Context
Last week, a team of climate scientists called World Weather Attribution (WWA) reported that heat waves across Asia, from the west to the southeast, had been rendered nearly 45-times more likely by climate change.
- Just a couple of decades ago, the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) argued that individual weather events could not be attributed to climate change, researchers now have been able to attribute some individual extreme events to climate change.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
- Refers: It is a United Nations body for assessing the science related to climate change.
- IPCC BureauFormation: IPCC was created by the United Nations Environment Programme (UN Environment) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1988
- Member states: It has 195 Member countries currently including India
- Objective: It was created to provide policymakers with regular scientific assessments on climate change, its implications and potential future risks, as well as putting forward practical adaptation and mitigation options.
- Governing Structure: The IPCC functions with a Secretariat and Plenary at the top.
- IPCC Bureau: It produces the full assessment report, synthesis reports, the methodology reports, and a special report.
- Working Group I: It deals with The Physical Science Basis of Climate Change
|
About Extreme Weather Events
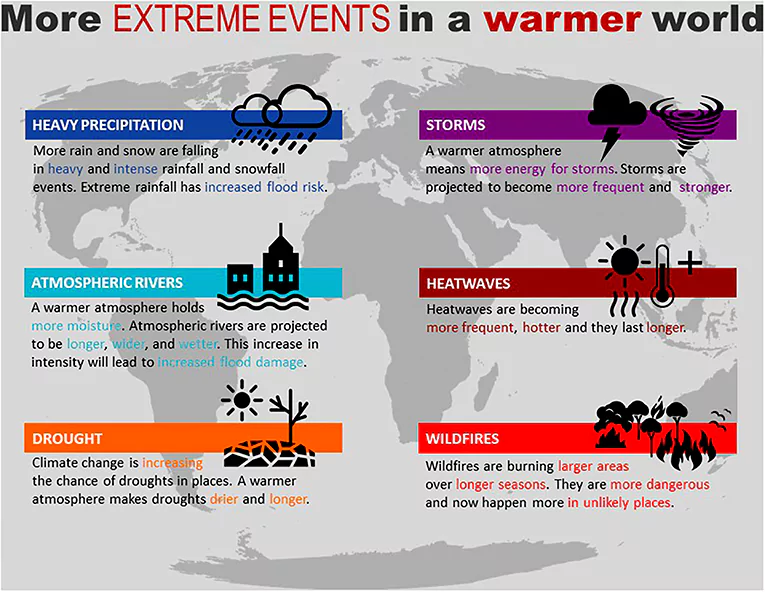
- Definition: When the weather conditions show significant differences than the usual weather, this is termed as extreme weather or severe weather.
- Time Duration: The extreme weather conditions may last for a while or sometimes it may take just one or two days to become normal.
- Impact: According to the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO), extreme weather, climate and water-related events caused 11,778 reported disasters globally, leading to more than two million deaths and USD 4.3 trillion in economic losses between 1970 and 2021.
- Over 90 per cent of the reported deaths worldwide occurred in developing countries.
- In India, 573 disasters occurred between 1970 and 2021 that claimed 1,38,377 lives.
- Concerns:
- Exercise to Pick Extreme Events to Attribute: Scientists used multiple approaches in their attribution exercise to answer the same question, and have added that the differences between them are immaterial.
- Difficult to Attribute: According to Climate Change: Evidence and Causes, a jointly produced publication of The US National Academy of Sciences and The Royal Society, it is quite difficult to attribute any particular extreme weather event to climate change.
- This is because there are multiple factors, like patterns of natural climate variability, such as El Niño and La Niña, that contribute to such events.
- The actual impacts of extreme events depend not only on the hazard or the extreme event but also on the vulnerability and the exposure of the population affected.
