Context:
- The Vice-President of India, emphasized the need to take education as a service to the nation and cautions against the draining of ‘brains, and foreign exchange to foreign locations.
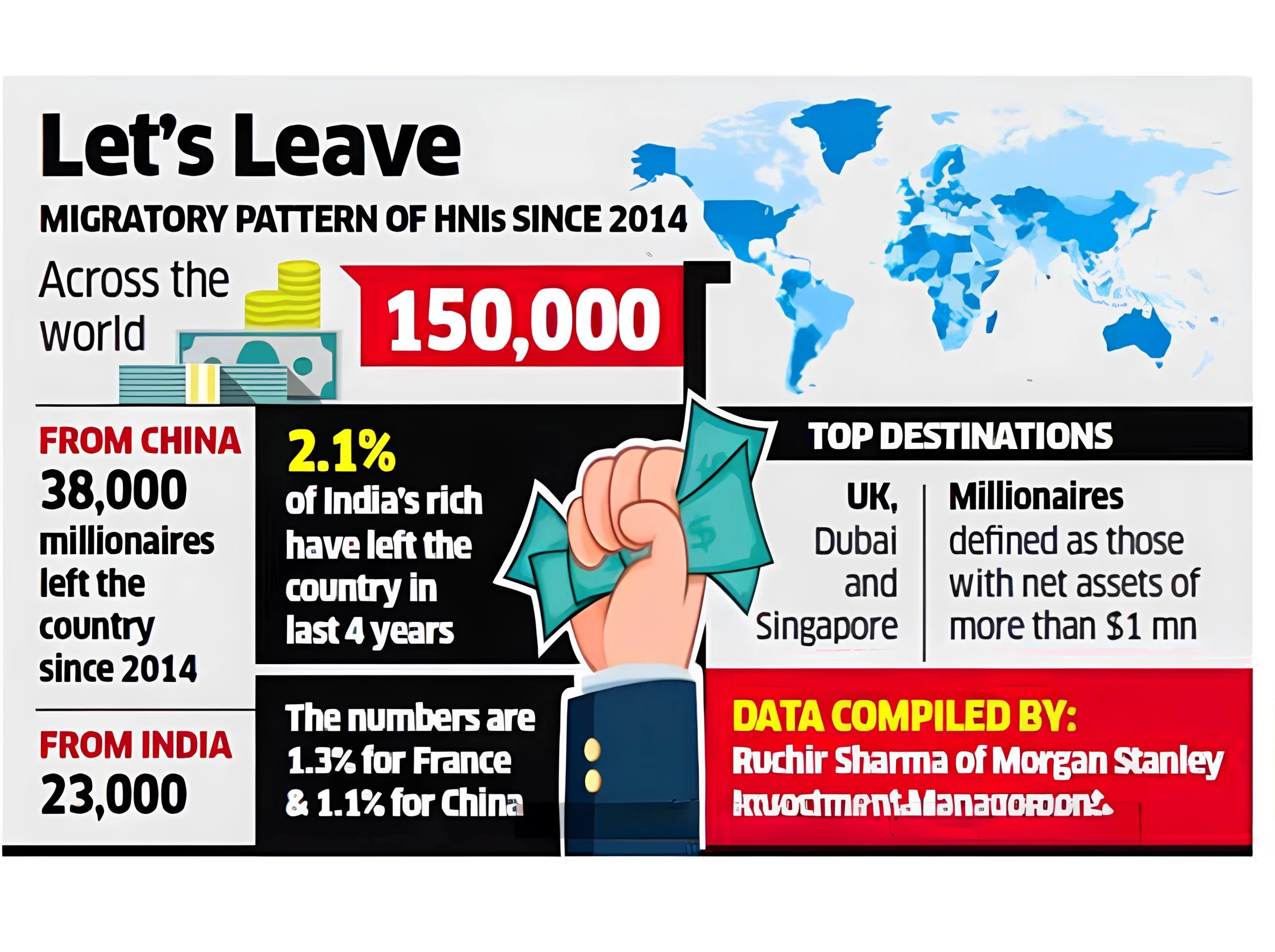
Statistics on India’s Brain Drain
- According to a Morgan Stanley bank report close to nine lakh Indians have given up their citizenship since 2015. In addition, 23000 millionaires have left India since 2014.
- India is also seeing a migration of talented students abroad. The British High Commission states that 1,17,965 Indians got a UK Visa for studies in a year till June 2022.
- Another report suggests that 1.8 million Indians will be spending close to $85 billion on studying abroad by the year 2024.
