India’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels are expected to increase by 4.6% in 2024, the highest among major economies, according to a new report by Global Carbon Project.
Key findings of the Report
- Highest Emission: India’s CO2 emissions from fossil fuels are expected to rise by 4.6% in 2024, the highest among major economies.
- Global Emission: Global CO2 emissions are set to reach a record 37.4 billion tonnes in 2024, a 0.8% increase from 2023.
- Largest contributions to global fossil CO2 emissions in 2023: China (31%), the USA (13%), India (8%), and the European Union (7%)
- These four regions account for 59% of global fossil CO2 emissions, while the rest of the world contributed 41%.
- Global Warming Warning: At this rate, there’s a 50% chance that global warming could exceed 1.5°C in approximately six years.
- Land and ocean CO2 sinks combined took around half of the total CO2 emissions
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Global Carbon Project
- The Global Carbon Project (GCP) is a non-governmental organization that studies the carbon cycle and other biogeochemical cycles.
- The GCP was established in 2001 by the Earth System Science Partnership (ESSP).
- It’s a core project of Future Earth and a research partner of the World Climate Research Programme.
- The GCP’s work is supported by hundreds of volunteer scientists.
- The GCP’s goals include:
- Quantifying greenhouse gas emissions: The GCP studies the causes and amounts of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Understanding the carbon cycle: The GCP studies the carbon cycle and other biogeochemical cycles, including the interactions between humans and the biophysical system.
- Supporting policy and action: The GCP’s research supports policy debate and action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- The GCP’s projects include:
-
- Global Carbon Budget: An annual update on carbon budget and trends
- Methane Budget: A regular update on the global methane budget and trends
- Global Carbon Atlas: A platform to explore and visualise data on carbon fluxes
Global warming
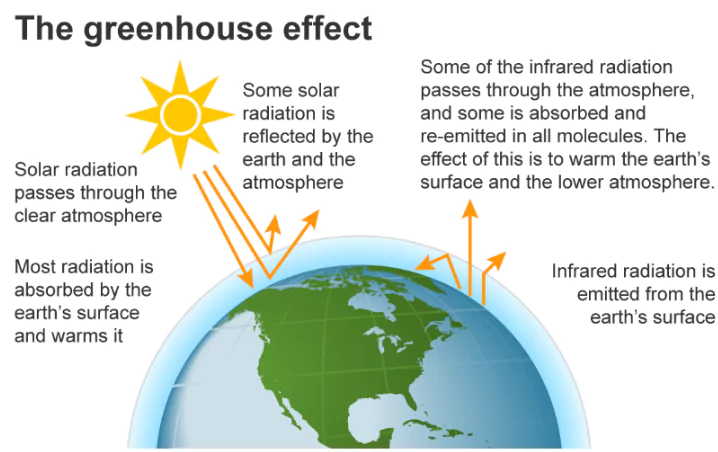
- Global warming is a pressing environmental issue that has far-reaching implications for the Earth’s climate system.
- It refers to the long-term increase in average temperatures due to the accumulation of greenhouse gasses (GHGs) in the atmosphere.
- This rise in temperature has several effects on global climate patterns, including increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, melting glaciers and polar ice caps, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems.
|
CO2’s Role in Global Warming
- Primary Driver: CO2 is responsible for approximately 70% of global warming.
- Radiative Forcing (RF): CO2 has the highest positive RF among climate drivers, as per the IPCC 2013 report.
- Increase Since Industrial Revolution:
- CO2 levels have increased by 50% since 1750.
- Now, atmospheric CO2 is 150% of pre-industrial levels (NASA data).
Reasons for CO2’s Dominant Impact
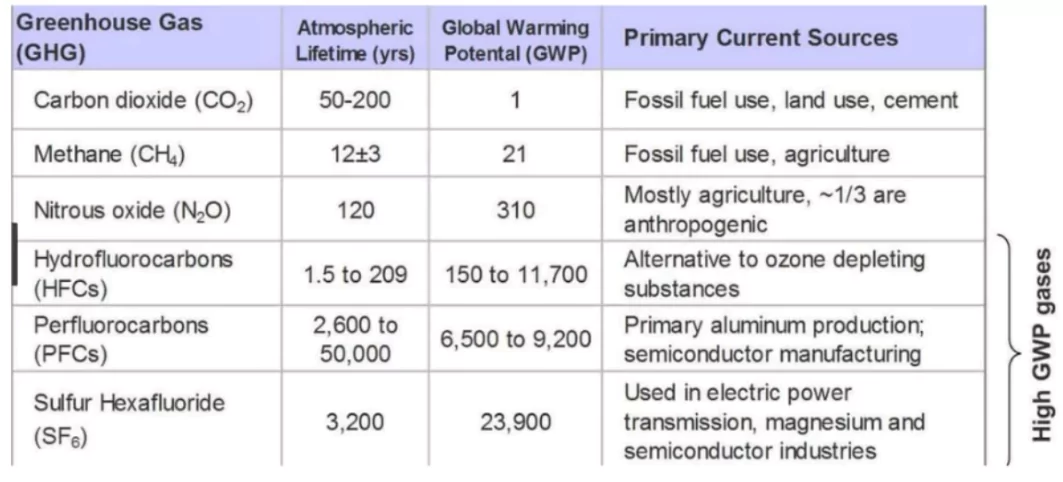
- Abundance: CO2 is more abundant in the atmosphere compared to CH4 and HFCs.
