India is witnessing rapid adoption of blockchain technology to strengthen governance, transparency, and digital trust through the National Blockchain Framework (NBF).
About Blockchain Technology
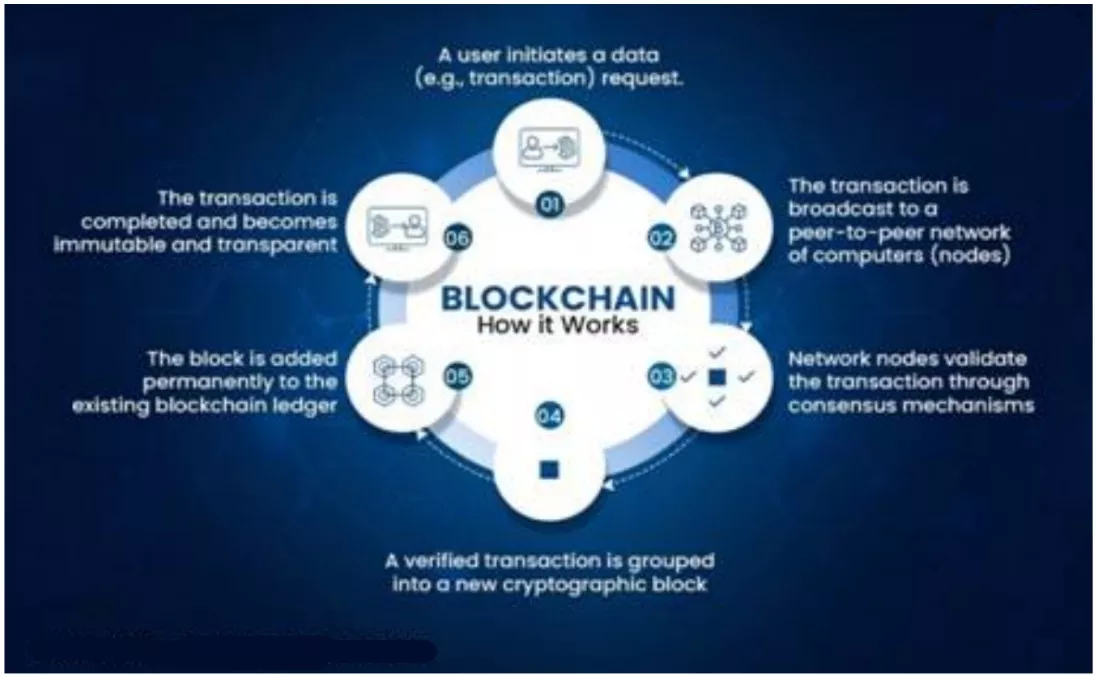
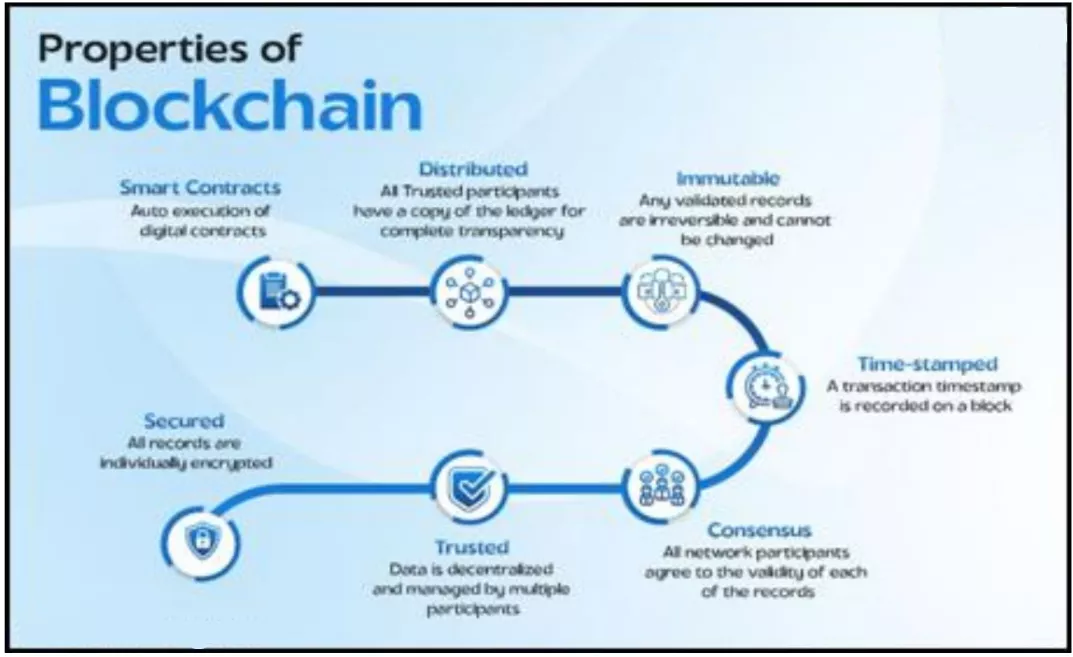
- Definition: Blockchain is a distributed, tamper-proof digital ledger where records are securely stored across multiple nodes.
