capacity tenfold to 10 million litres in the next three to five years.
- According to the Australian Strategic Policy Institute, India is among the top performers in the field of biomanufacturing in both the quality of research output and in the share among research publications.
- Cost-Effective Production: Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry are crucial for the pharmaceutical industry, enabling the cost-effective production of biopharmaceuticals and vaccines, enhancing India’s global competitiveness.
- India has significant potential in low-cost biomanufacturing, particularly in the production of enzymes, reagents, research materials, and equipment, with the cost of manufacturing in India being around 33% lower when compared to that in the U.S.
- Sustainable Practices: Bio Manufacturing emphasizes the use of renewable resources, contributing to sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods.
- The move will help in developing environment-friendly alternatives such as biodegradable polymers, bio-plastics, bio-pharmaceuticals and bio-agri-inputs, to further advance India’s sustainability mission to achieve net zero goals by 2070.
- Diversification of Industries: The diversification of Bio Manufacturing through bio-foundries can lead to the establishment of new industries and job creation.
- For example, Bio-foundries provide a platform for the rapid prototyping and testing of biological systems, facilitating innovation across industries, which can lead to increased efficiency and their applications in other industries like agriculture, energy, etc.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Challenges Associated with Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry in India
- Technological Barriers: India lacks access to cutting-edge technology with limited automation infrastructure, inadequate bioprocessing technologies, insufficient data integration and analytics, limited synthetic biology tools, etc. to scale up the Bio Manufacturing sector.
- Regulatory Framework: Due to the absence of regulatory guidelines customized to the scientific developments in synthetic biology, the research practices seem to have largely evolved with less government oversight, which may raise problems related to product safety and compliance.
- Further, regulating these technologies is a complex endeavor that involves balancing the potential benefits of scientific progress and its potential application for bioterrorism or biowarfare.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations and public engagement are crucial for shaping policies and regulations. The public perception of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and synthetic biology can impact the acceptance of bio-manufactured products.
- Concerns over Potential Chinese Dominance: China has expressed its intention to capture this market, leading to rising concerns about its dominance in the industry.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Initiatives to Promote Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry in India
- Establishment of DBT: India realized the potential of biotechnology very early and the country established the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) within the Ministry of Science and Technology in 1986 to support research and development activities in the sector.
- The national initiative “Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing: An integrated approach towards promoting Circular Economy for Green, Clean and Prosperous India” has been proposed by the Department of Biotechnology.
- Policy Initiatives:
- Proposed scheme of Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry in the Interim Budget 2024-25.
- India’s National Biotechnology Development Strategy envisions India as a “Global Biomanufacturing Hub” by 2025, and the strategy sets a target of $100 billion for the hub.
- International Cooperation: In 2021, the Quad (Australia, India, Japan, and the United States) set up a Critical and Emerging Technology Working Group to facilitate cooperation, monitor trends, and scout for opportunities related to developments in critical and emerging technologies, that included biotechnology.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
Way Forward
- Establishment of QUAD-led Bio Manufacturing Hub in India: Quad should establish a Bio Manufacturing hub in India with US’s funding, advanced biotechnology of Japan, Australia and the US, and India’s skilled manpower and the potential to provide affordable scale.
- Investment in Technology Infrastructure: India needs to commission detailed technology landscaping studies at the global level (Quad, BRICS, ASEAN, Asia Pacific) to understand regional and global science, applications, and environmental and biosecurity challenges in synthetic biology.
- The expansion of start-ups and the advancement of research would be aided by an increase in the number of biotech incubators, which is essential for the success of the Indian biotech industry.
- Strengthening physical infrastructure: Invest in upgrading India’s physical infrastructure for biomanufacturing including increasing fermentation capacity and improving manufacturing facilities.
- Resolving Ethical Concerns: Addressing ethical concerns proactively and involving the public in decision-making can build trust, mitigate resistance, and shape policies that reflect societal values.
- Establishment of Regulatory Guidelines: Develop comprehensive regulatory guidelines tailored to advancements in synthetic biology which will ensure product safety, compliance, and facilitate responsible scientific practices, fostering industry growth.
- It is important to develop a national strategy for biomanufacturing advancement in order to improve our country’s scientific and economic competitiveness.
- Ensure Quality Education and Training: Permanent training facilities can be established in universities, with experts from other countries providing the training. Recent policy changes in India allow the establishment of foreign universities and can encourage scholar exchange programmes.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Conclusion
The integration of Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry in India holds immense potential for driving economic growth, fostering innovation, and addressing global challenges. With strategic investments, regulatory reforms, and capacity building, India can position itself as a leader in Bio Manufacturing, contributing to a sustainable and bio-based future.
![]() 2 Feb 2024
2 Feb 2024



 High-throughput (HT) refers to the use of automated equipment to quickly test large numbers of samples for biological activity.
High-throughput (HT) refers to the use of automated equipment to quickly test large numbers of samples for biological activity.