The Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI) has highlighted opportunities and challenges for India under World Bank’s Business Ready (B-READY) framework that benchmarks business environments globally.
- The World Bank’s Business Ready (B-READY) framework is replacing the ‘Doing Business index’ due to past data irregularities in the reports
About the B-READY Report
- Objectives
- To provide a comprehensive assessment of business environments.
- To Evaluate the regulatory frameworks, public services, and their efficiency for firms.
- To support private sector development and improve investment climates globally.
- Key Features: Covers 10 areas of a firm’s lifecycle, including business entry, labour regulations, and international trade.
- Focuses on starting, operating, and closing or reorganizing business activities.
- Three Pillars of Assessment
- Regulatory Framework : Evaluates rules and regulations throughout a firm’s lifecycle.Promotes clarity, fairness, and sustainability.
- Public Services: Reviews government services and infrastructure supporting businesses. Highlights digitalization, transparency, and interoperability.
- Operational Efficiency: Measures ease of compliance with regulations and access to public services. Focuses on operational ease and regulatory efficiency.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
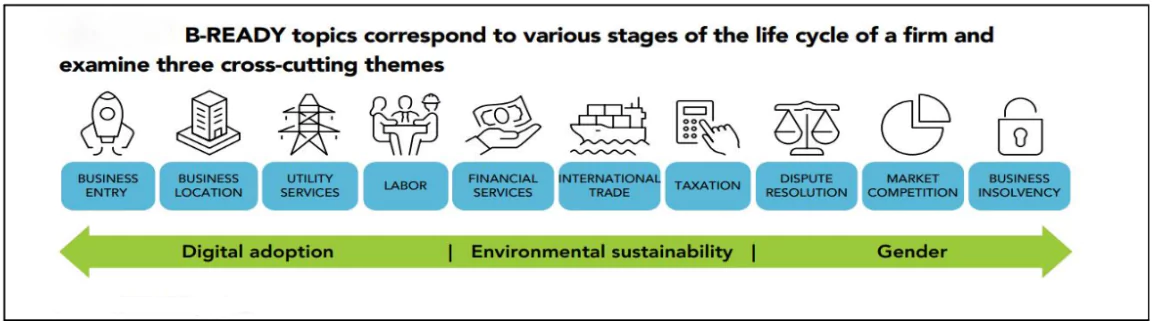
- Key Themes of B-READY
- Digital Adoption: Assesses the level of digital integration in government and business operations.It focuses on the use of technology to enhance the business environment.
- Environmental Sustainability: Evaluates regulatory provisions impacting business operations with sustainability as a priority. It highlights environmentally responsible practices and policies.
- Gender Inclusivity: Reviews the collection and use of gender-disaggregated data and Examines the implementation of gender-sensitive regulations and programs.
- Scoring Mechanism
- Topic Scores: Reflect firm flexibility and social benefits based on the three pillars.
- Pillar Scores: Cover 10 topics, standardized between 0 and 100.
- Data Collection and Updates:
- Expert questionnaires for regulatory and public service data.
- World Bank Enterprise Surveys for operational efficiency data.
- Frequency: Expert data updated annually and firm-level data updated every three years.
- India’s Participation: India will join the B-READY rankings in 2026.
Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI)
- GTRI is a Delhi based research and advocacy organization focused on promoting open and fair trade established in 2022.
- Role: GTRI conducts in-depth research on global trade issues, analyzes trade policies, and advocates for policies that benefit businesses, consumers, and the global economy.
- Key Activities:
-
- Policy Research: GTRI conducts research on a wide range of trade issues, including tariffs, non-tariff barriers, trade agreements, and the impact of trade on economic growth and development.
- Advocacy: GTRI advocates for trade policies that promote economic growth, job creation, and consumer welfare.
- Education and Outreach: GTRI engages in public education and outreach activities to raise awareness about the importance of international trade.
|
Key Highlights of GTRI on B-READY Report
- Global Comparisons: Countries like Singapore excel in parameters such as online business registration and trade facilitation.
- Germany and Singapore simplify customs to enhance trade efficiency.
- Opportunity for India : Likely to score well on Quality of Regulations, Effectiveness of Public Services, and Operational Efficiency.
- Challenges for India: Scores on business entry, labour regulations, and international trade expected to be moderate to low due to existing inefficiencies.
Challenges for India for Business
- Business Entry: India faces multiple steps and incomplete digital integration, unlike Singapore’s seamless one-day registration.
- Labour Regulations: Introduction of four labour codes is promising, but uneven implementation across states slows progress.
- International Trade: Customs delays, inconsistent enforcement, and high logistics costs hinder trade efficiency.
- India has reduced the average turnaround time at major ports from 4.3 days in 2012-13 to 2.1 days in 2022-23. However, this is still higher compared to top-performing ports like Jawaharlal Nehru Port near Mumbai, which has achieved turnaround times as low as 26 hours.
- Business Location: Acquiring land and necessary approvals for business operations in India can be a protracted process, with regulatory inconsistencies across states adding to the complexity. This unpredictability can deter investment and delay project initiation.
- Broader Issues: High logistics costs, burdensome GST compliance, slow dispute resolution, and limited SME credit access. These factors contribute to reduced trade efficiency and competitiveness.
- Logistics costs in India are estimated to be around 14-16% of GDP as per Economic Survey 2022-23, compared to approximately 12% in the U.S. and Europe, and about 8% in China.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Way Forward
- Leverage Global Insights: Draw lessons from top-performing countries like Singapore and Germany while adapting solutions to local contexts.
- Focus on Local Reforms: Accelerate implementation of labour codes and streamline business entry processes. Improve customs efficiency and reduce logistics costs to boost international trade.
- Balanced Approach: Avoid overemphasis on rankings. Address structural issues such as digital integration, dispute resolution, and access to green technologies.
- Policy Priorities: Ensure reforms cater to India’s unique economic complexity and vast business landscape.
By addressing these challenges with a focus on both global best practices and local reforms, India can strengthen its position in the B-READY framework and create a more conducive environment for businesses.
![]() 2 Jan 2025
2 Jan 2025

