Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: CTBT; Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, Nuclear Supplier Group (NSG), NPT, UNGA, Treaty on Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, P-5 Countries, and India’s Nuclear Policy-No first use.
Relevancy for Mains: India and the CTBT, India’s Nuclear Doctrine, ans Features of India’s Nuclear Policy. |
Treaty in Turmoil
- Russia has suspended participation in the New START nuclear arms reduction treaty with the United States in February 2023, after accusing the West of being directly involved in attempts to attack its strategic air bases.
- Further, Russia could look at revoking ratification of the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (CTBT) as the United States had signed, but not ratified, it.
What is CTBT?
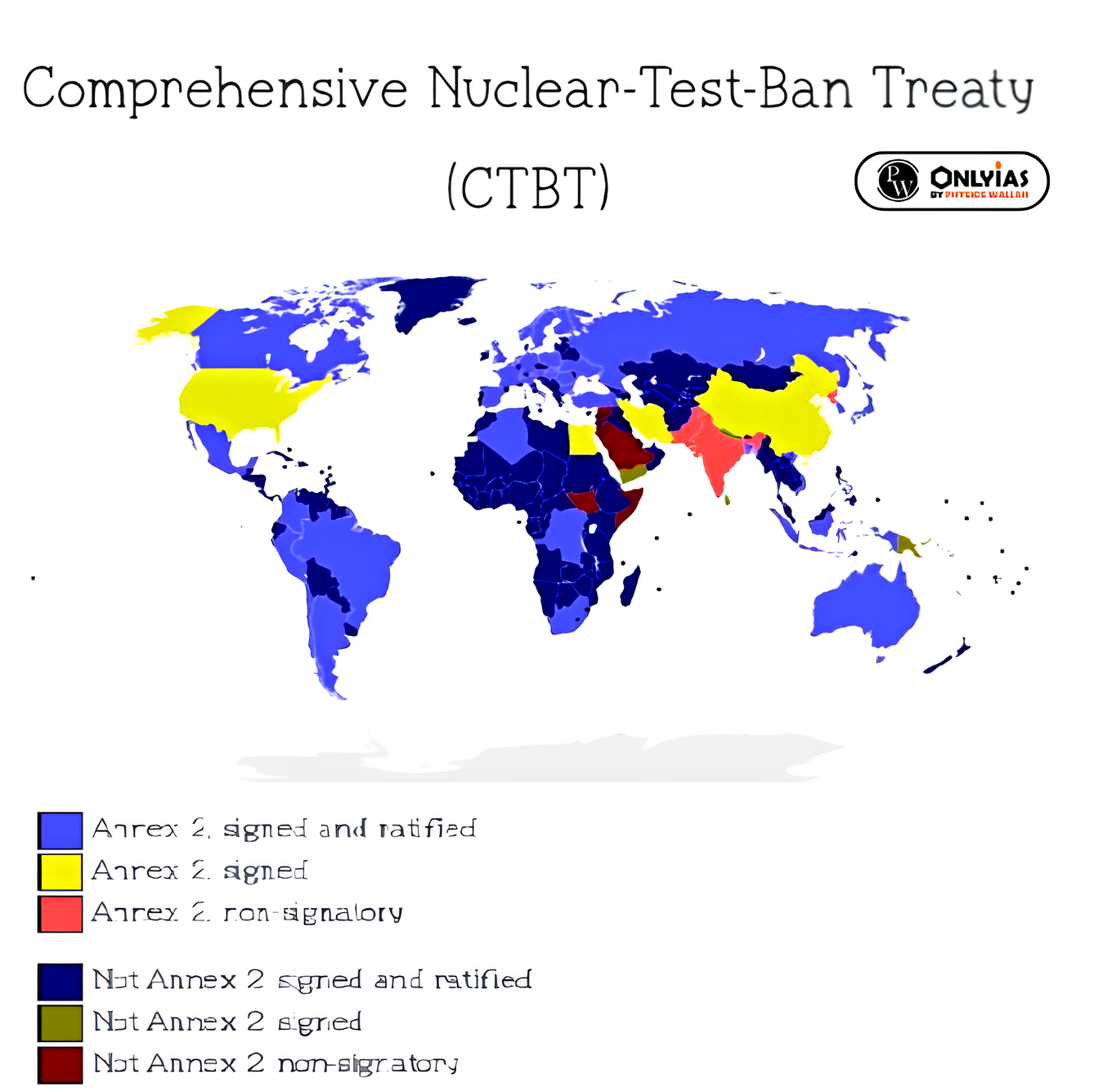
- The CTBT is a multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions, whether for military or peaceful purposes. It was negoitatied at the Conference on Disarmament in Geneva.