- This number shows how money from India is also draining out with its talent.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is a Brain Drain?
- Merriam-Webster defines brain drain as “the departure of educated or professional people from one country, economic sector, or field for another usually for better pay or living conditions.”
- India witnessed the sharpest increase in people migrating overseas, at nearly 10 million between 2000 and 2020, according to the “International Migration 2020 Highlights” report.
- According to a government survey, as many as 12% of scientists and 38% of doctors in the U.S. are Indians and in NASA 36% or 4 out of 10 scientists are Indians.
- In the corporate field 34% of employees at Microsoft, 28% at IBM, 17% at Intel, 13% at XEROX, and more than 12% at Google are Indians.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Brain Drain V/S Brain Gain
- In the long run brain drain may be converted into brain gain: something particularly relevant to India.
- Brain Gain: Return of Indian-origin highly trained professionals or Scientists to live and work in the country.
- Estimated at 32 million and with a presence in 189 countries, the Indian Diaspora produces an annual economic income of about $400 billion, almost 13 percent of India’s GDP (MEA).
- The 1 million Indians in the United States who represent only 0.1 percent of India‟ ‘s population earn the equivalent of about 10% of India‟ ‘s national income. The estimated volume of remittances in 2022 was $89.1 billion. Remittances account for nearly 3% of India’s GDP.
- Indian expatriates abroad, especially highly–qualified expatriates bring other benefits such as image improvement for the country, knowledge transfers, access to new markets and business networks.
- For example, the Indian Diaspora played an important role in the India-US civil Nuclear Deal.
|
What are the main reasons for brain drain in India?
- Lack Of Opportunity in Higher Education: One of the reasons for Indian students moving abroad can be the tough competition to get into premiere Indian universities.
- For Example, In 2022, there were more than 18.5 lakh applications for the NEET examination. Only 91,927 MBBS seats, 27,698 BDS seats, 50,720 AYUSH seats, and 525 B.VSc & AH seats were available.
- Similar trends are observed in other elite examinations in the country such as UPSC or the admission to IITs, where lakhs of students compete against each other.
- Employment Opportunities and Higher Pay: The job market in India is highly competitive. Every year, lakhs of new job seekers enter the market and jostle to find opportunities in the best companies. With so many people fighting for jobs, the salaries come down significantly as more and more people are willing to work at lower wages.
- Salaries in India for the same role stand in stark contrast with salaries in Europe, the US, or other international destinations.
- Taxation Policy: The high rate of tax and complexity of the regulatory regime in India may also be a factor that has seen the growth in HNIs migrating to other countries.
- The peak tax rate in India, including surcharge and cess, applicable for an individual with income above ₹ 1 crore is 35.88%. Comparatively, countries in the neighborhood like Singapore and Hong Kong have a much lesser peak rate of 22% and 17%, respectively.
- Visa Programme: The key factor for increasing Indian students studying abroad is the success of the work visa programs provided to international students and graduates.
- Between January and September 2021, almost 115,000 Indian students received approval to study in Canada, and during the previous five years, Indian PGWP applicants had an approval rate of more than 95%.
- Post-study visas, like the H-1B in the US, have mostly gone to Indians.
- Standard of Living: They migrate to first-world countries for better living standards, higher salaries, and access to advanced technologies to enhance future growth.
- India is placed in the Medium Human Development category. In the 2022 report, India had 0.645 and was ranked 131 among 189 countries.
- The rise of Millennials and Zillennials: The Youth (GEN-Z) challenging the antediluvian status quo. Those who go to study abroad, therefore choose to remain there. But they are also aware of Climate Change, gender discrimination, sectarian warfare, authoritarian bullying, rising crime graph, and political radicalism. It is, therefore, hardly a surprise that the highest immigration exits are happening from China, Russia, and India, along with Iran, Qatar, and Hong Kong.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
What are the negative impacts of brain drain in India?
There are several detrimental effects of brain drain on developing nations like India.
- Loss of Human Capital: It leads to a shortage of highly skilled professionals, making it challenging to develop critical sectors such as healthcare, education, and technology.
- The country is experiencing an alarming shortage of 150 million skilled workers, up from 138 million three years ago, according to TeamLease Services, a leading human resources development consultancy firm.
- Reduction in Innovation, Research, and Development may result from brain drain.
- The India Innovation Index 2021 has found that the overall spending on R&D by India has been relatively low across the country. This was reflected in the overall share of gross expenditure on R&D (GERD) as a percentage of GDP, at about 0.7%.
