Context: The Char Dham project in Uttarakhand, under which Silkyara tunnel is being developed, did not require an Environment Impact Assessment, the Union government told Parliament.
Silkyara Tunnel Collapse Highlights
- A landslide caused a portion of the 4.5 km tunnel to cave in on November 12 leaving 41 men trapped for 16 days. They were brought out alive following a lengthy rescue operation.
Read more about the Uttarakhand Silkyara Tunnel Collapse here.
What is an Environment Impact Assessment?
- According to the UN Convention (1991), Environment impact assessment (EIA) is defined as “a procedure for evaluating the likely impact of the proposed activity on the environment.
- EIA systematically examines both beneficial and adverse consequences of the project and ensures that these effects are taken into account during project design.
About Chardham Mahamarg Vikas Pariyojna
- Objective: To improve connectivity between four pilgrimage sites – Kedarnath, Badrinath, Yamunothri, and Gangotri – in Uttarakhand.
- Focus: The Char Dham project focuses on the widening of the existing roads in the region, along with ensuring adequate slope protection.
- Executing agencies:
-
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH)
- Uttarakhand State Public Works Department,
- Border Road Organization (BRO)
- National Highway and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Silkyara Tunnel: It is around a 4.5 Km long two-lane Bi-Directional tunnel with an escape passage on Dharasu –Yamunotri.
- Significance:
- This tunnel will provide all-weather connectivity to Yamunotri, encouraging regional socio-economic development, trade, and tourism within the country.
- It will reduce the travel distance from Dharasu to Yamunotri by about 20 km and travel time by about an hour.
|
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA): Background
- Genesis: Until the 1980s, most of the project activities were executed with minimum or without environmental consideration in India.
- In 1976-77, Environmental Impact Analysis was started in India, when the Department Of Science And Technology was asked by the Planning Commission to examine the river-valley projects from the environmental angle.
- Regulatory Framework in India: The EIA Notification, issued under the Environment (Protection) Act 1986, delineates the process and requisites for conducting an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) for diverse project categories.
