While addressing at 49th Civil Accounts Day celebrations Arvind Panagariya, Chairman of the 16th Finance Commission, emphasized that India should not rush into full capital account convertibility at its current per capita income level.
Key Highlights of the address
- Suggested Threshold: He recommended considering this reform only when per capita income reaches $8,000-10,000.
- Exchange Rate Management Concern: Full convertibility would remove exchange rate control from the government and RBI.
- Economic Optimism: Despite his caution he expressed confidence in India’s ability to become a developed nation by 2047, given its economic trajectory.
Balance of Payments (BoP)
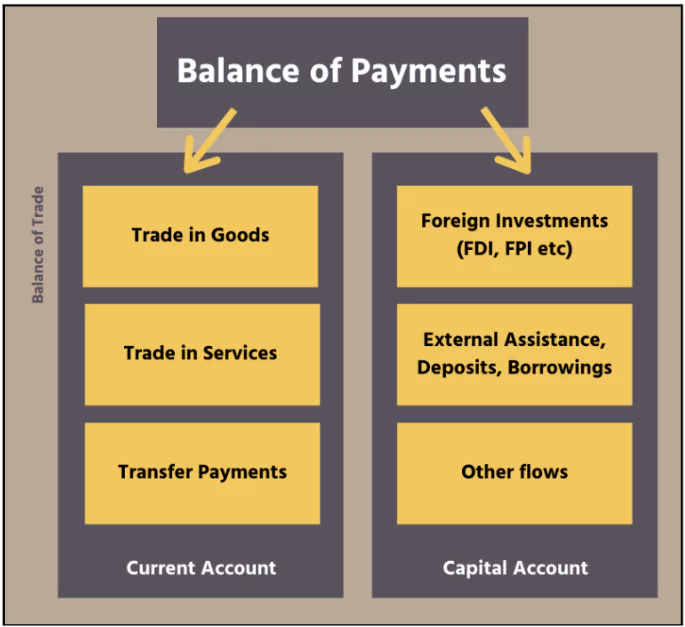
- Bop is a record of all transactions between a country and the rest of the world.
- BoP has Two Main Accounts:
- Current Account: Covers trade in goods and services (imports and exports).
- Capital Account: Deals with cross-border capital movements such as investments and loans.
About Capital Account Convertibility
- Capital Account Convertibility: Freedom to conduct investment transactions across borders without restrictions.
- Current Status of Capital Account Convertibility: Regulated.
- Capital Account Convertibility without Limits:
- Indian residents: No restrictions on converting rupees into foreign currency to acquire overseas assets.
- NRIs: No limitations on bringing foreign currency to invest in Indian assets.
About Current Account Convertibility
- Current Account Convertibility: Freedom to convert rupees into foreign currencies (and vice versa) without restrictions for making payments.
- India allows for 100 % Current Account Convertibility.
Partial Convertibility
- Current Account: Fully convertible.
- Capital Account: Still regulated.
|
Key Aspects of India’s Capital Account Framework
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- Largely liberalized but subject to sectoral caps and government approvals in sensitive industries.
- Sector-Wise Caps:
- Banking (Private): Up to 49% automatic, beyond that requires government approval up to 74%.
- Biotechnology (Brownfield): Up to 74% automatic, beyond that requires government approval.
- Defence: Up to 74% automatic, beyond that requires government approval.
- Healthcare (Brownfield): Up to 74% automatic, beyond that requires government approval.
- Pharmaceuticals (Brownfield): Up to 74% automatic, beyond that requires government approval.
Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)
- Permitted with Restrictions: Ownership limits apply in certain sectors.
- Sovereign Bonds: Allowed but within prescribed RBI limits to prevent excessive foreign influence.
Outward Investments by Indian Residents
- Allowed with Limits: Governed under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS).
- Remittance Cap: Indian residents can remit up to $250,000 per year for purchasing foreign assets such as stocks, bonds, or property abroad.
Advantages of Full Capital Account Convertibility
- Encourages Inflows: Free capital movement attracts higher foreign investment, boosting economic and infrastructure growth.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Greater financial integration improves India’s access to international markets.
- Investor Confidence: A more open capital account signals economic maturity and stability, improving India’s credit standing.
Challenges of Full Capital Account Convertibility
- Fluctuations: Unregulated capital flows can cause instability in exchange rates and inflation.
- Currency Risk: Sudden inflows or outflows may lead to excessive currency appreciation or depreciation.
- External Shocks: Greater exposure to global markets increases vulnerability to financial disruptions.
Tarapore Committee Recommendations on Full Capital Account Convertibility (CAC)
- Fiscal Consolidation: Maintain fiscal deficit within 3-3.5% of GDP to ensure macroeconomic stability and sustainable economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Objectives: Align domestic inflation rates with global levels and adjust interest rates to reflect inflation differentials for a stable financial environment.
- Institutional Strengthening: Strengthen the monetary policy framework to enhance decision-making and ensure effective management of capital flows.
- Banking System Reforms: Improve banking sector resilience through restructuring, stronger safeguards, and capacity-building to handle increased capital mobility.
- Adequacy of Foreign Exchange Reserves: Ensure sufficient forex reserves to absorb external shocks, as a critical factor in implementing full capital account convertibility.
India should cautiously approach full capital account convertibility, prioritizing economic stability. While it offers benefits like investment growth and market integration, risks like volatility and external shocks necessitate a gradual transition.
![]() 5 Mar 2025
5 Mar 2025