- India retains 40th rank out of 132 economies in the Global Innovation Index 2023 rankings published by the World Intellectual Property Organization.
- Economic Disparity: The exodus of talented people can make already-existing social and economic disparities worse by depriving the country’s marginalized communities of qualified professionals who can assist in meeting their needs.
-
- It can also worsen economic inequality because most highly skilled and educated individuals can afford to emigrate.
- Loss of Revenue: Another effect on areas that experience brain drain is the loss of revenue. Governments rely on income taxes to fund their social programs and infrastructure projects. A mass exodus leads to a drop in tax receipts, stunting economic growth and development.
- Foreign Exchange: Close to 200,000 students travel abroad yearly for higher education programs. Due to this, almost Rs 50,000 crore flows out of India every year for higher education programs.
- By 2024, Indian students studying abroad are estimated to increase to 1.8 million and student spending to hit 80 billion USD (MEA).
- Economic Development: Furthermore weakening the nation’s economy is the possibility of brain drain causing a general decline in productivity and innovation.
- According to the McKinsey Global Institute, 2001, India’s labor Productivity is only 15% of US productivity resulting in wastage of scarce resources.
- The (country’s) economy is harmed because each professional represents surplus spending units. Professionals often earn large salaries, so their departure reduces consumer spending in that region or the country.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Government Initiative:
- Three-Pronged Strategy for Arresting ‘Brain Drain’
- Creating research infrastructure, environment for scientific pursuit, and academic / research institutions.
- Creation of Opportunities for overseas scientists of Indian origin.
- New Opportunities for Postdoctoral Research.
- Establishment of Research Parks: The government has sanctioned the establishment of Research Parks at IITs- and IISc to augment the research ecosystem in the country to enable the students to pursue their R and D interests in India, through innovative research.
- Global Initiative for Academic Network (GIAN): This seeks to tap the talent pool of scientists and entrepreneurs from abroad, including those of Indian origin, to augment the country’s existing academic resources.
- Visiting Advanced Joint Research (VAJRA) Faculty Scheme of SERB: It provides a platform for overseas scientists including Non-Resident Indians to undertake collaborative research in Indian Institutions and Universities for a finite period of time.
- National Education Policy 2020: It allows the top 100 international institutes to set up campuses in India.
|
Way Forward – Solution to India’s Brain Drain
- Knowledge Economy: As the knowledge economy is more productive and less labor-intensive than other sectors. However, it is also important to ensure that India has the infrastructure and skilled workforce to support the knowledge econometain talent, India needs to invest in research and development, innovation, and education.
- The government can also incentivize businesses to invest in these areas.
- Quality Higher Education and Skill Developmenty.
- To create a knowledge economy that can r
- India has a large and young population, but a significant proportion of the workforce is unskilled or under-skilled.
- To address this challenge, India must invest in high-quality education and skill development. The government can increase funding for education and training programs, and it can also work with the private sector to develop and deliver these programs.
- Foreign Institutes in India:
- Allowing foreign higher education institutions to set up campuses in India can be a way to provide Indian students with access to world-class education without having to leave the country. This can help to reduce brain drain and also make India a more attractive destination for foreign students.
- For Example: Two Australian universities will soon set up campuses at Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City).
- Research and Development and Innovation:
- India must invest more in research and development (R&D) to become an innovation powerhouse. This will help to create high-paying jobs and attract and retain talent.
- The government can increase funding for R&D institutions, and it can also provide tax breaks and other incentives for businesses to invest in R&D.
- Higher Wages and Employment Opportunities:
- Offering Competitive and better employment opportunities to skilled workers in India. Both the public and private sectors can do this.
- The government can increase salaries for government employees and invest in creating new jobs in the public sector. The private sector can also offer higher wages and better employee benefits.
- Taxation Policy:
- A favorable taxation policy for entrepreneurs can help to reduce brain drain and also create jobs. The government can reduce the tax burden on startups and small businesses, and it can also provide tax breaks for businesses that invest in research and development.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
In addition to the above solutions, the government can also work to improve the overall quality of life in India. This includes investing in infrastructure, improving public services, and reducing corruption. By making India a more attractive place to live and work, the government can help to reduce brain drain and attract talent from around the world.
Also Read: International Migration Outlook 2023: Analysis of Trends, Impacts, and Challenges
Conclusion:
Addressing the challenges of brain drain in India requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing investments in education, research, and innovation, along with favorable policies that create opportunities, improve quality of life, and ultimately transform the brain drain into a brain gain for the nation’s sustainable development.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Coaching
![]() 31 Oct 2023
31 Oct 2023

