The Drugs Consultative Committee (DCC) has recommended a total ban on two antibiotics: chloramphenicol and nitrofurans.
DCC’s Decision and FSSAI Actions
- The DCC’s decision aligns with the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
- In 2018, FSSAI banned the use of several antibiotics and veterinary drugs, including nitrofurans and chloramphenicol, in processing meat, poultry, eggs, seafood, and fishery products.
- The FSSAI notification set strict residue limits for these antibiotics:
- 0.001 milligrams per kilogram for most antibiotics.
- 0.0003 milligrams per kilogram specifically for chloramphenicol.
- The DCC’s recommendation needs final approval from the Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB).
- DTAB is the highest authority on drug regulations in India
- Scope of the Ban:
- The ban is specifically for the use of these antibiotics in food animal production systems.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Reasons for the Ban on Chloramphenicol and Nitrofurans
- Rejected Shrimp Exports:
- Chloramphenicol and nitrofurans are banned in shrimp farming but are still being detected.
- This leads to rejections of shrimp exports, especially to strict markets like EU, US and Japan.
 Public Health Risk:
Public Health Risk:-
- Misuse of these antibiotics in animals can cause development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the global health issue of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
- This can make it harder to treat human infections.
- Protecting Important Medicines:
- Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used in various human infections.
- Banning its use in animals helps preserve its effectiveness for human medicine.
- Aligning with Food Safety Standards:
- FSSAI already banned these antibiotics in meat, poultry, eggs, and seafood.
- This ban strengthens existing regulations on antibiotic residues in food products.
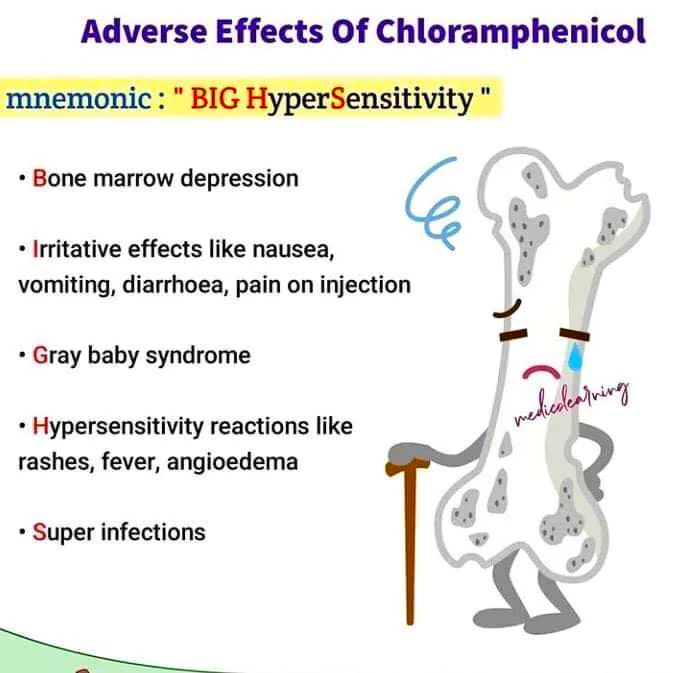
About Chloramphenicol
- Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic
- Recognized by WHO as a Highly Important Antimicrobial (HIA).
- Used for Treating:
- Superficial eye infections.
- Enteric fever.
- Typhoid fever.
- Central nervous system infections like acute bacterial meningitis.
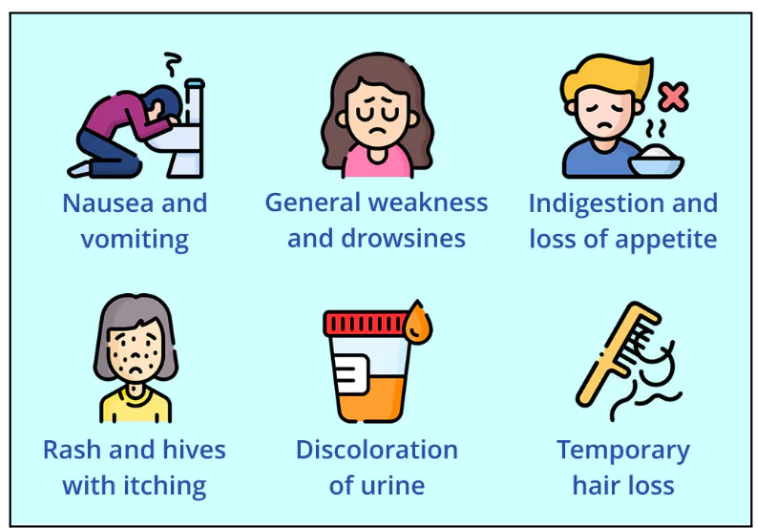
About Nitrofuran
- Nitrofurans are a group of drugs.
- They are mainly used as antibiotics or antimicrobials.
- Classified by WHO as Important Antimicrobials (IA).
- Application: Nitrofurantoin, a common nitrofuran derivative, is used for treating urinary tract infections.
- Banned: Banned in food-producing animals in many countries, including parts of the European Union and the USA.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Benefits and Challenges of Banning Chloramphenicol and Nitrofurans in Food Animal Production Systems
| Benefit |
Description |
| Reduced risk of antibiotic resistance |
Misuse in animals can contribute to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a threat to human health. A ban could help to curb this problem. |
| Improved food safety |
Residues in meat, poultry, and seafood can pose a health risk to consumers. A ban could help to ensure that these products are safe to eat. |
| Expanded export opportunities |
Meets the requirements of export markets that have already banned these antibiotics. A ban in India could help to meet the requirements of these export markets. |
| Challenge |
Description |
| Impact on animal health |
Can be effective antibiotics for treating infections in animals. A ban could make it more difficult to control these infections. |
| Economic impact on farmers |
May need to find alternative treatments, which could be more expensive. |
| Enforcement |
Requires effective measures to ensure compliance. |
Antibiotics
- Antimicrobial Drugs are commonly known as Antibiotics.
- Effective against bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites.
- Uses:
- Treat infections in humans and animals.
- Sometimes used to protect plants from infections.
- Importance:
- Essential in modern medicine for controlling and eliminating various microbial diseases.
|
![]() 6 Jul 2024
6 Jul 2024
 Public Health Risk:
Public Health Risk: