Context
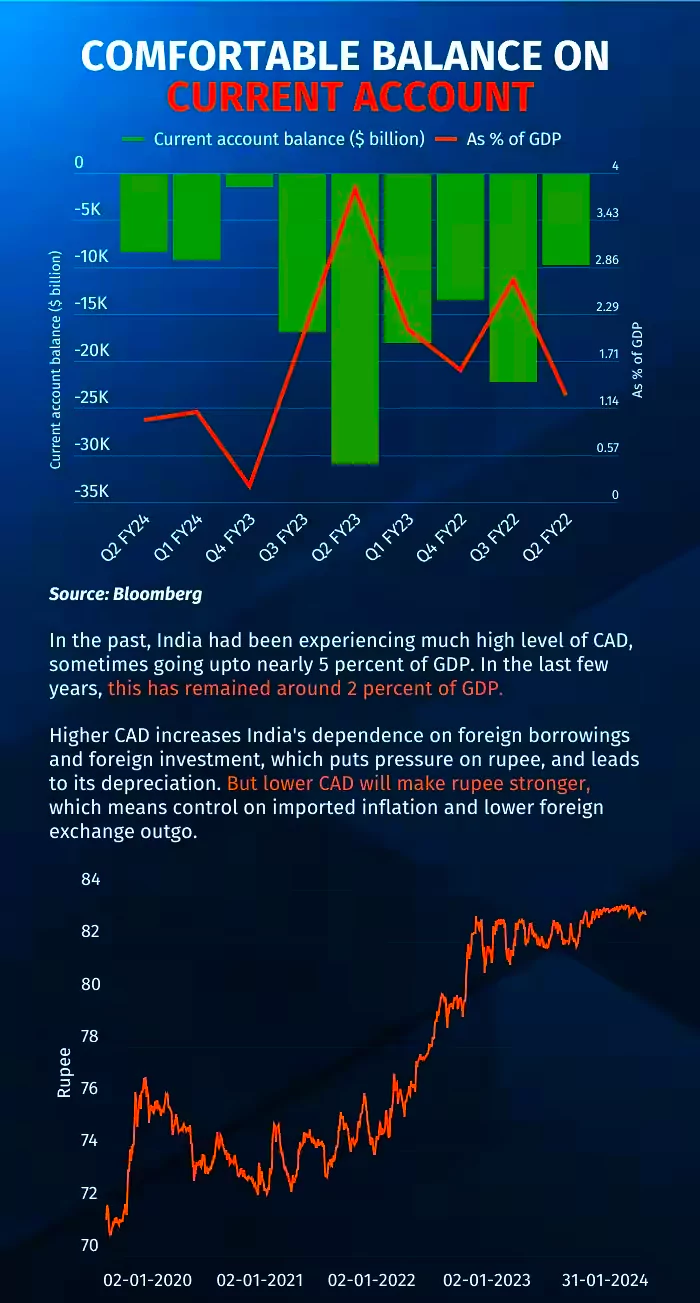
Recently, RBI revealed in its data that India’s current account deficit (CAD) narrowed to $10.5 billion, or 1.2 % of gross domestic product (GDP), in the third quarter (October-December) of FY2024.
Key Highlights of RBI Data
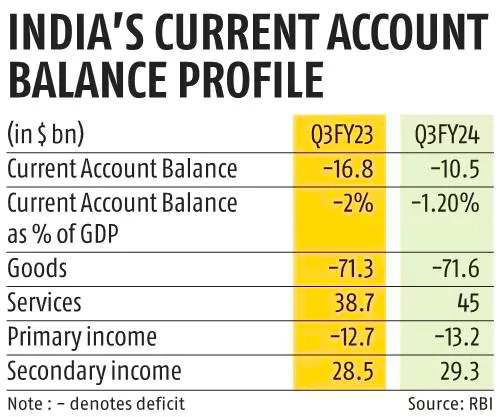
- Current Account Deficit narrowed down to $10.5 billion in the 3rd Quarter from $16.8 billion, or 2% of GDP, in the year-ago quarter.
- In the second quarter of FY2024, the country CAD stood at $11.4 billion, or 1.3 per cent GDP.
- Merchandise trade deficit was marginally higher at $71.6 billion (in Q3 FY2024) than $71.3 billion during Q3 FY2023.
- Services exports grew by 5.2 % on a y-o-y basis due to the rising exports of software, business and travel services.
- Net services receipts increased from a year ago that helped cushion the current account deficit.
- Private transfer receipts (representing remittances by Indians employed overseas) amounted to $31.4 billion, an increase of 2.1 per cent over their level during the corresponding period a year ago.
- Foreign direct investment recorded a net inflow of $4.2 billion as compared with a net inflow of $2 billion in Q3 FY2023.
