Minority Rights Day, celebrated on December 18 annually, emphasizes the importance of protecting the rights of minorities.
About Minorities
- The term ‘minority’ generally refers to groups differing in religion, language, ethnicity, or culture from the majority population.
- While the Indian Constitution uses the term in several places, it does not explicitly define ‘minority.’
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Minority Rights Day
- The UN General Assembly adopted the declaration on the ‘Rights of Persons Belonging to National, Ethnic, Religious, and Linguistic Minorities’ on December 18, 1992, which is globally observed as Minority Rights Day to emphasize the importance of protecting minority rights.
- Theme of 2024 Minority Rights Day: “Promoting Diversity and Protecting Rights”
|
- Recognition of Minority: The Supreme Court has consistently held that minorities should be identified at the State level.
- For example, Hindus are a minority in Punjab, Kashmir, and northeastern states and can enjoy minority rights in these regions.
- The debate on minority rights should be lifted from its current framework of communalism versus secularism and placed in the theoretical field of democracy and substantive equality.
- Notably, Franklin D. Roosevelt asserted that “no democracy can survive without recognizing the rights of minorities.”
- Protection of Diversity: The Indian Constitution recognizes that universal individual rights are insufficient in a multicultural society.
- Instead, collective rights aim to create an environment conducive to the flourishing of minority cultures.
- Judicial Interpretation: Recent judgments, such as in the Aligarh Muslim University (2024) case, affirm the constitutional guarantee of minority rights as a facet of equality and non-discrimination.
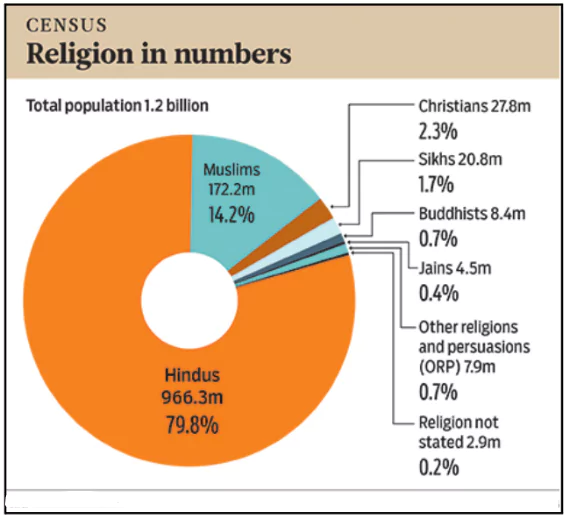 Minorities Recognised in India: In 2014, the Jain community was added to the list of officially recognized minority communities in India.
Minorities Recognised in India: In 2014, the Jain community was added to the list of officially recognized minority communities in India.- This brought the total number of recognized minority communities to six:
- Muslims
- Christians
- Sikhs
- Buddhists
- Parsis
- Jains
Constitutional Provisions for Rights of Minorities
- Articles Related to Minority Rights:
- Article 29(1): Grants minorities the right to conserve their language, script, and culture.
- Article 30: Provides religious and linguistic minorities the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- Articles 350A & 350B: Ensure primary education in the mother tongue and appoint a Special Officer for linguistic minorities.
- Article 30(2): Prohibits the State from discriminating against minority institutions when granting aid.
- Personal Laws and Customary Practices: The Constitution protects religion-based personal laws, such as those of the Nagas, under customary practices.
