Recently, the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) has updated Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) to prevent the deterioration of air quality in Delhi-NCR.
What is Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)?
Air Quality Index
- This index is issued by the government agencies.
- It measures the level of air pollution and gives risks information to public.
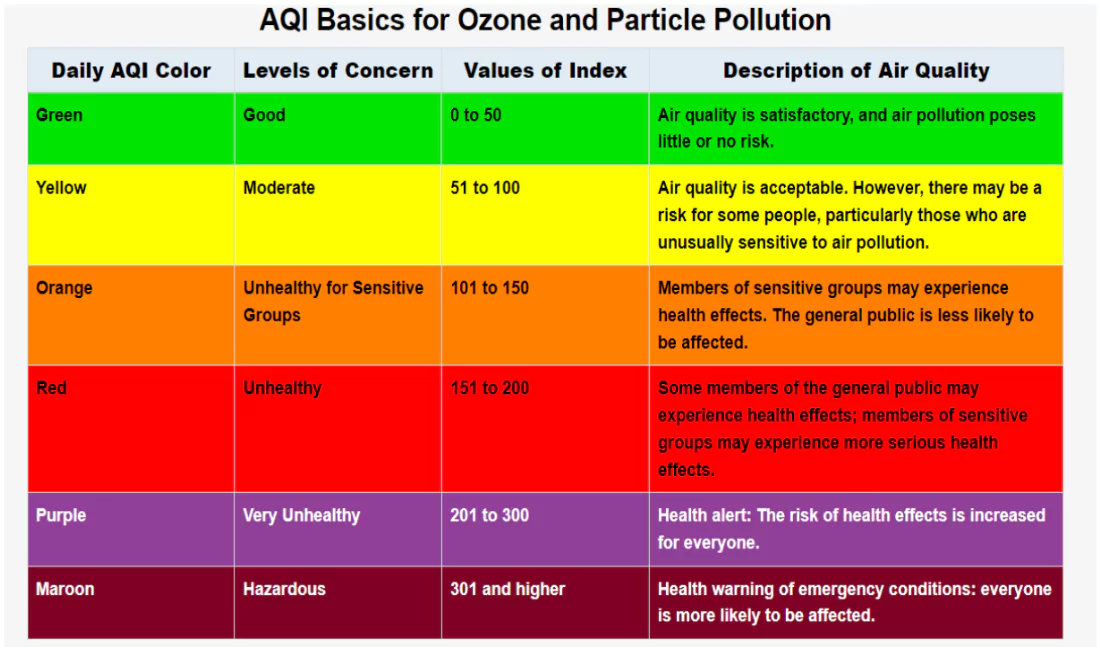
|
- This body monitors air pollution in the National Capital Region (NCR).
- It also coordinates with different states and departments.
- Jurisdiction: covers Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Powers: It can impose fines on polluters.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- GRAP is a set of emergency actions to prevent further worsening of air quality in Delhi-NCR when pollution levels cross a certain limit.
- Approval: GRAP was approved by the Supreme Court in 2016 after the M.C. Mehta vs. Union of India case.
Health Crisis Due to Pollution
- Global and Indian Impact: Air pollution was the second-largest risk factor for death globally in 2021, with India accounting for 2.1 million deaths.
- Delhi’s Mortality: Delhi alone recorded 12,000 deaths in 2021 due to air pollution.
|
- Start: It was officially implemented in 2017.
- GRAP Purpose: Works as an emergency alert system, guiding governments to act based on pollution severity.
-
Implementation
-
- Current Authority (Since 2021): The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) is responsible for implementing GRAP measures.
- Previous Authority (Until 2020): The Supreme Court-appointed Environment Pollution (Prevention & Control) Authority (EPCA) managed GRAP implementation until it was dissolved in 2020.
- Forecasting: CAQM uses air quality and weather forecasts provided by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Key Features of Revised Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- Focus Shift: GRAP now focuses on the overall Air Quality Index (AQI) instead of just PM2.5 and PM10 levels.
- Expanded Pollutants: The AQI includes eight pollutants: PM2.5, PM10, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, ozone, ammonia, and lead.
- Four Pollution Stages: GRAP categorizes pollution into four stages based on AQI levels: Poor, Very Poor, Severe, and Severe+.
- Stage I: Poor (AQI 201-300)
- Stage II: Very Poor (AQI 301-400)
- Stage III: Severe (AQI 401-450)
- Stage IV: Severe+ (AQI > 450)
-
Evolution from Reactive to Proactive Measures
-
- Old Approach: Earlier, actions were triggered only after 3 consecutive days of severe pollution.
- New Approach: Now, the system forecasts pollution levels for 3 days.
- Impact of Vehicles: Half of Delhi’s pollution during winters is due to vehicles, according to the Decision Support System (DSS).
Challenges in Implementing Revised Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- Construction Restrictions: Construction activities that cause dust pollution are banned under Stage III, except for critical public projects.
- Coordination Issues: There are concerns about the ability of NCR departments to coordinate and enforce measures effectively.
- Vehicle Emissions Control:
- The pollution under-control certificate system is not effective in identifying polluting vehicles.
- Remote sensing devices have been introduced to identify gross polluters.
- Vehicle Compliance: A study shows 89% of Delhi’s vehicles meet BS-IV or BS-VI standards, while 11% are pre-BS-IV models.
- Public Awareness: Citizens often remain unaware of pollution alerts and necessary actions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way forward
- While the revised GRAP helps control winter pollution, it focuses on symptoms, not causes.
- Long-term progress needs systemic reforms, such as better waste management and year-round vehicle emissions control.
- Coordinated Efforts:
-
- GRAP should be implemented consistently, aligned with the Policy to Curb Pollution for Delhi-NCR, which offers short-, medium-, and long-term solutions for all sectors.
![]() 24 Sep 2024
24 Sep 2024