- Project Categorization: Projects are classified into two categories, A and B, based on their potential environmental impacts, with Category A projects requiring environmental approval without undergoing a screening procedure. In contrast, Category B projects undergo a screening procedure.
- Government Oversight: The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) and State Environmental Impact Assessment Authorities (SEIAAs) play pivotal roles in implementing and overseeing the EIA process in India.
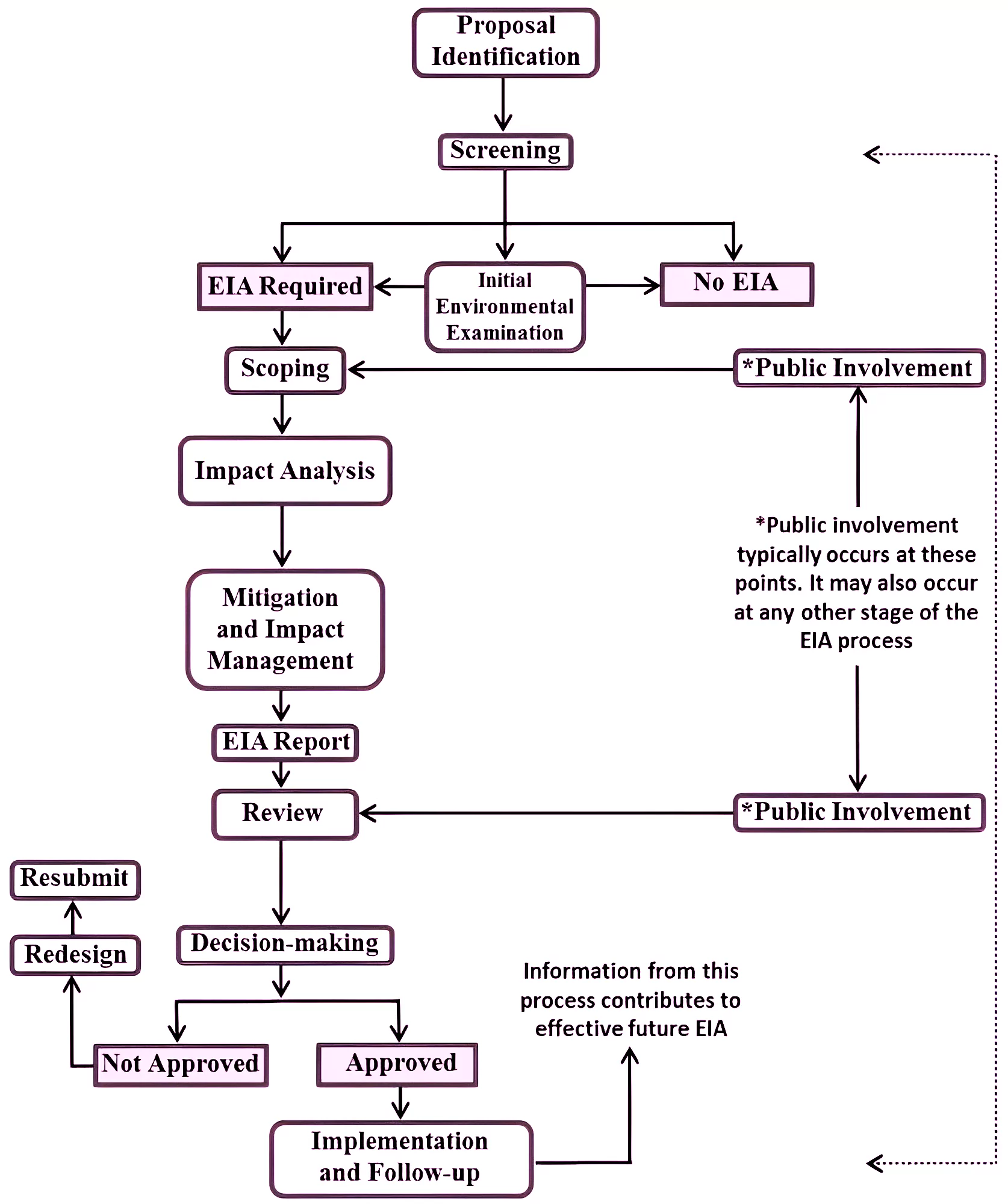
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA): Process
- Screening: Determines whether the environmental and social impacts of a proposed development project would be significant enough to develop an EIA.
- Scoping: Establish the boundaries of the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), set the basis of the analyses that will be conducted at each stage, describe the project alternatives, and consult the affected public
- Collection of data: The baseline data has to be collected which states the environmental status of a study area.
- Public hearing: Mainly after the completion of a project, certain groups of people living close by to a project are thereby informed of the same.
- Decision making: The discussion leads to the consulted authorities taking charge of the project to take it to a final decision.
- Risk assessment: Inventory analysis and hazardous property and index also lead to EIA procedures.
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA): Advantages
- Integration of Environmental Considerations: It ensures that environmental considerations are explicitly addressed and incorporated into the development decision-making process.
- Adverse Impact Mitigation: It anticipates and avoids, minimizes, or offsets the adverse biophysical, social, and other relevant effects of development proposals.
- Preservation of Natural Systems: It protects the productivity and capacity of natural systems and the ecological processes that maintain their functions; and
- Promotion of Sustainable Development: It promotes development that is sustainable and optimizes resource use and management opportunities.
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA): Limitations
- Lack Of expertise in the team conducting Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) studies in the concerned fields for developing EIA
- Improper scoping for the EIA
- No checks on the competence and liability of EIA consultancies.
- Lack of exhaustive ecological and socio-economic indicators.
- Lack of reliable data sources, and no credibility of the primary data collected by the data collectors.
News Source: DTE
![]() 9 Dec 2023
9 Dec 2023

