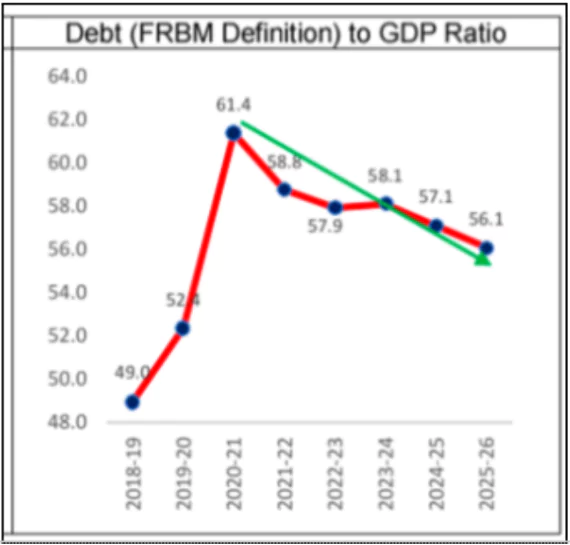
The Union Government has announced a transition from fiscal deficit to Debt-to-GDP ratio as the primary fiscal anchor starting from FY 2026-27 with an aim to reduce the Debt-to-GDP ratio to 50±1% by 2031.
About Debt-to-GDP Ratio
- Definition: Measures the total accumulated debt of a country, including past and present borrowings, relative to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- In numerical terms, the debt-to-GDP ratio is expressed as a percentage, to illustrate the number of years it would require to repay debt if GDP is dedicated solely to debt servicing
- Indicates:
- The level of debt compared to the size of the economy.
- A country’s ability to repay its debt based on economic performance.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course

- Debt-to-GDP Ratio Trends in Global Economies:
- The global debt-to-GDP ratio in 2023 showed varied trends across economies
- Advanced economies (AEs) excluding the U.S. saw a 9 percentage point decline to 268% of GDP, driven by reductions in private and public debt.
- The U.S. contributed to the global reduction, with private debt falling to 150% of GDP, though public debt rose to 123%.
- Emerging markets (EMs) excluding China experienced a 3 percentage point increase to 126% of GDP, driven by rising public debt.
- China’s total debt surged to 289% of GDP, with both public and private debt rising significantly.
 Low-income developing countries (LIDCs) also saw debt increase to 88% of GDP, primarily due to higher public debt, despite falling private debt.
Low-income developing countries (LIDCs) also saw debt increase to 88% of GDP, primarily due to higher public debt, despite falling private debt.
- Interpretation:
- High Debt-to-GDP Ratio: Indicates high borrowings, raising concerns about repayment capacity.
- Low Debt-to-GDP Ratio: Suggests better fiscal health with manageable debt levels.
Debt-GDP Reduction Target
- To achieve the debt-GDP reduction target, the government has outlined three scenarios based on different nominal GDP growth rates:
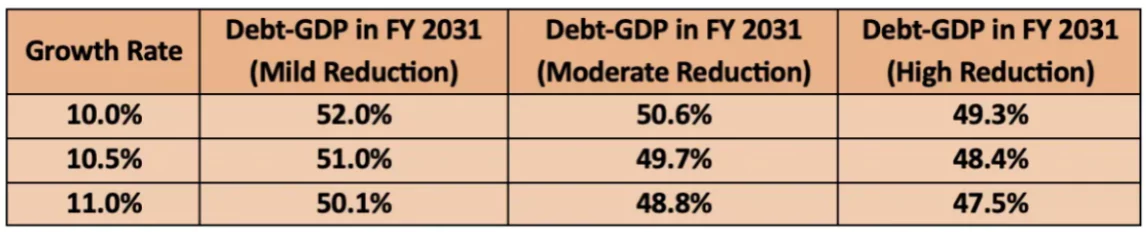
- This approach allows flexibility in choosing mild, moderate, or aggressive fiscal consolidation, balancing growth needs with debt sustainability.