- Institutional Support: Establishment of bodies like the National Commission for Minorities and the National Commission for Minority Educational Institutions to address minority issues.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Institutional Framework for Minorities in India
| Body |
Objective |
| National Commission for Minorities |
To safeguard the interests of minority communities, investigate and monitor matters relating to their social, economic, and educational development. |
| National Commission for Minority Educational Institutions |
To ensure the protection of the rights of minority educational institutions as enshrined in Article 30 of the Indian Constitution. |
| National Minorities Development and Finance Corporation (NMDFC) |
To provide financial assistance to minority communities for various developmental activities, including education, business, and skill development. |
| Maulana Azad Education Foundation (MAEF) |
To promote and develop education among minority communities, especially in higher education. |
| State Minority Commissions |
To address the specific needs and grievances of minority communities at the state level. |
| Waqf Boards |
To manage and administer the Waqf properties, ensuring their proper utilization for the benefit of the Muslim community. |
Challenges in Fulfilling Minority Rights
- Lack of a Clear Definition: The absence of a constitutional definition of ‘minority’ creates ambiguity and inconsistencies in implementation.
- Majoritarian Pressures: Minority rights often face resistance in a predominantly majoritarian societal framework, impacting their effective realization.
- State Regulation: While minority institutions enjoy autonomy, the government enforces regulations to maintain standards, which sometimes lead to conflicts over administrative control.
- Socioeconomic Inequalities: Many minority groups face systemic disadvantages that hinder access to education, employment, and social opportunities.
Landmark Cases Related to Minority Rights
- TMA Pai Foundation vs. State of Karnataka (2002): Upheld the rights of minority institutions to admit students of their choice, subject to reasonable restrictions.
- Clarified the extent of state regulation over minority institutions.
- St. Stephen’s College vs. University of Delhi (1992): Affirmed the right of minority institutions to maintain their character and autonomy.
- Recognized the right of minority institutions to set their own admission criteria, including reservation policies.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Government schemes and programs for minorities in India
| Category |
Scheme/Program |
Objective |
| Educational Empowerment |
Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF) |
Support for higher studies, particularly in science and technology fields. |
| Padho Pardesh |
Subsidizing interest on educational loans for overseas studies. |
| Free Coaching and Allied Schemes |
Free coaching for competitive exams. |
| Nai Udaan |
Financial assistance for students preparing for UPSC, SSC, and state PSC exams. |
| Economic Empowerment |
Seekho aur Kamao |
Learn-and-earn program focusing on skill development and livelihood opportunities. |
| USTTAD (Upgrading Skills and Training) |
Upgrading traditional arts and crafts to enhance employability. |
| Nai Manzil |
Providing skill development training and placement assistance for minority youth. |
| Concessional Credit through NMDFC |
Offering financial assistance to minorities through the National Minorities Development & Finance Corporation (NMDFC). |
| Infrastructure Development |
Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK) |
Improving socio-economic conditions and infrastructure in minority-concentrated areas. |
| Special Needs |
Nai Roshni |
Leadership development for minority women. |
| Hamari Dharohar |
Preserving and promoting the cultural heritage of minority communities. |
| Jiyo Parsi |
Supporting the Parsi community to increase its population through advocacy and medical assistance. |
| Waqf Management |
Qaumi Waqf Board Taraqqiati Scheme |
Computerization of waqf records for better transparency and management. |
|
Shahari Waqf Sampatti Vikas Yojana |
Development of urban waqf properties to enhance income for community welfare activities. |
| Research and Support |
Corpus Fund to Maulana Azad Education Foundation (MAEF) |
Supporting educational initiatives for minorities. |
|
Equity to NMDFC |
Strengthening financial institutions that support minority communities. |
| Grant-in-Aid to State Channelizing Agencies |
Supporting state-level development programs for minorities. |
Conclusion
- Minority rights are not just safeguards for vulnerable groups but are also essential for upholding democratic principles and equality.
- The Constitution, through Articles 25-30, aims to ensure the preservation of diversity while maintaining a balance between autonomy and regulation.
- However, challenges like ambiguity in definition, societal resistance, and administrative conflicts must be addressed to fully realize the vision of equality for all communities
![]() 18 Dec 2024
18 Dec 2024

 Minorities Recognised in India: In 2014, the Jain community was added to the list of officially recognized minority communities in India.
Minorities Recognised in India: In 2014, the Jain community was added to the list of officially recognized minority communities in India.