Context: Recently a report on mRNA vaccine technology was published by WHO’s Science Council highlighting the potential benefits and limitations of mRNA vaccine technology was released.
Report on mRNA vaccine technology: WHO
- Importance of R&D: The report reveals the importance of research and development (R&D) efforts to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and outlines the challenges of inequitable access.
- Global distribution: mRNA Global distribution of COVID-19 vaccinations was uneven because of a lack of resources for research and development as well as obstacles pertaining to intellectual property.
- Customized mRNA: The ability to get easily customized, increases their potential as effective personalized therapies with fewer side effects.
About mRNA
- Messenger RNA (abbreviated mRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis.
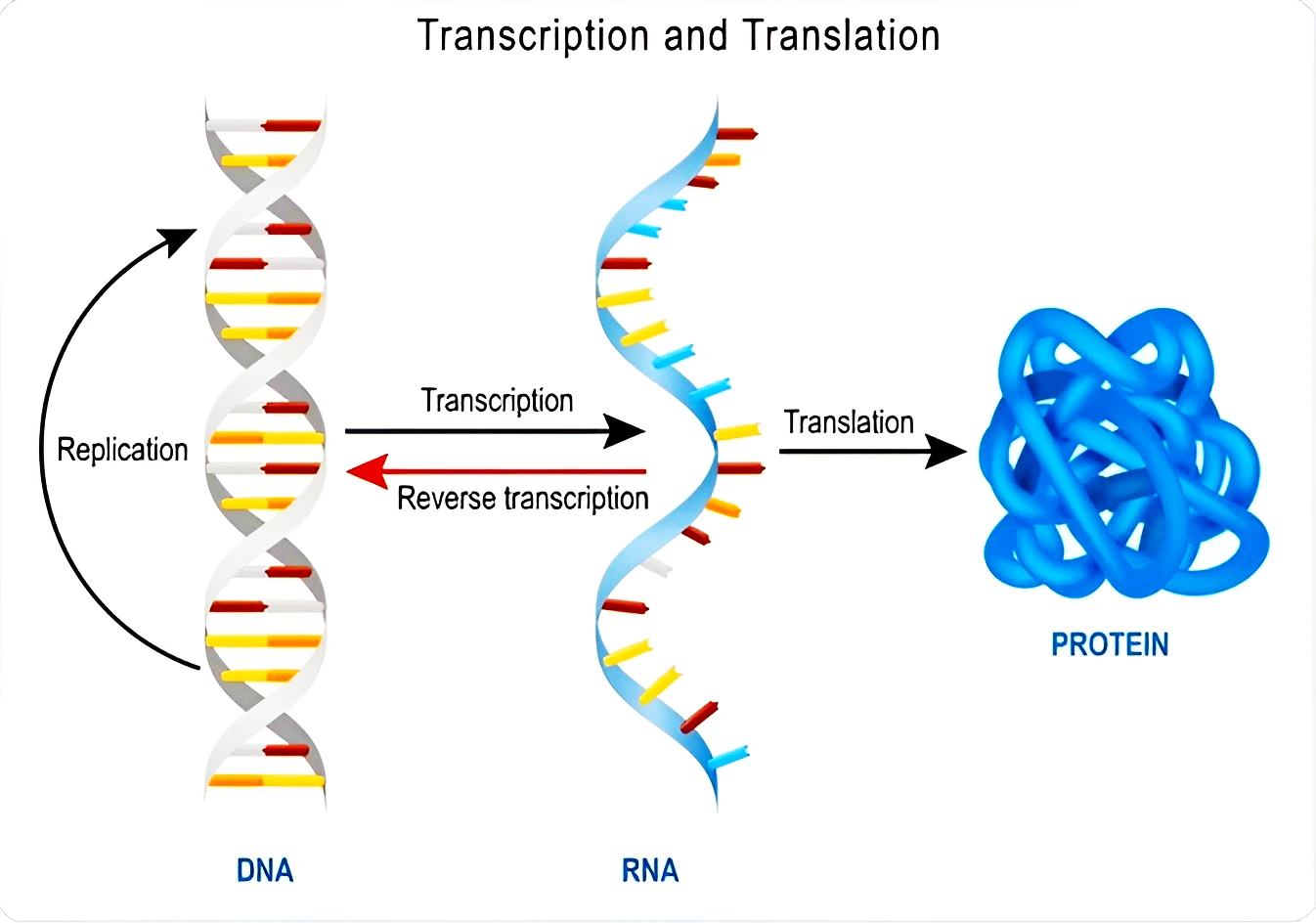
- Formation: mRNA is made from a DNA template during the process of transcription
- Purpose: Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts.
About RNA:
- Ribonucleic acid (abbreviated RNA) is a nucleic acid present in all living cells that has structural similarities to DNA.
- It contains the following nitrogenous bases: adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.
- Function: To create proteins via translation.
Types of RNA:
- tRNA: Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA) molecules carry amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- rRNA: rRNARibosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules form the core of a cell’s ribosomes (the structures in which protein synthesis takes place)
Protein synthesis:
- Protein synthesis is a two stage process involving:
- Transcription: It refers to the transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA in the nucleus.
- Translation: In this process the instructions in mRNA are read, and tRNA brings the correct sequence of amino acids to the ribosome. Then, rRNA helps bonds form between the amino acids, producing a polypeptide chain.
|
Application of mRNA
- Precisional drugs: It has scope in preventing and treating many intractable diseases.
- For Example: mRNAs are used to treat propionic acidaemia, a disease where children have low levels of two liver proteins (which prevents toxic by-products from building up in the body)
- Easy to customize: Easy to customize for any protein, mRNAs can be edited to meet the needs of the patient through targeted drug delivery
- mRNA-based cancer therapeutics: It helps in encoding tumor antigens for cancer vaccines, cytokines for immunotherapy, tumor suppressors to inhibit tumor development.
To Read More about mRNA Vaccines:
![]() 19 Dec 2023
19 Dec 2023