- Key Features: It enables trust, transparency, and immutability without requiring intermediaries.
- Distinction from AI: Unlike AI, which relies on computational power, blockchain’s strength lies in its ability to create verifiable trust and prevent unauthorized data manipulation.
Types of Blockchain
- Public Blockchain: Open to all participants (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Private Blockchain: Access limited to authorized users; preferred for government and enterprise applications.
- Consortium Blockchain: Managed jointly by multiple organizations for shared governance.
- Hybrid Blockchain: Combines public transparency with private control, allowing selective data access.
National Blockchain Framework (NBF)
- Launch and Budget: Officially launched on September 4, 2024, with a budget of ₹64.76 crore, the framework provides a unified architecture for blockchain-based governance solutions.
- Developer and Purpose: Developed by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) to enable secure, scalable blockchain adoption across public services.
- Core Technology: At its core lies the Vishvasya Blockchain Stack, India’s indigenous blockchain platform offering:
- Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS): Provides shared blockchain infrastructure, allowing government entities to deploy applications without managing their own infrastructure.
- Distributed Infrastructure: Deployed across NIC data centres in Bhubaneswar, Pune, and Hyderabad, ensuring fault tolerance, scalability, and resilience.
- Permissioned Blockchain Layer: Only verified and authorized participants can join or validate transactions, enhancing security.
- Open APIs & Integration Services: Offers APIs and modules for authentication and data exchange, enabling seamless integration with e-Governance platforms.
Innovative Components
- NBFLite: A sandbox environment enabling startups, academia, and researchers to develop and test blockchain applications.
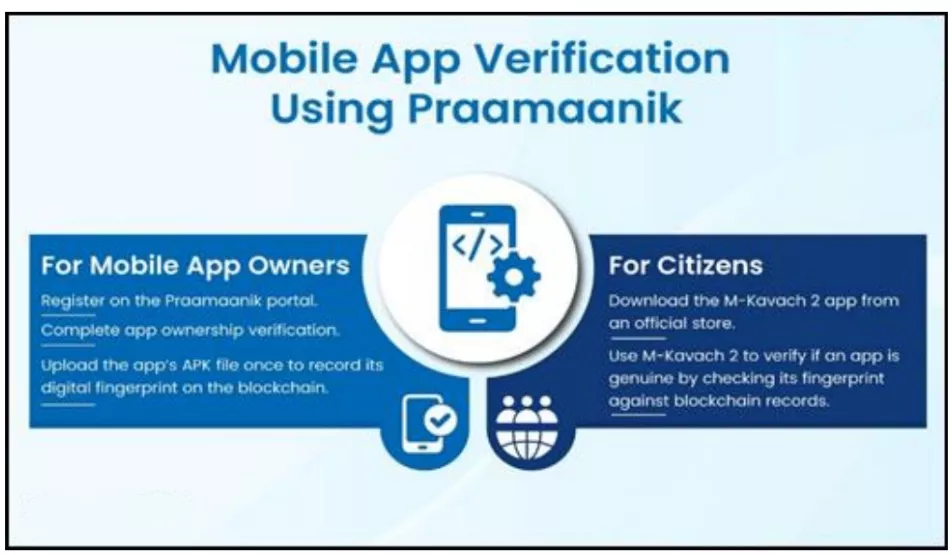
- Praamaanik: Blockchain-based verification system ensuring authenticity of mobile apps and protecting users from fraud.
- National Blockchain Portal: Promotes standardization, cross-sector adoption, and interoperability across governance and industry.
