The BSE Sensex closed lower for the sixth consecutive day, reflecting a major sell-off among Foreign institutional investors/ Foreign Portfolio Investors (FIIs/FPIs).
- The market was impacted by mixed corporate earnings and concerns over the tightening of the U.S. tariff regime on imports.
About Bond Yield
- Bond yield refers to the return an investor earns from holding a bond until maturity.
- It is influenced by interest rates, market demand, and economic conditions.
Yield Curve and Variations
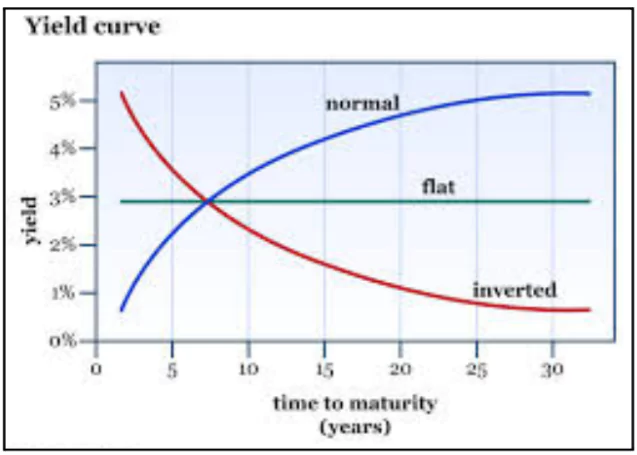
- The yield curve represents the relationship between bond yields and their maturity periods.
- Types of Yield Curves:
- Normal Yield Curve: Long-term bonds have higher yields than short-term bonds, indicating economic growth.
- Inverted Yield Curve: Long-term yields are lower than short-term yields, signaling a possible recession.
- Flat Yield Curve: Short-term and long-term yields are similar, reflecting economic uncertainty.
- Bond Price and Yield Relationship:
- When bond prices fall, yields rise.
- When bond prices rise, yields fall.
Difference Between Bond Yield and Interest Rates
| Aspect |
Bond Yield |
Interest Rate |
| Definition |
The return an investor earns from holding a bond, expressed annually. |
The percentage charged by a lender for borrowing money. |
| Application |
Relevant to fixed-income securities like bonds, where yield includes interest (coupon) payments. |
Applies to loans, bonds, and other debt instruments, determining borrowing costs. |
| Relationship to Market |
Inversely related to bond prices.
When bond prices rise, yields fall, and vice versa. |
Set by lenders or central banks (e.g.RBI) and affects overall borrowing costs. |
| Types |
Includes yield-to-maturity (YTM), which calculates total expected return on a bond. |
Includes nominal, real, and effective interest rates, considering inflation and compounding. |
| Example |
A bond with a 10% yield on a $1,000 investment provides a $100 annual return. |
A 10% interest rate on a $1,000 loan requires the borrower to pay $100 in interest per year. |
RBI’s Role in Managing Bond Yield
- Conducting Open Market Operations (OMO): RBI buys government securities from banks and investors via auctions. This increases demand for bonds, helping control rising yields.
- RBI decides the quantum of each OMO based on yield movements and liquidity conditions.
- Operation Twist : RBI buys longer-term bonds while selling shorter-term bonds simultaneously.
- This prevents excess liquidity while stabilizing longer-term yields.
- Intervening in Weekly Debt Auctions: The government borrows weekly via bond auctions where investors place bids. RBI can partially devolve securities on underwriters if yields exceed comfort levels.
- Extending Held-to-Maturity (HTM) Limits: RBI raised the HTM limit to 23% of banks’ deposits, insulating them from market depreciation losses.
- If yields rise further, RBI may extend the timeline to support bond demand.
- Strengthening the Retail Debt Market: RBI’s Retail Direct Scheme encourages direct investment in government securities.
- Enhancing awareness and accessibility could broaden the investor base and stabilize yields.
About Stock Market
- Definition of Stock Market: The stock market is a platform where shares of publicly listed companies are bought and sold.
- It allows investors to trade company stocks and enables businesses to raise capital.
- Global Stock Markets:
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE): The world’s largest stock exchange.
- NASDAQ: National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations is known for technology stocks like Apple, Microsoft, and Google.
- Indian Stock Markets:
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): Asia’s oldest stock exchange.
- National Stock Exchange (NSE): India’s largest exchange, home to the NIFTY 50 index.
Impact of Rising Bond Yield in U.S. on Indian Market
- Higher Returns with Lower Risk: When U.S. bond yields increase, the risk-reward ratio of Indian equities declines. FIIs and FPIs reduce their equity exposure in emerging markets like India and move funds to safer U.S. bonds.
- Stronger U.S. Dollar : Rising U.S. bond yields increase demand for the U.S. dollar, strengthening it against other currencies.
- A weaker rupee makes Indian assets less attractive to foreign investors.
- FIIs sell Indian stocks and repatriate their funds, further weakening the rupee.
- Higher Borrowing Costs for Indian Companies: Higher global bond yields lead to increased domestic borrowing rates. Indian companies relying on foreign debt face higher interest costs.
- Corporate profitability declines, negatively impacting stock market sentiment.
Relation Between Bond Yield and Stock Market
- Stock Markets and Bond Yields Have an Inverse Correlation
- Rising Bond Yields leads to Bearish Stock Market
- Higher Borrowing Costs for Companies: Increased bond yields result in higher interest rates on loans and corporate bonds.
- Higher borrowing costs reduce corporate profits, leading to a decline in stock prices.
- Attractive Fixed-Income Returns: Higher bond yields make bonds more attractive than stocks.
- Investors shift money from equities to bonds, leading to a stock market sell-off.
- Inflationary Pressures: Rising bond yields often reflect higher inflation expectations.
- Higher inflation erodes future corporate earnings, making stocks less attractive.
- Tighter Monetary Policy: Rising bond yields suggest central banks (RBI, U.S. Fed) are tightening monetary policy.
- Higher interest rates slow economic growth, negatively affecting stock market performance.
- Falling Bond Yields leads to Bullish Stock Market
-
- Lower Borrowing Costs: Lower bond yields reduce interest rates, making borrowing cheaper for businesses.
- This boosts corporate profits, leading to stock market gains.
- Less Attractive Bonds: When bond yields fall, bonds provide lower returns.
- Investors move funds to riskier assets like stocks, increasing demand for equities.
- Economic Growth Expectations: Falling bond yields may indicate loose monetary policy, promoting economic expansion.
- This benefits stock markets by supporting higher earnings and valuations.
![]() 13 Feb 2025
13 Feb 2025