 Foreign portfolio investment recorded a net inflow of $12 billion, higher than $4.6 billion during Q3 FY2023.
Foreign portfolio investment recorded a net inflow of $12 billion, higher than $4.6 billion during Q3 FY2023. - External commercial borrowings to India recorded a net outflow of $2.6 billion in Q3 FY2024 as compared with a net outflow of $2.5 billion a year ago.
- Non-resident deposits recorded a higher net inflow of $3.9 billion than $2.6 billion a year ago.
- Increase in Foreign exchange reserves (on a balance of payment (BoP) basis) to the tune of $6 billion.
What is the Current Account Deficit and Its Trends?
- Current account deficit is the difference between exports and imports of goods and services.
- It is a key indicator of the country’s external sector.
- Components: It is the sum of Balance of Trade (Export minus Imports of Goods and Services) + Net Factor Income from Abroad (Interest income and Dividends, etc) and Net Transfer Payments ( Eg- Foreign Aid)
- Formula: Current Account = Trade Balance+Net factor income+Net transfer payments
- “Twin deficit” : The situation in which one nation has a current account deficit (trade deficit) and Fiscal deficit at the same time.
- Fiscal Deficit= Total Expenditure- Total Receipts (excluding borrowings).
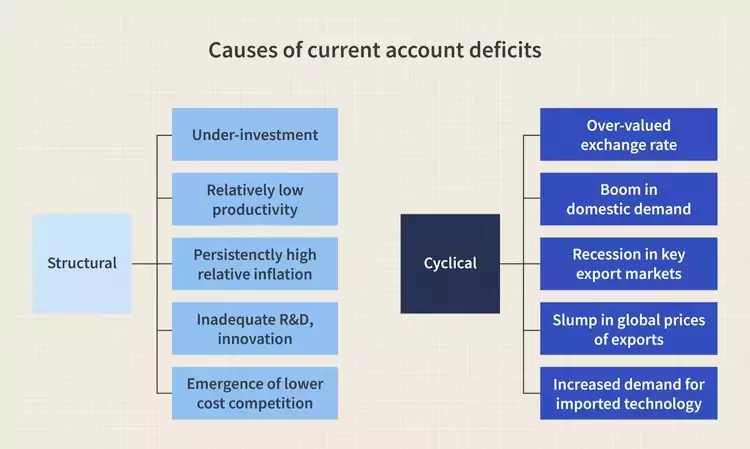
Causes of Current Account Deficit
Implication of Current Account Deficit
- Depreciation of Rupee: A large current account deficit for a continued period of time can lead to depreciation of rupee, and the demand for foreign currency (especially dollars) will see a rise.
- Inflation: Depreciation of rupee, as a result of continued deficit in the country’s current account, will see prices of imported goods becoming costlier, and in turn pushes the country towards inflation.
- Elevated Interest Rates: It will affect the investment & consumption cycle of the economy.
- Economic Growth: Persistent CAD affects economic imbalances which further hinders sustainable growth prospects of the country.
- Trade Balance: Due to Current account deficits Competitiveness & stability of Domestic Industries will get affected.
How can India Moderate Current Account Deficit?
Following are the factors that can moderate India’s current account deficit:
- Reduce the price of commodities.
- Appreciation of rupee.
- Lessen debt taken from developed nations.
- Reduce foreign ownership of assets.
- Improve the quality of imported goods.
- Reduce non-essential imports of gold, mobiles, and electronics.
- Increase value of exports.
Balance of Payment and Its Components
- Definition: Balance Of Payment (BOP) is a bookkeeping system that summarizes the country’s economic transaction with other countries of the world for a particular period.
- Impact: BoP keeps track of the trade and investments and transfers in a country with the rest of the world.
- Components: The BoP is composed of Capital and Current Accounts.
|
Current Account |
Capital Account |
| Definition |
The current Account is the account that records the goods exports and imports, as well as trade in services and transfer payments. |
Capital Account is the account that keeps track of Borrowing and Lending of Capital assets and non-financial assets between the countries. |
| Components |
The current account is made up of visible trade( Goods), invisible trade (Services), transfer payments, net factor income, and remittances |
The current account is made up of borrowings, lendings and investments. |
| Impact |
The current account of a country keeps track of the country’s transactions with other countries. |
The capital account of a country keeps track of the country’s investment and loans with other countries. |
Also Read: Why Have GDP And GVA Growth Rates Diverged?
![]() 27 Mar 2024
27 Mar 2024

 Foreign portfolio investment recorded a net inflow of $12 billion, higher than $4.6 billion during Q3 FY2023.
Foreign portfolio investment recorded a net inflow of $12 billion, higher than $4.6 billion during Q3 FY2023. 