The Chennai Vladivostok eastern maritime corridor has become operational and is carrying oil, food and machines, Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways said at the Sagarmanthan: The Great Oceans Dialogue.
About Chennai Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (VCMC)
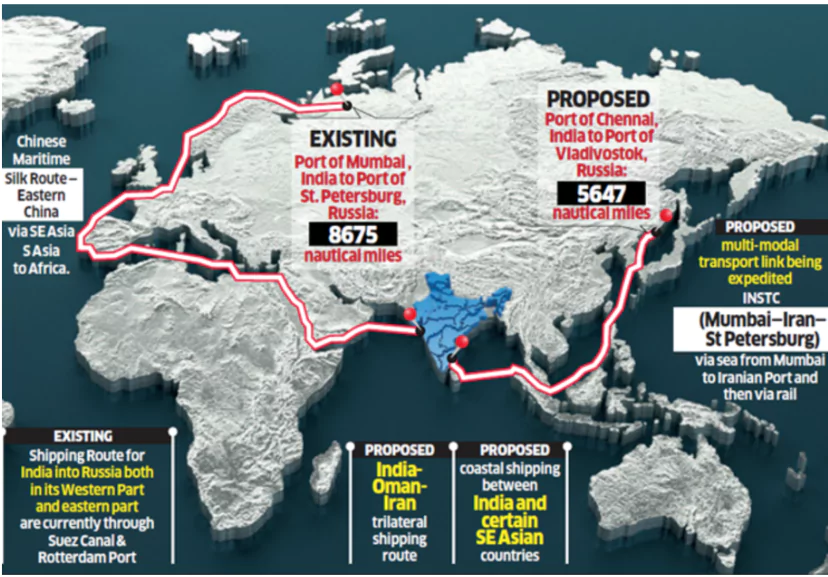
- The Chennai Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (VCMC) is a proposed sea route that connects the ports of Chennai and Vladivostok, and is part of the Eastern Maritime Corridor.
- The route will pass through the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea, the Strait of Malacca, the Bay of Bengal, and the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago.
- The Eastern Maritime Corridor connects ports on India’s east coast with ports in the far-east region of Russia
- Background: The VCMC was signed in 2019 by Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi during a visit to Vladivostok, Russia.
- Location: Vladivostok is Russia’s largest port on the Pacific Ocean, and is located about 50 kilometres from the China-Russia border.
- Distance: The VCMC is about 5,600 nautical miles long.
- Purpose: The VCMC aims to improve trade relations between India and Russia, and provide a more cost-effective way to transport goods between the two countries.
- Benefits: The VCMC could reduce the time it takes to transport cargo between the two countries by up to 16 days.
- The Mumbai-St. Petersburg route via the Western Sea Route and Suez Canal spans 8,675 nautical miles, taking 40 days for a container ship to reach Russia’s Far East region.
- Significance: The VCMC could be a strategic move for India and Russia, and could potentially alter the regional balance of power.
- However, there are also security implications to consider, such as the potential for heightened tensions in the South China Sea.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
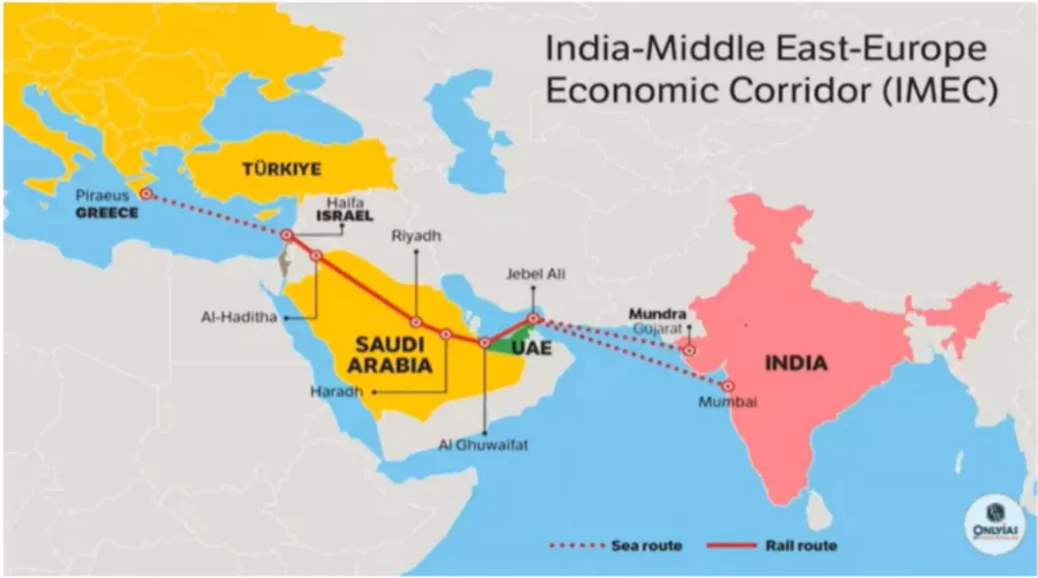
About India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC)
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) was announced during the G20 Summit in New Delhi.
- A Memorandum of Understanding was signed between the European Union and seven countries, namely India, the United States, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), France, Germany, and Italy.
 Purpose:
Purpose:-
- The IMEEC aims to establish a reliable and cost-effective ship-to-rail transit network to complement existing maritime routes.
- The corridor is intended to enhance trade efficiency, reduce costs, secure regional supply chains, and foster economic cooperation.
- It will also help in generating employment opportunities and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- Structure:
- The IMEEC will comprise two separate corridors:
- The Eastern Corridor will connect India to the Gulf.
- The Northern Corridor will link the Gulf to Europe.
- The corridor will include:
- A shipping route connecting Mumbai and Mundra (Gujarat) to the UAE.
- A rail network connecting the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan with the Israeli port of Haifa, leading to the Mediterranean Sea.
- A sea route from Haifa to Piraeus (Greece) and onward to Europe.
- Additional infrastructure will include undersea cables for data transmission and long-distance hydrogen pipelines to support climate and decarbonization goals.
![]() 19 Nov 2024
19 Nov 2024


 Purpose:
Purpose: