Recently, China hosted its ninth Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) summit, drawing over 50 African leaders to Beijing.
Overview of China-Africa Summit 2024
- Financing Offer: Chinese President Xi Jinping announced $51 billion in soft loans, grants, and investments to African nations.
- This package focuses on fostering cooperation in key areas such as trade connectivity, green development, industrial chain collaboration, and health.
- Human Capital Development:
- Provision of 60,000 training opportunities for women and youth.
- Invitation for 1,000 African political party members to visit China.
- Training for 7,000 African military and police personnel.
- Trade Benefits: Zero tariff treatment for 100% of tariff lines for all 33 African Least Developed Countries (LDCs), aimed at boosting African exports to China.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC)

- Inception: The FOCAC began with its first summit in Beijing in 2000.
- Summits: Since then, more summits have been held in Beijing, Ethiopia, Egypt, South Africa, and Senegal.
- Membership: FOCAC includes 53 African countries, representing the entire continent except Eswatini, which maintains diplomatic ties with Taiwan, opposing Beijing’s “One China” policy.
- Purpose: Over the past 24 years, FOCAC has become an effective platform for dialogue, interaction, and cooperation between China and African nations.
- Despite occasional reservations, African countries view the forum as a useful way to strengthen ties with China.
Main Elements of the Beijing Declaration of the Latest Summit
The document, largely influenced by Chinese drafting, is structured into six sections.
- Jointly Negotiated Document: It promotes synergy between China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), Africa’s Agenda 2063, and the UN’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- It also incorporates China’s Global Development Initiative (GDI), Global Security Initiative (GSI), and Global Civilization Initiative (GCI), along with a review and outlook for FOCAC.
- Commitment to Governance and Development: Both China and Africa are committed to enhancing exchanges on governance, modernization, and poverty reduction based on their respective civilizational characteristics.
- China supports Africa’s inclusion in the G20 and both sides stand for a multipolar world, and reforms to strengthen the UN.
- Economic Partnership: China has recognized progress in the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) and is ready to sign a framework agreement for economic partnership.
- China’s Flagship Initiatives: The GDI, GSI, and GCI are embedded in the joint strategy, aimed at fostering comprehensive security and development.
- China supports increased UN funding for Africa’s independent peacekeeping, counterterrorism, and maritime security efforts.
- FOCAC Next Summit: The tenth FOCAC summit is confirmed to be held in 2027 in Congo.
Major Concerns Associated with China- Africa Growing Cooperation
The growing cooperation between China and Africa has led to both opportunities and concerns. Here are some of the major concerns:
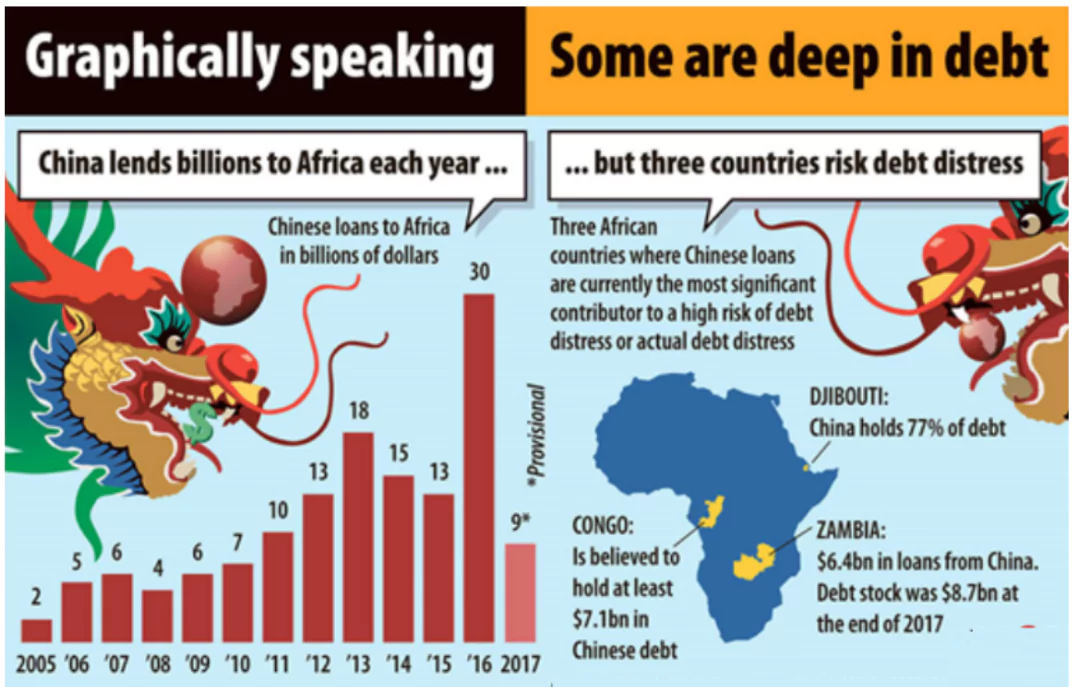
- Debt Dependency: Many African nations have taken on significant debt to finance infrastructure projects under China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), this could lead to “debt-trap diplomacy”.
- Several countries, like Zambia and Djibouti, have faced challenges in managing their debt, raising concerns over financial stability.
- Loss of Sovereignty: If African countries are unable to repay loans, there are concerns that China could take control of strategic assets like ports or mines, threatening national sovereignty.
 China’s increasing economic presence may give it leverage in the political and economic decisions of African countries.
China’s increasing economic presence may give it leverage in the political and economic decisions of African countries.
- Environmental Impact: Many projects, particularly in mining and infrastructure, have been criticized for damaging ecosystems and contributing to deforestation, water pollution, and biodiversity loss.
- Trade Imbalance: Africa’s role in the supply chain often revolves around raw material exports, while value-added industries remain underdeveloped, stunting local economic growth.
- Governance and Transparency Issues: Many deals between African governments and Chinese companies or banks are not transparent.
- This lack of openness raises concerns about corruption and the terms of the agreements, which may not always favor African interests.
- Security Implications: China’s growing economic influence is often accompanied by a rising military presence, such as the establishment of its first overseas military base in Djibouti.
- Surveillance and Data Concerns: Chinese tech companies’ growth in Africa raises concerns over potential Chinese control and surveillance, risking data privacy and security.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Major Concerns Associated with China- Africa Growing Cooperation for India and the World
The growing cooperation between China and Africa has global implications, affecting various regions, including India.
| Basis |
Concern for India |
Concern for World at Large |
| Strategic and Geopolitical Competition |
China’s growing ties are viewed by India as part of its broader “String of Pearls” strategy. |
Increasing Chinese presence may spark competition with other global powers, leading to geopolitical tensions in key regions. |
| Economic Competition and Trade Imbalances |
Africa is a critical supplier of natural resources, Chinese investments could limit India’s access to these materials. |
China’s dominance could affect global markets, driving up prices for critical commodities, and impacting industries worldwide. |
| Debt Diplomacy |
China’s expansive investments dwarf India’s efforts through development aid and educational initiatives, forcing India to rethink its development strategy in Africa. |
Many African nations are already facing rising debt levels, a financial collapse in Africa could have ripple effects on global markets, leading to financial instability in emerging economies. |
| Military Expansion and Security Risks |
China’s military base in Djibouti, strategically located along key sea lanes of communication that are vital for India’s energy imports. |
China’s expanding influence allow it to project naval power into critical sea lanes, including the Suez Canal and the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait. |
| Impact on Global Governance and Institutions |
India has traditionally positioned itself as a leader of the Global South. However, China’s growing influence challenges India’s role and leadership. |
China’s influence may strengthen its ability to build parallel global institutions that challenge Western-dominated frameworks, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or the World Bank. |
Major Steps Taken by India to Boost India- Africa Ties
India has taken several significant steps to strengthen its ties with Africa, recognizing the continent’s strategic importance.