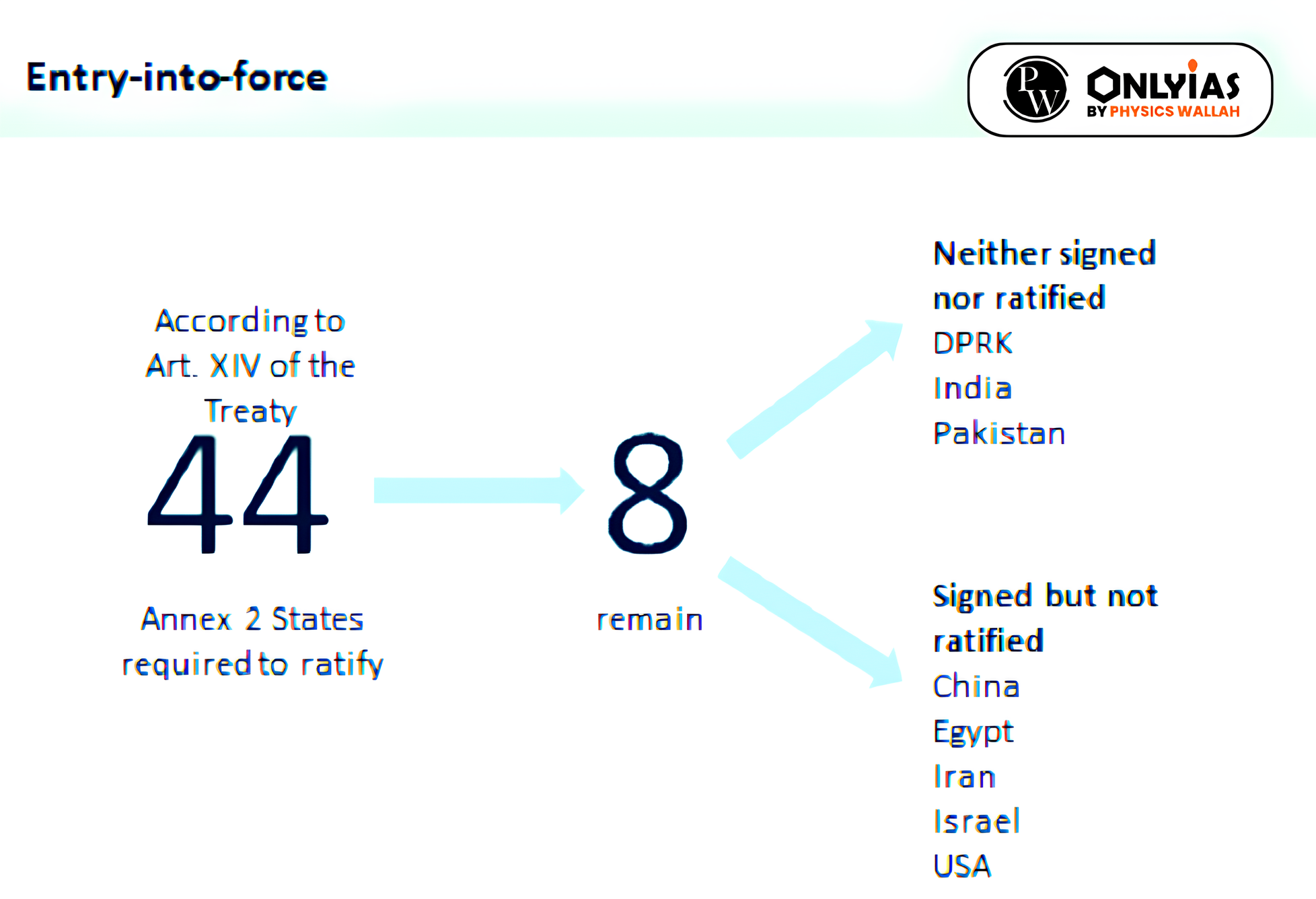
- The CTBT has been signed by 187 countries and ratified by 178 but cannot go into force until eight countries have signed and ratified it.