Impact of Climate Change on Extreme Weather Events
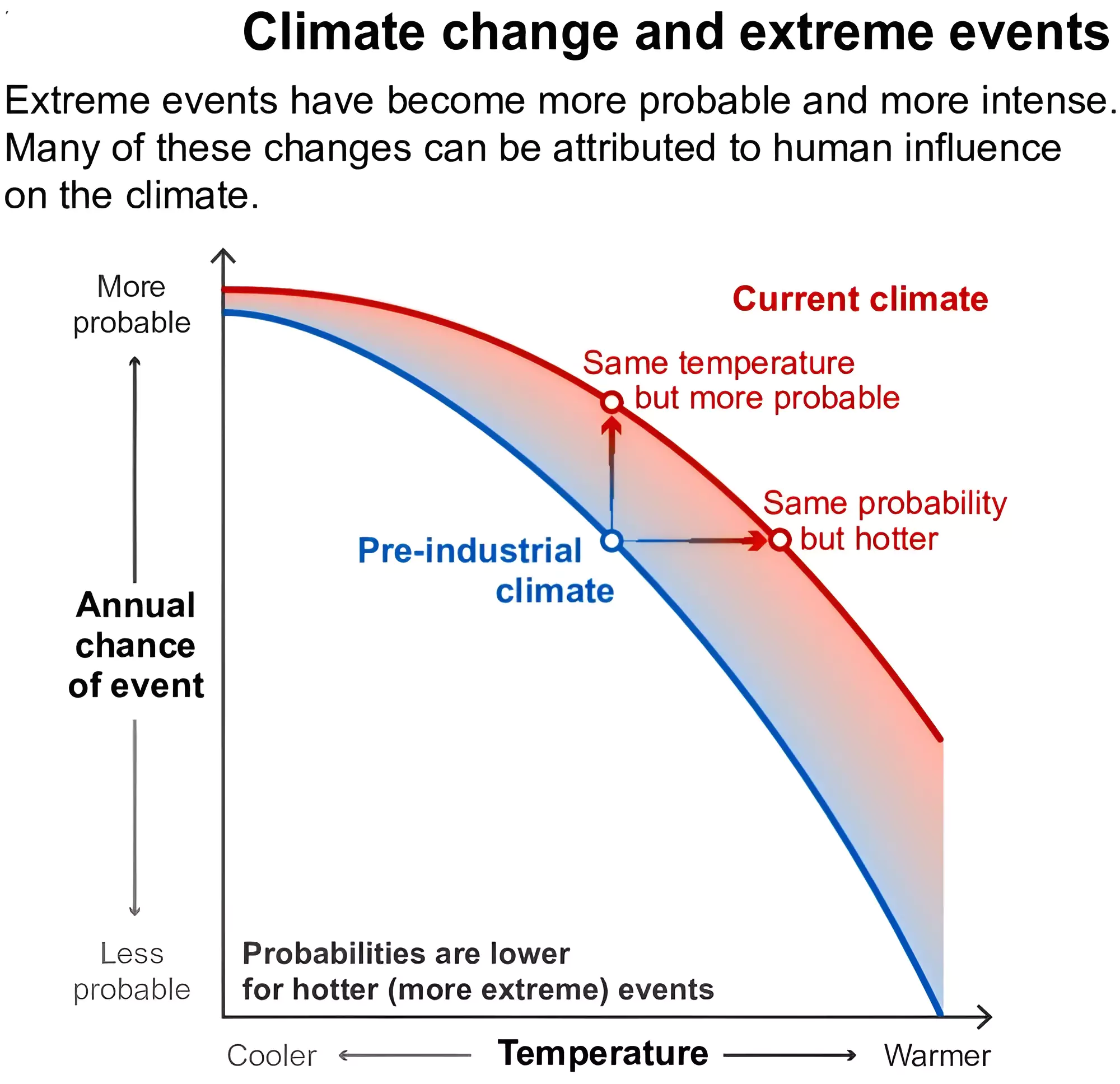
- Extreme Temperature: The average global temperature on Earth has increased by at least 1.1 degree Celsius since 1850, primarily due to human activities that have released unprecedented levels of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- The rise in the temperatures has resulted in more frequent and more intense extreme weather events across the world. These events include heat waves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires.
- Heat Waves: Climate models show that heat waves might become about 12 times more frequent by 2040s due to climate change.
- Loss & Damage: While no formal cost-benefit analysis of an attribution exercise has been reported, many experts have argued that attributions are critical for the ‘loss and damage’ process.
Loss and Damage Fund
Loss and Damage Fund was proposed during COP-27 in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt in 2022. It will operate through an independent secretariat located at the World Bank and has received commitments of at least $450 million from various countries. However, a significantly larger sum is necessary to fulfill its intended purpose.
- Aims: The loss and damage fund provides support to less affluent nations (such as Small Island Nations like Tonga, Fiji) that have contributed minimally to climate change but are disproportionately vulnerable to severe climate-related incidents.
- Based on the Polluters Pay Principle: This principle holds accountable entities responsible for environmental damage, making them liable for expenses related to remedial measures and compensating those affected by their actions.
- Interim Host and Operational Period: The World Bank will serve as the “interim host” for the fund for a duration of four years, operating in line with the principles of the UNFCCC and the Paris Agreement.
- Eligibility and Contributions:
-
- All developing nations can apply for funds, and every country has been “invited” to contribute voluntarily.
- A specific allocation has been set aside for Least Developed Countries and Small Island Developing States.
|
Way Forward
- Adequate Financing: There is a need to take stock of the international finance aspects of adaptation, mitigation, and L&D.
- Responsibility: Governments should consider an agreement on historical responsibilities to fund developing countries and close adaptation gaps, build adaptation capacity, and finance mitigation for the global good.
- Analysis: The real world is severely resource-constrained and needs a cost-benefit analysis based on a clear role for attribution in the overall climate action landscape.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 23 May 2024
23 May 2024