- India-Africa Forum Summit (IAFS): India initiated the India-Africa Forum Summit (IAFS) in 2008 as a platform for dialogue and cooperation between India and African nations.
- Development Assistance and Lines of Credit (LoC): India has become the second-largest issuer of credit to Africa, after neighboring China.
- Over the last ten years, the country has extended $32bn in credit across 42 African nations. India has also opened up 195 project-based lines of credit worth about $12 billion across Africa.
 Focus on Education and Health: India has been supporting the establishment of institutions like the Pan African E-Network, aimed at tele-education and telemedicine.
Focus on Education and Health: India has been supporting the establishment of institutions like the Pan African E-Network, aimed at tele-education and telemedicine.- Duty-Free Tariff Preference (DFTP) Scheme: To support African countries, particularly the Least Developed Countries (LDCs), India has implemented the DFTP scheme, which allows African countries to export their goods to India at reduced or zero tariffs.
- Defense and Security Cooperation: India provides naval training, maritime surveillance support, and anti-piracy assistance to countries like Kenya and Tanzania.
- UN Peacekeeping Operations: India is a key contributor to United Nations peacekeeping missions in Africa.
- Indian forces have been deployed in conflict zones such as Congo, Sudan, and South Sudan, showcasing India’s commitment to Africa’s peace and security.
- Support in Multilateral Platforms: India and Africa share common interests on global issues such as climate change, reforming international institutions like the UNSC, and promoting multilateralism.
- India has consistently supported Africa’s demand for greater representation in global governance structures.
- Focus on Global South Solidarity: India views Africa as a key partner in strengthening the voice of the Global South.
- India and African nations collaborate in platforms such as BRICS, the G77, and the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) to advocate for equitable global governance.
- Pharmaceutical Exports: India is one of the leading suppliers of affordable generic medicines to Africa.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, India supplied vaccines to several African countries as part of its Vaccine Maitri (Vaccine Friendship) initiative.
Way Forward for India in Response to Growing China-Africa Cooperation
- Strengthen Strategic Partnerships: This involves leveraging platforms like the India-Africa Forum Summit (IAFS) to enhance bilateral cooperation.
- Emphasizing areas of mutual interest such as trade, investment, and technology transfer can help India remain a key player in Africa.
- Expand Development Assistance: To counterbalance China’s significant financial investments, India should increase its lines of credit and development aid to Africa.
- By scaling up initiatives, India can build stronger, long-term relationships with African countries and position itself as a preferred partner.
- Enhance Trade Relations: Building on the Duty-Free Tariff Preference (DFTP) scheme, India should work towards increasing trade volumes with African countries.
- Address Debt Diplomacy: India should work with international financial institutions and African nations to develop solutions to the debt challenges exacerbated by China’s investments.
- By offering alternative financial support and debt relief mechanisms, India can help stabilize Africa’s financial situation.
- Support Regional Integration: By engaging with regional organizations and frameworks, India should support African regional integration efforts, such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
- Focus on Capacity Building: Expanding education and training programs, similar to the Pan African E-Network, can solidify India’s role in Africa.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
India must intensify strategic partnerships, enhance aid, and support regional integration to effectively counterbalance China’s growing influence in Africa and solidify its own role.
![]() 11 Sep 2024
11 Sep 2024


 China’s increasing economic presence may give it leverage in the political and economic decisions of African countries.
China’s increasing economic presence may give it leverage in the political and economic decisions of African countries. Focus on Education and Health: India has been supporting the establishment of institutions like the Pan African E-Network, aimed at tele-education and telemedicine.
Focus on Education and Health: India has been supporting the establishment of institutions like the Pan African E-Network, aimed at tele-education and telemedicine.