Mumbai police have confirmed that Dharmaraj Kashyap is not a minor using Bone Ossification test.
Age Determination Key in Dharmaraj Kashyap Case under Juvenile Justice Act
- The case involved the accused Dharmaraj Kashyap, who claimed to be 17 years old during the investigation into the murder of former Maharashtra MLA Baba Siddique.
- It brings into focus the significance of age determination in India’s criminal justice system, particularly in relation to the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Bone Ossification Test
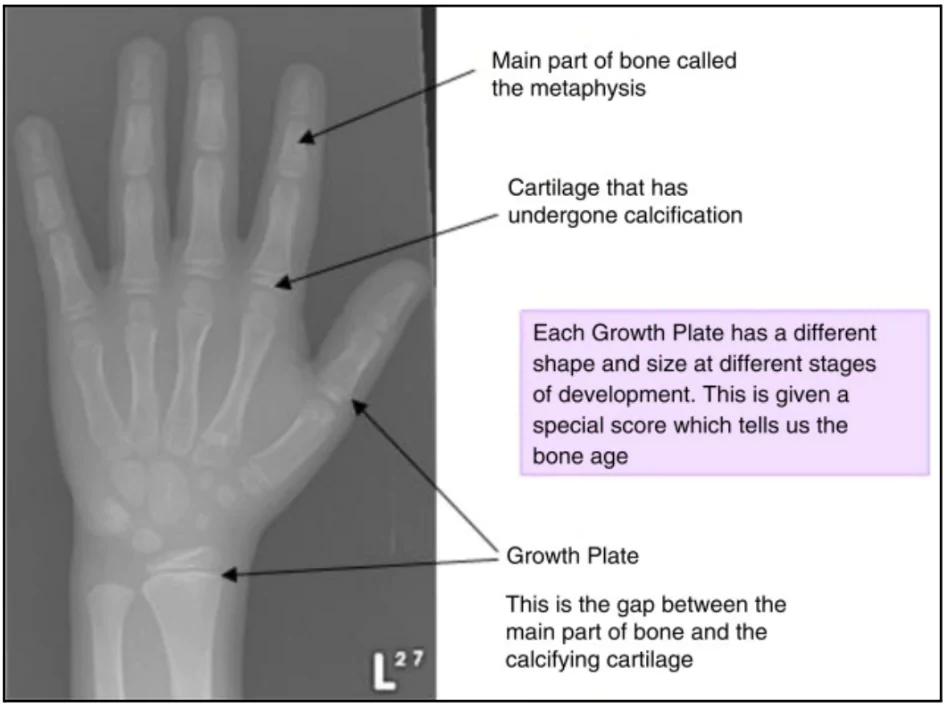
- Ossification: It is the natural process of bone formation, which continues until late adolescence. The stage of bone development helps determine the approximate age of an individual.
- Procedure of Test : X-rays are taken of certain bones, such as the clavicle, sternum, and pelvis to determine the degree of growth in our bones skeletal development.
- These bones are chosen because they tend to undergo the most dramatic changes in their form as a person ages.
- The results are compared with standard reference points for bone maturity.
- Reliability: Although the ossification test provides an estimated age range, it is not entirely accurate due to individual variations in bone maturation.
- Vinod Katara vs. The State of UP (2022): The Session Court said that the bone ossification test is not an exact science that can provide us with the exact age of the person.
- Margin of error: Courts have acknowledged this variability and often allow a margin of error of up to two years.
- The Delhi High Court ruled that in POCSO (Protection of Children from Sexual Offences) Act cases where the age of the victim is determined through an ossification test, the upper age in the test’s reference range should be considered.
- Courts have established that the ossification test cannot overrule valid documentary evidence of age.
- Documentary proof (such as Aadhaar cards or birth certificates) takes precedence, and the test is used only when such documentation is unavailable or disputed.
Legal Framework for Age Determination
- Section 94 of the J J Act: If a person’s appearance clearly indicates they are a minor, the JJB can proceed without further age confirmation.
- However, if there is doubt, a thorough process must be undertaken, starting with documentary evidence such as a school certificate or birth certificate.
- Use of ossification test: Only in the absence of valid documentary evidence should medical tests like ossification be used as the last resort.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Importance of Age Determination in Criminal Justice
- Juvenile status: In India, individuals under 18 years of age are considered minors, and their treatment under the law differs significantly from that of adults.
- Minors are tried under the Juvenile Justice (J J) Act, which emphasizes rehabilitation and correction rather than punishment.
- Juvenile Justice Board (JJB): A child in conflict with the law is brought before the JJB, which includes a magistrate and two social workers.
- The JJB has discretion in determining the rehabilitation measures, such as community service or up to three years in a special home.
- Special cases for children above 16 years: The 2021 amendment to the J J Act allows minors aged 16 to 18, accused of heinous crimes (punishable with seven or more years of imprisonment), to be tried as adults if they are assessed to have the mental and physical capacity to understand the nature and consequences of the crime.
![]() 16 Oct 2024
16 Oct 2024