- China, Egypt, Iran, and Israel have signed CTBT but not ratified it. North Korea, India and Pakistan have not signed. While Russia ratified the agreement in 2000, the US is still to do so.
- While the US signed CTBT but did not ratify the treaty, it has observed a moratorium on nuclear weapon test explosions since 1992 that it has no plans to abandon.
- When the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) adopted the CTBT in September 1996, 2048 nuclear explosions were already conducted worldwide. 18 years later, the number of explosions has further increased to 2055.
- Given this, the CTBT has an important role in ensuring a world where nuclear weapons tests are barred and thus constrain the development of new nuclear weapons and new nuclear weapon countries.
Also read: UNGA’s 78th Session: Promoting Peace, Prosperity, and Sustainability
Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO)
- IT was set up in 1996 with its headquarters in Vienna, Austria.
- It is an interim organization tasked with building up the verification regime of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) in preparation for the Treaty’s entry into force, as well as promoting the Treaty’s universality.
|
What are the implications if Russia move out from CTBT?
- Global Disarmament: Since the CTBT, 10 nuclear tests have taken place. India conducted two in 1998, Pakistan also two in 1998, and North Korea conducted tests in 2006, 2009, 2013, 2016 (twice) and 2017, according to the United Nations. It would be a big setback to the Nuclear disarmament movement.
- Nuclear Arms Race: This move would enable Russia to build and deploy more nuclear weapons targeting its adversaries without the treaty’s constraints. Both sides could get sucked into a dangerous arms race.
- Russia-Ukraine Crisis: The missile attacks against each other by both Russia and Ukraine have also led to a growing escalation of mutual suspicion. The present Russian decision has only aggravated the crisis.
- Russia-West Relations: The Russian decision can be described as symbolic and strategic in nature. It wants to pressurize the West by sending an ambiguous message strategically. Russia has tried not to appear aggressive and has attempted to put all the blame on the US this will further erode Russia and West ties.
- Global Politics and Security: Taking a cue from the present stand-off between Russia and the United States over the current nuclear question, many countries like North Korea, Pakistan, Turkey, Iran, and China may go for further proliferation of nuclear weapons without any scrutiny..
- Undermining Future Agreements: Arms control has been a progression from one treaty to the next. If Russia revokes its ratification. it will leave the world without a common starting point for future efforts.
- For example, the Treaty on Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) did not find support from any of the P-5 countries.
What is the Indian viewpoint on the Global Nuclear Disarmament issue and the NPT and CTBT?
- Complete Disarmament: India has consistently advocated global nuclear disarmament since the concept’s inception in the United Nations.
- Two-Front Nuclear War: India, faced with two nuclear neighbors (Pakistan and China) with one declaring its nuclear arsenal as India-specific, reluctantly had to become a nuclear weapon state.
- Universal Non-discriminatory and verifiable Treaty: India remains committed to negotiating a universal, non-discriminatory and internationally and effectively verifiable treaty banning the production of fissile material for nuclear weapons or other nuclear explosive devices, one that considers India’s national security interests.
- Delinking Disarmament and Non-Proliferation: In 1965, India was a member of the eighteen nation disarmament committee (ENDC) that advocated for delinking disarmament and non-proliferation.