Blockchain Use Cases in Governance
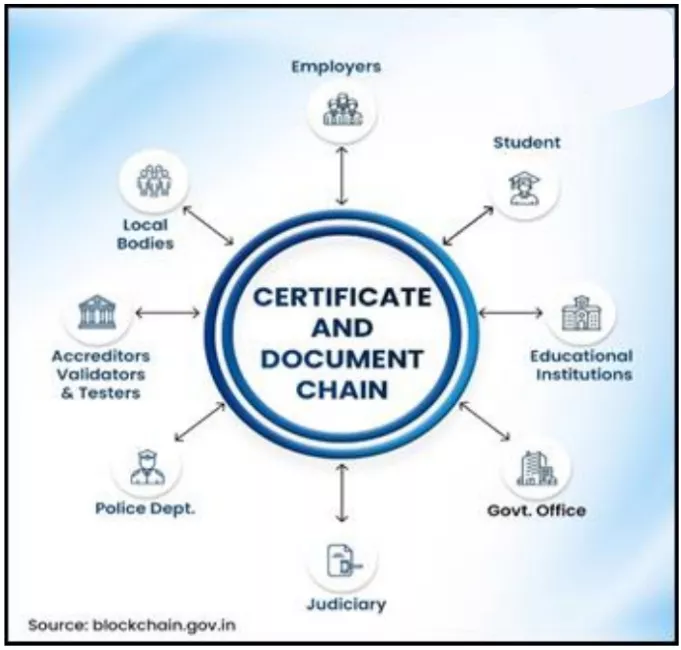
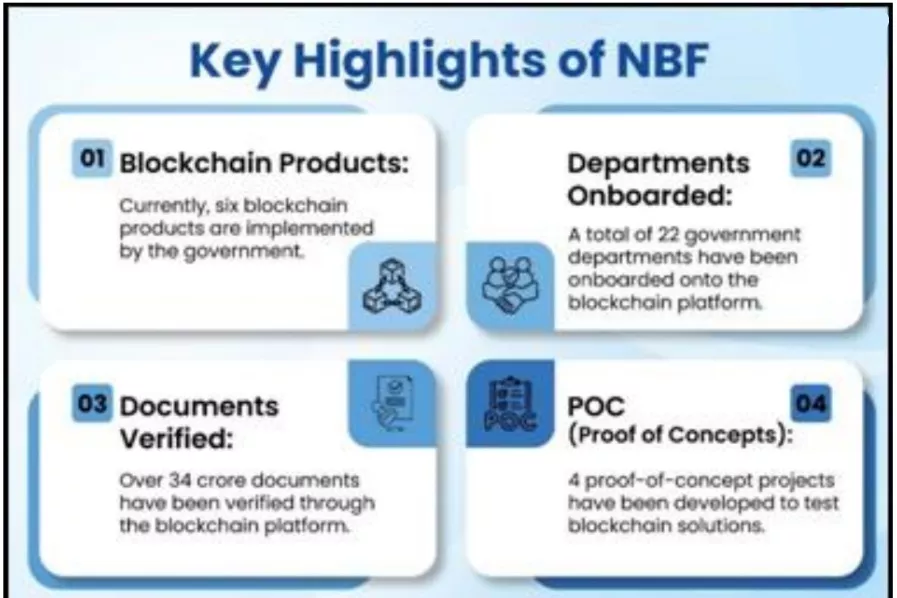
- Certificate & Document Chain: Enables tamper-proof issuance and verification of academic, income, birth, and caste certificates. Over 34 crore documents verified.
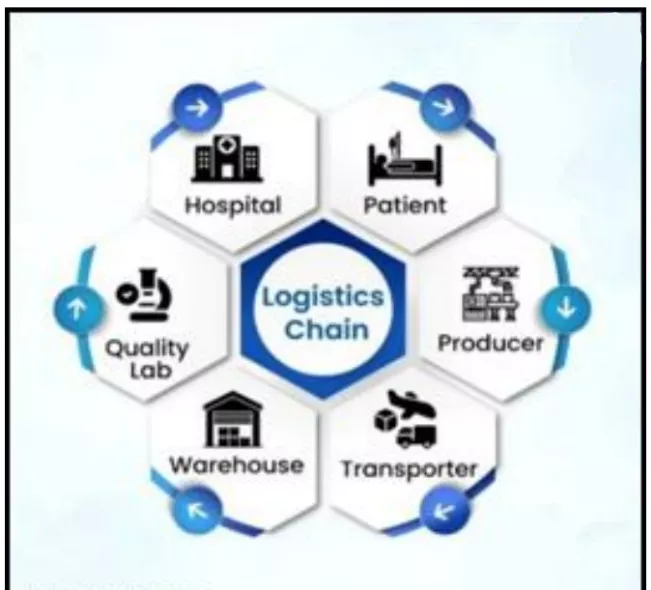
- Logistics Chain: Used in Karnataka’s Aushada system for medicine tracking from manufacturer to hospital, ensuring quality, traceability, and authenticity.
