China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), popularly known as the “artificial sun”, has achieved a groundbreaking advancement in nuclear fusion research.
- It successfully exceeded the Greenwald Limit, marking a breakthrough in plasma confinement and density.
The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) Reactor

- EAST is a tokamak, a donut-shaped device that uses powerful magnetic fields to confine and control hot plasma.
- Location: Hefei, China
- Achievement:
- World leader in experimental fusion reactors and has repeatedly set records for sustained high-temperature plasma operation.
- In 2025, EAST achieved stable plasma at over 100 million°C for more than 1,000 seconds (a world record at the time).
- Role: It serves as a key testbed for technologies that will support larger projects like ITER (the international experimental reactor under construction in France).
The Greenwald Limit
- The Greenwald Limit is an empirical rule discovered in 1988 by physicist Martin Greenwald.
- Empirical means it is based on observations, not a strict fundamental limit like the speed of light.
- It sets a practical upper limit on how dense the plasma can be before it becomes unstable and escapes magnetic confinement, damaging the reactor.
- Importance:
- Higher plasma density is desirable because fusion power increases dramatically with density (roughly proportional to the square of density).
- Overcoming this limit has been a major goal in fusion research.
Exceeding the Greenwald Limit
- EAST maintained plasma density 1.3–1.65 times the Greenwald Limit.
- Usual operational range: 0.8–1.0.
- Significance:
-
- First validation of a density-free regime in a major superconducting tokamak.
- Brings fusion closer to practical, limitless clean energy.
What is Nuclear Fusion?
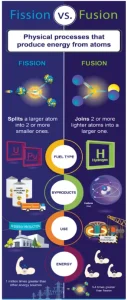
- Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the sun and stars.
- Nuclear fusion occurs when two light atomic nuclei (usually isotopes of hydrogen) combine under extreme heat and pressure to form a heavier nucleus, releasing enormous energy.
- Fusion vs Fission: Unlike nuclear fission (used in current power plants), fusion produces minimal radioactive waste and no greenhouse gases, offering a clean, virtually unlimited energy source.
- Challenges: However, achieving controlled fusion on Earth has been challenging for over 70 years.
- Reactors must heat plasma (the super-hot, fourth state of matter) to millions of degrees while confining it long enough for fusion to occur.
Advantages of Nuclear Fusion
- Near-limitless Fuel Supply: Deuterium is abundant in seawater; tritium can be bred inside reactors.
- No long-lived Radioactive Waste: Produces mostly short-lived waste and inert helium gas (unlike fission’s long-term high-level waste).
- Safety: No risk of meltdown; no runaway chain reaction.
- Clean Energy: Zero carbon emissions during operation.
- Energy Density: Millions of times higher per unit mass than fossil fuels.
![]() 13 Jan 2026
13 Jan 2026



