BSNL, the state-owned telecom provider, has introduced India’s first direct to device satellite internet service, aiming to provide broadband connectivity to remote areas.
- The service was launched in collaboration with Viasat, a US-based communications company.
- Announced at the Indian Mobile Congress (IMC) 2024 and communicated by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2024
- The India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2024 is a key event for the global and Indian telecom sectors that took place from October 15–19, 2024 at Pragati Maidan in New Delhi.
- Theme: The theme for IMC 2024 is “The Future is Now”.
- Topics: The event will feature discussions on emerging technologies like 6G, 5G, AI, satellite communications, semiconductors, and EV.
- Organization: The Department of Telecommunications and the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) are organizing the event.
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Direct to Device Satellite Technology
- Direct to Device satellite technology is a connectivity solution that allows devices to directly communicate with satellites in orbit, bypassing traditional ground-based cellular towers.
- This technology provides network coverage in areas where cellular or Wi-Fi networks are unavailable, ensuring connectivity in remote or underserved regions.
How It Works
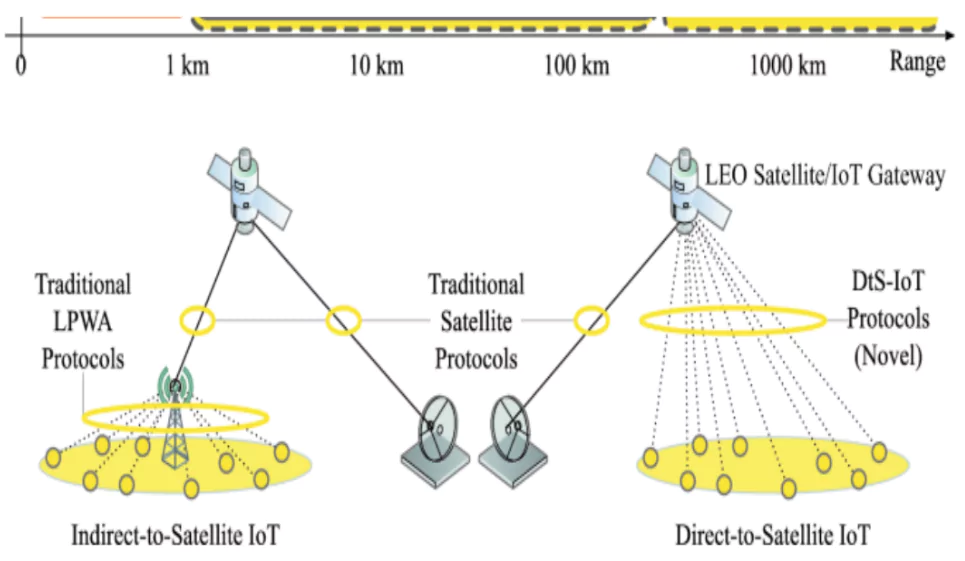
- Satellite Signal Transmission: Devices on the ground receive signals directly from satellites positioned in orbit, typically geostationary or low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN): Uses NTN technology for seamless two-way communication between devices and satellites.
- Geostationary Satellites: Positioned at an altitude of 36,000 km, these satellites provide broad coverage and reliable connections.
Key Features of D2D Satellite Technology
- Wide Area Coverage: D2D satellite technology can cover vast geographical areas, including remote regions with limited or no terrestrial network infrastructure. This makes it ideal for countries with diverse terrains or large rural populations.
- High-Speed Internet Access: This technology offers high-speed internet access, enabling seamless browsing, streaming, and online activities. This can bridge the digital divide and promote economic development in remote areas.
- Reliable Connectivity: D2D satellite technology is less susceptible to disruptions caused by natural disasters or infrastructure failures, ensuring reliable connectivity even in challenging weather conditions.
- Emergency Communication: It can be utilised for emergency communication in disaster-stricken areas or regions with limited network coverage, enabling vital communication during crises.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Support: D2D satellite technology can support IoT devices, facilitating remote monitoring and control of various systems. This can drive smart city initiatives and digital transformation.
Potential Benefits for India
- Connectivity for Remote Areas: Ideal for rural and sparsely populated regions where traditional infrastructure is hard to maintain.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Global Examples of Direct-to-Device Satellite Technology
- SpaceX’s Starlink: Aims to provide global satellite internet coverage, including direct-to-cell capabilities.
- AST SpaceMobile: Developing a satellite-based cellular network for direct connection to standard mobile phones.
- Lynk Global: Focuses on direct-to-phone satellite communication for emergency and remote areas.
- Constellation Network: Building a satellite-based network for IoT device connectivity.
|
- First Service for Regular Users: Unlike emergency-focused satellite communication, this service is available for regular public use.
- Economic Empowerment: It could support UPI payments and digital transactions, crucial for financial inclusion in underserved areas.
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Connects remote and underserved areas, promoting digital inclusion.
- Disaster Management: It facilitates communication and coordination during emergencies.
- National Security: It enhances communication capabilities for defense and strategic purposes.
- Travel and Safety: It is beneficial for travellers and adventurers needing reliable communication channels.
- Revival and Innovations by BSNL: Part of BSNL’s larger effort to revamp its services and stay competitive in the telecom sector.
Challenges
- High Initial Cost: Deployment and maintenance of satellite infrastructure can be expensive.
- Latency: There are chances to increase latency in real-time applications like video calls.
- Regulatory Framework: Requires clear regulations and spectrum allocation for seamless operation.
- Device Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility with various devices and operating systems are challenging.
- Propagation challenges: Overcoming signal loss and interference in diverse environments
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
D2D satellite technology holds immense potential to revolutionise connectivity, especially in countries like India. It can bridge the digital divide, empower remote communities, and contribute to socio-economic development. However, addressing challenges related to cost, latency, and regulatory frameworks is crucial for its successful implementation.
![]() 18 Nov 2024
18 Nov 2024