- Judiciary Chain: Stores notices, summons, and orders securely; 665 documents verified.
- Inter-Operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS): Links case and judicial records across agencies; 39,000 documents verified.
- Property Chain: Ensures transparency in land and property transactions; over 34 crore property documents verified.
Institutional and Regulatory Role
- Centre of Excellence in Blockchain Technology (NIC): Offers training, consultancy, and pilot projects using Hyperledger and Ethereum.
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI): Adopted Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) to track SMS transmissions, improving consumer protection.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): Implements blockchain for the Digital Rupee (e₹) and transparent financial transactions.
- National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL): Uses blockchain for Debenture Covenant Monitoring, improving capital market oversight.
Capacity-Building Initiatives
- Skill Development Programmes: Trained 21,000+ officials in blockchain and emerging technologies.
- Post Graduate Diploma in FinTech & Blockchain Development: 900-hour professional course.
- BLEND: C-DAC Online Course: Online course for students and professionals on blockchain design and applications.
- FutureSkills PRIME: Re-skilling initiative to build a future-ready digital workforce.
Future Use Cases
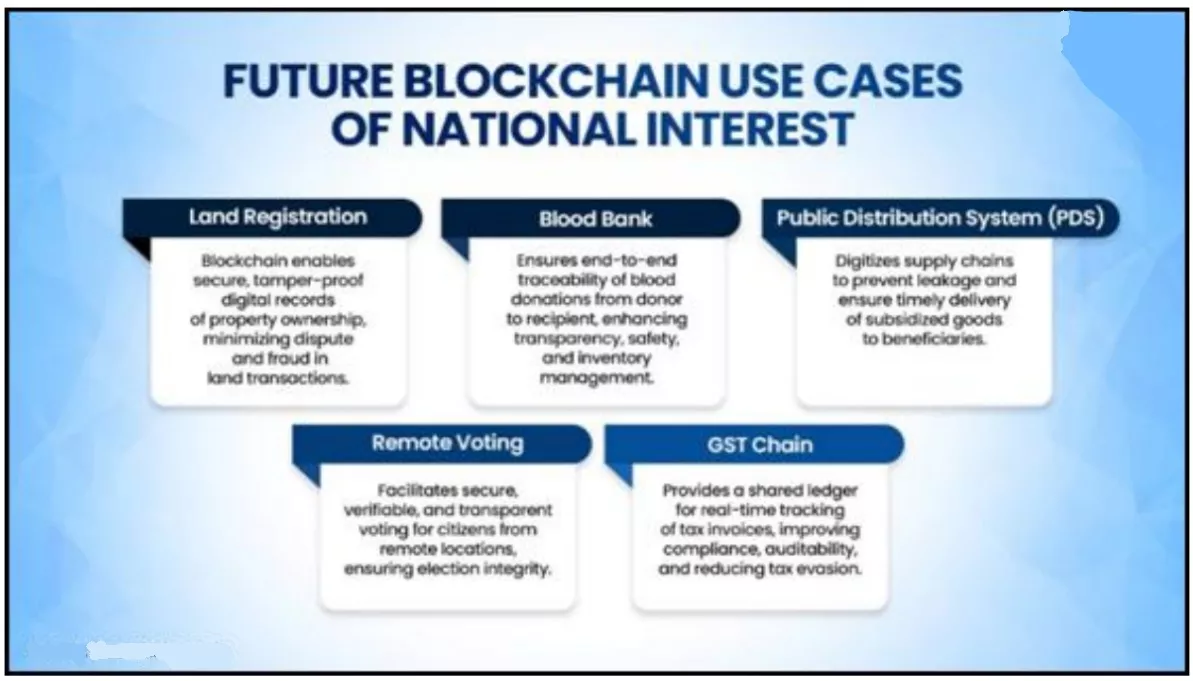
- Pilot projects include blockchain-based Land Records, Blood Bank management, GST Chain for tax monitoring, and PDS tracking to enhance transparency and efficiency.
Significance
- Strengthens Digital India and Aatmanirbhar Bharat missions.
- Builds trust, efficiency, and security in governance systems.
- Positions India among global leaders in blockchain-led public sector innovation.
![]() 27 Oct 2025
27 Oct 2025