- Longevity: CO2 remains in the atmosphere longer:
- CH4: Leaves the atmosphere in about a decade (converts to CO2).
- CO2: 40% stays for 100 years, 20% for 1000 years, and 10% for up to 10,000 years.
- N2O: Stays for about a century.
- Potency vs. Impact:
- CH4 is 80 times more potent than CO2, and HFCs are thousands of times more powerful, but CO2’s sheer volume makes it the most impactful.
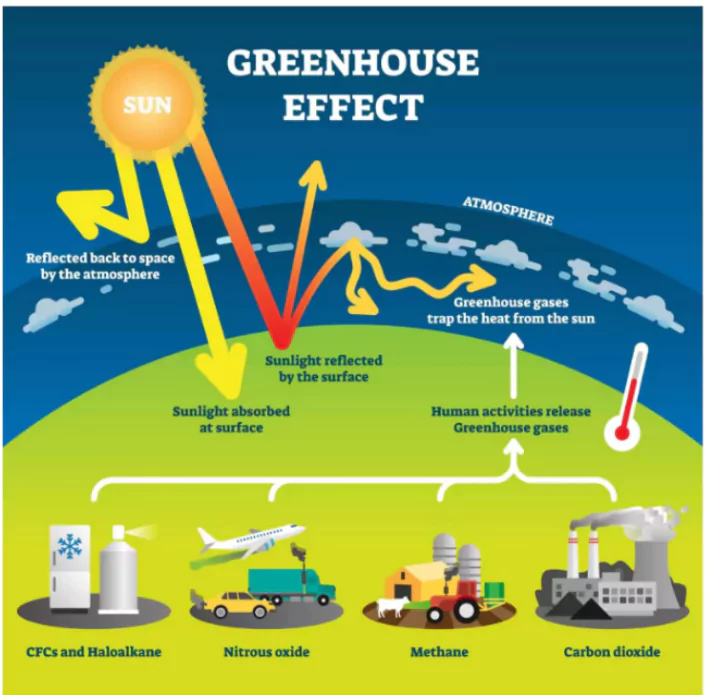
About Greenhouse Gases
- Greenhouse gases are a type of atmospheric gases that have the capability of raising the surface temperature by absorbing solar radiation.
- Types: Carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapor.
- Effects: The greenhouse effect, which is caused by greenhouse gases, is a natural phenomenon that is necessary for life to thrive on earth.
- However, if the greenhouse effect is amplified more than that is necessary, it leads to a phenomenon known as global warming.
- Sources: The amount of carbon dioxide and other radiation absorbing gases have increased due to anthropogenic activities such as industrial and vehicular emissions, paddy cultivation, fossil fuel extraction etc.
- Excessive emission of these greenhouse gases reduces the ability of the earth to sequester them naturally, leading to global warming.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
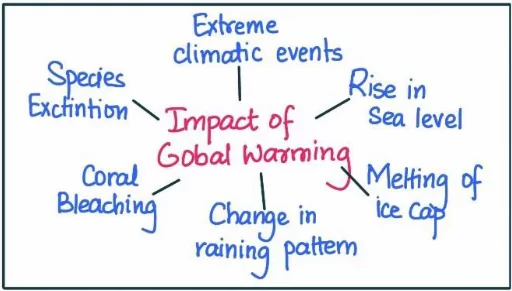
Effects of Greenhouse Gases
- Warming of Earth: Due to greenhouse gases, the sun’s heat gets trapped in Earth’s atmosphere. This process makes Earth much warmer.
- Melting of Polar Ice: Due to rise in global temperatures, polar ice gets melted. This could affect Earth’s climate drastically.
- Depletion of Corals: Rise in sea surface temperatures could harm the survival of corals, which are vulnerable to hot temperatures.
- Rise in Sea Levels: The melting of polar ice could lead to rise in sea levels, which could inundate low lying coastal areas.
- Climate Vagaries: Climate change, which is a consequence of the greenhouse effect, will create vagaries in climate. It could lead to disasters such as cyclones, floods, landslides etc.
Greenhouse Gas Control Strategies
- Electric Vehicles: It will reduce emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide.
- Promoting Renewable Energy: Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, biofuel, tidal etc must be promoted to reduce dependency on coal.
- Afforestation: Growing trees will lead to sequestration of carbon.
- This will keep the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in check.
- Climate-friendly Agriculture: Crops that emit methane must be avoided. If it is not possible, then methane footprint must be reduced.
- Geoengineering: The method such as carbon capture allows artificial reduction of carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere.
![]() 18 Nov 2024
18 Nov 2024





