Recently, Cyclone rain-triggered landslides in the northeast & collapse of a stone quarry in Aizawl, Mizoram spotlights needs for building resilience to multistate disaster.
What is landslide and Its Causes?
Landslides are sudden movement of rock, boulders, earth or debris down a slope is termed as landslide.
- Factor: when the pull from gravity exceeds the strength of the geomaterial forming the slope of a hill or mountain.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Causes of landslides
- Due to Natural Factors: Occurs mainly in mountainous terrains where there are conducive conditions of soil, rock, geology and slope.
- Natural causes that trigger it include heavy rainfall, earthquakes, snow melting and undercutting of slopes due to flooding.
- Due to the Anthropogenic activities: such as excavation, cutting of hills and trees, excessive infrastructure development, and overgrazing by cattle.
Landslide Concerns & Vulnerability
India is among the top five landslide-prone countries globally, where at least one death per 100 sq km is reported in a year due to a landslide event.
- According to the Geological Survey of India (GSI), About 0.42 million square km of India’s landmass, or about 13% of its area, spread over 15 states and four Union Territories, is prone to landslides,
- This covers almost all the hilly regions in the country.
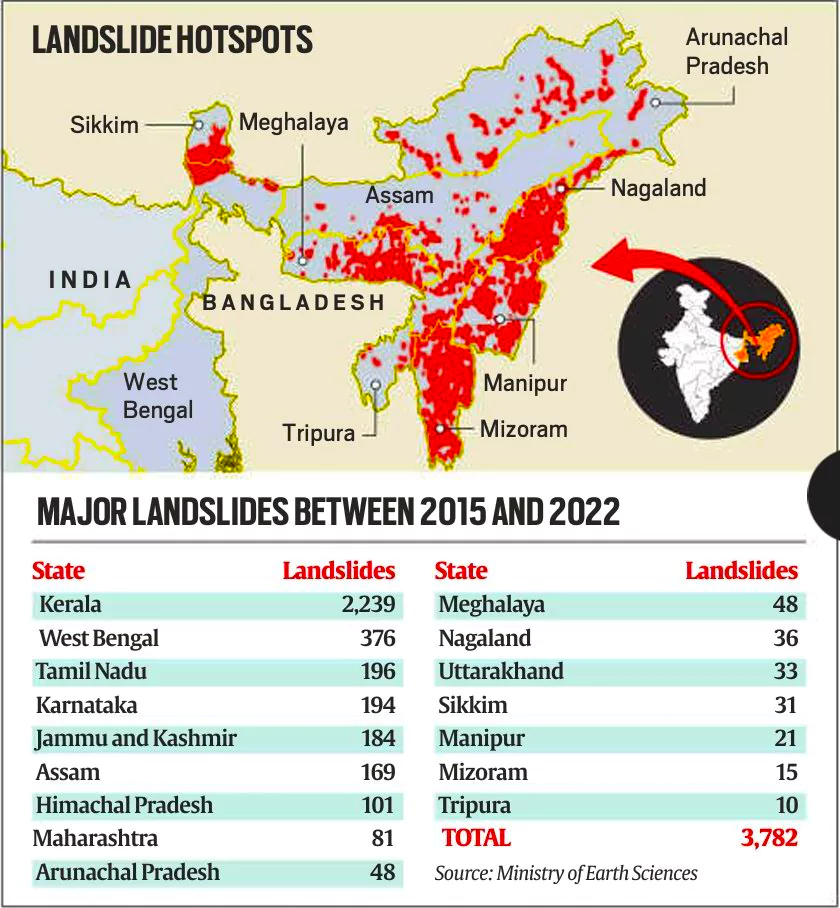
- North Eastern States: About 0.18 million square km, or 42% of this vulnerable area is in the Northeastern region, where the terrain is mostly hilly.
- Between 2015 and 2022, the eight states in this region, including Sikkim, recorded 378 major landslide events which resulted in loss of life or damage to property.
- These events constituted 10% of all major landslides in India during this period.
- In the country as a whole, Kerala saw the largest number of landslides 2,239 most of which occurred after the disastrous 2018 floods in the state.
Landslide Trigger Multi-hazard Disasters
One event can trigger another, and can lead to multiple disasters simultaneously. Over the last few years, India has witnessed events in which heavy rainfall has resulted in a breach of glacial lakes, causing flash floods that have resulted in landslides and flooding.
- Effect: Massive power outages, transport and communication failures, disruption of health services, and difficulties in rescue and relief operations have followed.
- Lack of Regulations & Ineffective Implementation: Many hilly areas lack proper building regulations & not enforced effectively. The risk from landslides has been exacerbated by the failure to maintain terrain’s ability to withstand the load.
- New constructions, infrastructure development, and agricultural practices can heighten the risk of landslides.
Why is it difficult to predict landslides?
- Complexity of Geomaterials: Underneath the ground, geomaterials consist of multiple, intertwined layers of various rocks and particulate materials like sand, silt, and clays.
- Their strength can vary significantly, from a factor of one to 1,000, and their spatial distribution influences slope stability.
- Incomplete Data and Uncertainty: Accurate slope stability assessment necessitates three-dimensional mapping of these materials and their strengths.
- No sensor can provide this comprehensive information that forces geologists and geotechnical engineers to rely on partial data from select locations and extrapolate it to the entire slope.
- Runout Distance and Safe Zones: While it is known that larger landslides have longer runout distances, predicting the exact size of a landslide is difficult, making the determination of runout distances and safe zones uncertain.
- Timing of Landslides: To Determine when a landslide will occur is also uncertain.
- Only Mechanical analysis can estimate the vulnerability of a slope under specific scenarios, including earthquake magnitude and groundwater distribution.
- However, To predicate the timing of these triggers is as challenging as predicting weather and seismic activity.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
What are the Measures taken by the Government which need to be expedited?
To effectively mitigate and manage landslide risks, the government has initiated several measures aimed at early warning and sustainable development. These efforts, ranging from advanced rainfall prediction systems to the implementation of the National Landslide Risk Management Strategy, are crucial in reducing the impact of landslides on vulnerable communities. Below is a summary of the key measures and their current status.
Early Warning
- An early warning system is still being tried out & deployed on a trial basis at a few locations.
- These warning systems are linked to rainfall forecasts from IMD.
- The rainfall prediction is combined with soil and terrain information to calculate whether it is likely to result in displacement of land.
In any case, since earthquakes themselves cannot be predicted, we cannot have a landslide early warning based on earthquakes. But rainfall-based early warning systems for landslides seem to work well.
Rainfall forecasts
- Reliable location-specific predictions are available at least a day in advance.
- Scientists create a rainfall threshold for land movement and soil displacement at each landslide-prone location.
- If the rainfall forecast is higher than the threshold, an early warning for landslides is issued.
- Usually, a single day’s rainfall does not trigger landslides, unless there is a cloudburst event. Sustained heavy rainfall over a week or 10 days is what becomes dangerous.
A National Landslide Risk Management Strategy (2019)
- It mentions vulnerability mapping, identifying the most vulnerable locations, development of an early warning system, and preparation of mountain zone regulations.
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- It has been working with GSI and other agencies to mitigate and manage the risks from landslides.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Need for Regulated & Sustainable Development
- Development is essential for infrastructure and economic activities but it must be regulated by maintaining the area’s carrying capacity.
Also Read: Landslide Susceptibility Map For India: By IIT Delhi
![]() 29 May 2024
29 May 2024