Significance of maintaining Low Debt-to- GDP ratio:
- A prudent debt-to-GDP ratio is essential for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring economic resilience.
- Low Debt-to GDP Ratio is necessary to create space for growth-enhancing expenditures, which is critical to achieve the growth ambitions in the broader economy.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Rationale for the Shift to Debt-to-GDP Ratio
- Long-Term Financial Sustainability: Assesses the nation’s ability to manage debt over time.
- More Reliable Fiscal Measure: Captures the cumulative impact of past and present fiscal policies, unlike the annual fiscal deficit, which only measures short-term performance.
- Global Best Practices: Aligns with international fiscal standards, promoting greater flexibility in economic management.
- Enhances Transparency: It encourages shift from rigid annual fiscal targets towards more transparent and operationally flexible fiscal standards.
- Ensures proper disclosure of off-budget borrowings, reducing hidden liabilities.
Limitations of Debt-to-GDP Ratio
- Ignore Debt Composition: Does not differentiate between internal (domestic) debt and external (foreign) debt.
- Does Not Reflect Fiscal Policy Efficiency: Fails to capture whether government spending is productive or wasteful.
- No Direct Correlation with Default Risk: Some high-debt countries remain solvent due to strong economic fundamentals.
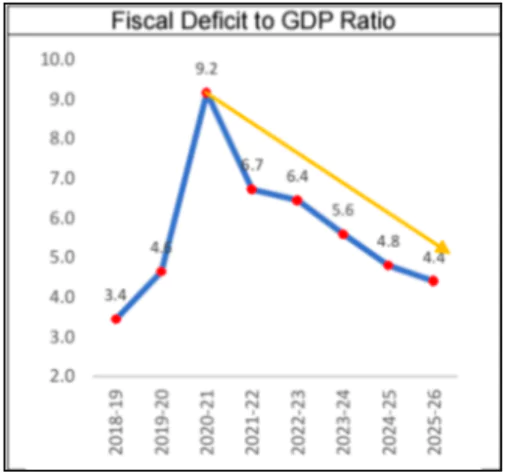
About Fiscal Deficit
- Definition: The difference between total government expenditure and total revenue (excluding borrowings) within a financial year.
- Indicates: The amount of borrowing required to meet government spending needs.
- Formula:
| Fiscal Deficit = Total Government Expenditure − Total Revenue (Excluding Borrowings) |
- Interpretation:
 High Fiscal Deficit: Suggests the government is spending more than its earnings, leading to increased borrowing.
High Fiscal Deficit: Suggests the government is spending more than its earnings, leading to increased borrowing.- Low Fiscal Deficit: Indicates better financial management, reducing reliance on debt.
- Need of Controlling Fiscal Deficit:
- Impact on Inflation: A persistently high fiscal deficit can lead to inflation as the government may resort to printing more money to fund expenditures.
- Improves Credit Ratings: Lower fiscal deficit demonstrates fiscal discipline, improving India’s credit ratings and reducing borrowing costs.
- Better Public Debt Management: A lower fiscal deficit helps the government secure cheaper credit in international markets and attract investors.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
- The shift from fiscal deficit to Debt-to-GDP ratio as the primary fiscal anchor reflects India’s commitment to fiscal sustainability and transparency.
- By adopting a structured debt-reduction strategy, the government aims to enhance financial stability, improve creditworthiness, and create fiscal space for growth-oriented investments, ensuring long-term economic resilience and responsible debt management.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 6 Feb 2025
6 Feb 2025


 Low-income developing countries (LIDCs) also saw debt increase to 88% of GDP, primarily due to higher public debt, despite falling private debt.
Low-income developing countries (LIDCs) also saw debt increase to 88% of GDP, primarily due to higher public debt, despite falling private debt.
 High Fiscal Deficit: Suggests the government is spending more than its earnings, leading to increased borrowing.
High Fiscal Deficit: Suggests the government is spending more than its earnings, leading to increased borrowing.