- India opposed the signing of the NPT (treaty of Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons which it views as discriminatory (dividing the world into Nukes haves and haves not).
- In 1988, India Proposed a Comprehensive Proposal for complete Universal disarmament (Rajiv Gandhi Action Plan)- to the UN General Assembly Special Session on Disarmament.
India and the CTBT
- India’s stand on the CTBT is principled. India has declared that it would be unable to sign and ratify the CTBT in its discriminatory form.
- However, India has pledged to continue its voluntary and unilateral moratorium on further nuclear testing.
- The Post 1998 Pokhran test India stipulated its Nuclear doctrine in 2003 and reiterated its commitment to complete disarmament.
India’s Nuclear Doctrine
- A nuclear doctrine states how a nuclear weapon state would employ its nuclear weapons during peace and war.
- India’s nuclear doctrine is an important variable determining nuclear stability in South Asia- Because the doctrine is considered restrained.
Salient Features of India’s Nuclear Policy:
- Building and maintaining a credible minimum deterrence;
- A posture of “No First Use” nuclear weapons will only be used in retaliation against a nuclear attack on Indian territory or on Indian forces anywhere;
- Massive Retaliation: Nuclear retaliation to a first strike will be massive and designed to inflict unacceptable damage.
- Control and Command: Nuclear retaliatory attacks can only be authorised by the civilian political leadership through the Nuclear Command Authority.
- Non-use of nuclear weapons against non-nuclear weapon states;
- However, in the event of a major attack against India, or Indian forces anywhere, by biological or chemical weapons, India will retain the option of retaliating with nuclear weapons;
- A continuance of strict controls on export of nuclear and missile related materials and technologies, participation in the Fissile Material Cutoff Treaty negotiations, and continued observance of the moratorium on nuclear tests.
|
India and the NPT
- The UN Security Council adopted unanimous resolution 1887 on nuclear non-proliferation which among other actions called on states not party to the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) to join it.
- However, India responded to the resolution by declaring categorically that it would not join the NPT as a non-nuclear weapon state since nuclear weapons constitute an integral part of India’s security. To date, the NPT recognises only the five permanent members of the UN Security Council (US, Russia, UK, France and China) as nuclear weapon powers.
- India’s stated position on the NPT is that it “cannot accept externally prescribed norms or standards on matters within the jurisdiction of its Parliament or which are not consistent with India’s constitutional provisions and procedures, or are contrary to India’s national interests or infringe on its sovereignty.”
- India and Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW):India did not participate in the negotiations on the TPNW and did not sign it.
- India believes that this Treaty does not constitute or contribute to the development of customary international law; nor does it set any new standards or norms.
What is the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)?
- It entered into force in 1970 with following objectives:
- Prevent spread of nuclear weapons and technology proliferation.
- Promote cooperation in peaceful use of nuclear energy.
- Complete nuclear disarmament.
- It is signed and ratified by 190 countries.
- Non-Parties: India, Israel, North Korea, Pakistan, and South Sudan.
|
Conclusion
Considering the present pessimistic environment, the Russian revocation of the Treaty may not seem shocking or startling. Still, it is unfortunate for arms control efforts.
In this regard, India supports the commencement of negotiations on a comprehensive Nuclear Weapons Convention in the Conference on Disarmament, which is the world’s single multilateral disarmament negotiating forum working on the basis of consensus.
Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW): It was entered into force on 22 January 2021
- IT includes a comprehensive set of prohibitions on participating in any nuclear weapon activities.
- These include undertakings not to develop, test, produce, acquire, possess, stockpile, use or threaten to use nuclear weapons.
|
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
What is/are the consequence/consequences of a country becoming the member of the ‘Nuclear Suppliers Group’?
- It will have access to the latest and most efficient nuclear technologies.
- It automatically becomes a member of “The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)”.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: A |
![]() 7 Oct 2023
7 Oct 2023


