A new international Fund to boost biodiversity finance, namely, “Cali Fund” was launched recently at COP16 to The Convention on Biological Diversity in Rome.
About The “Cali Fund – For the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits from the use of Digital Sequence Information on Genetic Resources (DSI)”
- Adoption: The Cali Fund was part of a Multilateral Mechanism on the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the use of digital sequence information on genetic resources adopted at COP 15 of the CBD in 2022 alongside the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
- Established: The fund was officially created at COP16 in Colombia 2024, setting up a global system for sharing benefits from DSI.
- Goal: The Fund is a forward step towards meeting Goal C and Target 13 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) goal of stopping and reversing biodiversity loss by 2030.
- Managed By: The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and United Nations Environment Programme will manage the fund.
- Hosted By: The Multi-Partner Trust Fund Office (MPTFO) will handle administrative tasks.
- Secretariat: Cali Fund Secretariat will be hosted by the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) secretariat.
- Objective: To mobilize funding from the private sector for biodiversity action, ushering a new era for biodiversity finance in support of the three objectives of the CBD and the implementation of the Kunming- Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
- Mechanism:
- Private Sector Contribution: The Fund will receive direct contributions from the private sector as companies making commercial use of digital sequence information on genetic resources are expected to contribute a portion of their business revenue to the Fund.
- Benefactors: At least 50 per cent of the Cali Fund resources will be allocated to the self-identified needs of indigenous peoples and local communities, including women and youth.
- Contributors: Large companies and other major entities in sectors highly dependent on the use of DSI like,
- Pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, plant and animal breeding and agricultural biotechnology, industrial biotechnology, laboratory equipment associated with the sequencing and use of DSI on genetic resources and information, scientific and technical services related to DSI on genetic resources, including artificial intelligence.
- Exemption: Academic, public databases, public research institutions and companies operating in the concerned sectors but not relying on DSI are exempt from contributions to the Cali Fund.
- Significance:
- Support Biodiversity Conservation Projects: The Fund will contribute to the success and support of various biodiversity conservation projects across the world.
- Help Implement Biodiversity Action Plans: The Fund will support the delivery of National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs) by developing country parties under KMGBF and CBD
- Fund Scientific Research: The fund will boost scientific research on biodiversity and bridge existing gaps in the way countries generate, access, use, analyze and store DSI.
- Collective Action: The fund will be a pioneer in initialising collective action in support of biodiversity as it for the first time brings the private sector in its ambit recognising their responsibilities to give back to nature.
About The Digital Sequence Information (DSI) on Genetic Resources
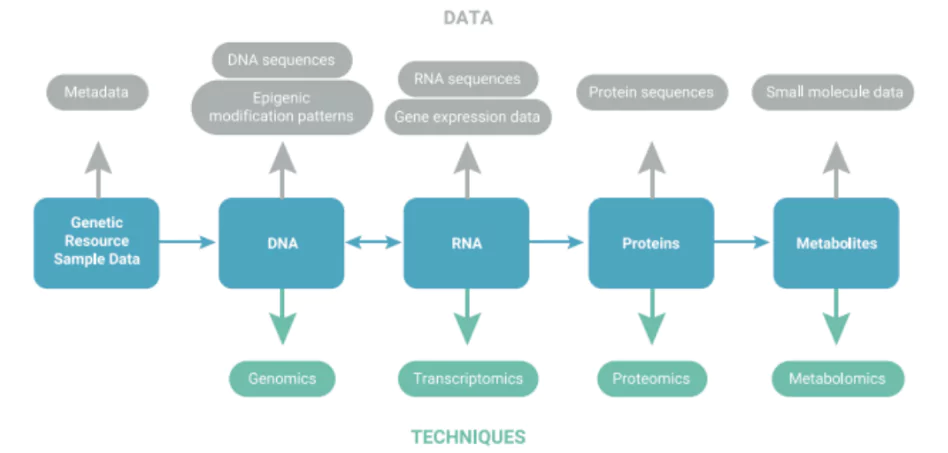
- Digital sequence information on genetic resources is a ‘placeholder’ term used in international policy discussions, particularly under the Convention on Biological Diversity to refer to data derived from dematerialized genetic resources, including DNA, RNA, and Protein sequences.
- Scope: DSI and its implications is actively discussed under various instruments including,
- The Convention on Biological Diversity, the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, the WHO Pandemic Influenza Preparedness Framework and the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea.
- Significance:
- DSI is essential for research in various fields, including public health, medicine, biodiversity, plant and animal breeding, and evolution research.
- Conservation and Sustainable Use: DSI is a critical tool for the conservation and sustainable use of genetic resources to deal with vital issues such as human, animal and plant health, food security, climate change mitigation and the environment.
- Environmental and Biological Research: It contributes to the understanding of the molecular basis of life and evolution and how gene therapies provides new cures for diseases, new energy sources and other new products.
- Mitigation Efforts: It plays important roles in taxonomy, identifying and mitigating risks to threatened species, tracking illegal trade, identifying the geographical origin of products and planning conservation management.
About the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- CBD is an international treaty for the conservation of biodiversity, the sustainable use of the components of biodiversity, and the equitable sharing of the benefits derived from the use of genetic resources
- Adoption: The CBD was adopted in 1992 during the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit.
- Membership: It is a legally binding treaty with 196 countries ratifying the convention.
- The United States is the only UN member state that has not ratified it.
- Secretariat: Montreal, Canada.
- Objective:
- Conservation of biological diversity (genetic diversity, species diversity, and habitat diversity).
- Sustainable use of biological diversity.
- The fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources.
- Protocols:
- The Cartagena Protocol: It entered into force in 2003 and aims to safeguard biological diversity from potential risks posed by genetically modified organisms (GMOs) resulting from biotechnology.
- Parties: It currently has 173 Parties
- Focus: It is on safe transport, handling, and use of living modified organisms, considering their potential adverse effects on biodiversity and human health.
- The Nagoya Protocol: It entered into force in 2014 and provides a transparent bilateral legal framework to providers and users for the fair and equitable sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources.
- Members: It has 141 Parties.
About The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
- It is an international Framework to protect and restore biodiversity by 2030 and reach the global vision of a world living in harmony with nature by 2050.
- Adoption: It was adopted during the fifteenth meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP 15) of Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in 2022.
- Targets: The Framework provides 4 goals for 2050 and 23 targets for 2030 and replace Aichi Biodiversity Targets.
|
![]() 28 Feb 2025
28 Feb 2025

