Indians are likely to lose over ₹1.2 lakh crore over the next year to cyber-frauds, shows a projection made by the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), which runs under the Union Home Ministry.
Key Highlights of the Projections
- Projected Losses: Losses through cyber fraud is expected to be 0.7% of the country’s GDP.
- Mule Bank Accounts: These accounts, used to facilitate illegal transactions and launder money, are significant contributors to online financial scams.
- Around 4,000 mule accounts were identified each day that are involved in facilitating fraud.
- ATM Fraud Hotspots: I4C has identified 18 ATM hotspots across India where money is fraudulently withdrawn, and withdrawals have been traced to overseas ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia.
- Scam Compounds: Fraud compounds resembling call centers have been identified in Southeast Asia (Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos), and recently, in Azerbaijan, from where scammers target people in India using Indian mobile numbers.
- Crypto-linked Money Laundering: Between March and May, cryptocurrency worth ₹5.5 crore was laundered out of the country through international crypto exchanges using over 350 transactions.
- Total Losses Reported: Financial fraud losses reported through the MHA’s cybercrime portal and helpline until June 30, 2023, totaled ₹11,269 crore, though unreported cases exist.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Action suggested to avoid such frauds
- Banking System Vulnerabilities: The government emphasises that banks should improve their systems to detect and flag unusual transactions.
- Special monitoring of high-value transfers in accounts with low balances, multiple account logins from single IP addresses, and sudden increases in transaction volume.
- Action Plans: The MHA is set to meet with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India to develop mechanisms to curb mule accounts and prevent further losses.
What is cyber fraud?
- Cyber fraud is a blanket term to describe crimes committed by cyberattackers via the internet.
- These crimes are committed with the intent to illegally acquire and leverage an individual’s or business’s sensitive information for monetary gain.
Examples of Cyber Fraud Threats
- Phishing Scams: Fake emails from seemingly trusted sources trick users into revealing sensitive data, like passwords or financial information.
- Malware Attacks: Malicious software designed to harm systems, steal data, or create backdoor access for attackers.
- Ransomware: Criminals encrypt files and demand payment for decryption, often through email attachments or malicious links.
- DDoS Attacks: Overwhelm servers or networks to disrupt services, using botnets or exploiting protocol vulnerabilities.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals emotionally to extract confidential information through personalised contact.
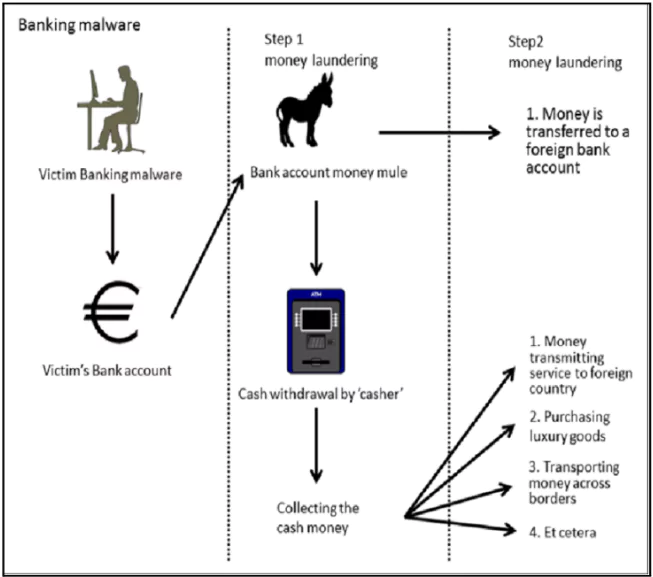
About Mule bank Account
- Money mule account : Refers to a bank account that is used to receive and transfer funds acquired illegally on behalf of others.
- Money Mule: Someone who transfers or moves illegally acquired money on behalf of someone else.
- Person may become a money mule intentionally or unintentionally by receiving illegally acquired funds and helping in its transfer to others.
- For Example: Fraudsters may approach prospective victims (mule account holders) with some offers and ask the victims to lend, share or rent their bank accounts/ cards.
- Money mules add layers of distance between crime victims and criminals, which makes it harder for law enforcement to accurately trace money trails.
- Mode of transactions: Move funds in various ways including through bank accounts, cashier’s checks, virtual currency, prepaid debit cards, or money service businesses.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre
- I4C is an initiative of the Ministry of Home Affairs to deal with cybercrime in the country in a coordinated and comprehensive manner.
- It was approved in October 2018.
Objectives of I4C
- To act as a nodal point to curb Cybercrime in the country.
- To strengthen the fight against Cybercrime committed against women and children.
It has seven components
- National Cyber Crime Threat Analytics Unit
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal
- National Cyber Crime Training Centre
- Cyber Crime Ecosystem Management Unit
- National Cyber Crime Research and Innovation Centre
- National Cyber Crime Forensic Laboratory Ecosystem
- Platform for Joint Cyber Crime Investigation Team.
|
![]() 24 Oct 2024
24 Oct 2024


