Recently, Scientists warned that due to climate change-induced rising sea levels, Delos, a small island in the Aegean Sea near bustling Mykonos, could disappear within the next 50 years.
Impact of Rising Sea Level on Delos Island
- Studies suggest that higher temperatures and humidity can change the chemical makeup of materials found in cultural heritage monuments.
- This risk is amplified by evident structural deterioration caused by seawater erosion, notably impacting structures such as trade and storage buildings dating back to the first and second centuries BCE.
Delos Island
- About: Delos, situated in the Aegean Sea as part of the Cyclades archipelago, is a rocky island. It was initially inhabited in the 3rd millennium B.C. and gained prominence in the 1st millennium B.C.
- Today, Delos remains mostly uninhabited, featuring rugged granite terrain that spans approximately 1.3 square miles.
- History: Delos was revered as a holy sanctuary for a thousand years before being recognised as the birthplace of Apollo and Artemis in Olympian Greek mythology.The island’s Sacred Harbour includes three conical mounds linked to a goddess, Athena.
- UNESCO designated Delos as a World Heritage Site for its outstanding archaeological remains, significant influence on Greek architecture, and its sacred importance in Ancient Greece.
- Archaeological Importance: Extensive excavations have unearthed artefacts now exhibited at the Archaeological Museum of Delos and the National Archaeological Museum of Athens.
- The island has been inhabited since the third millennium BCE and functioned as a significant cult center for deities such as Dionysus and Leto.
- Delos underwent purification rituals to ensure the proper veneration of gods, which included relocating graves that were visible from the temple.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Aegean Sea
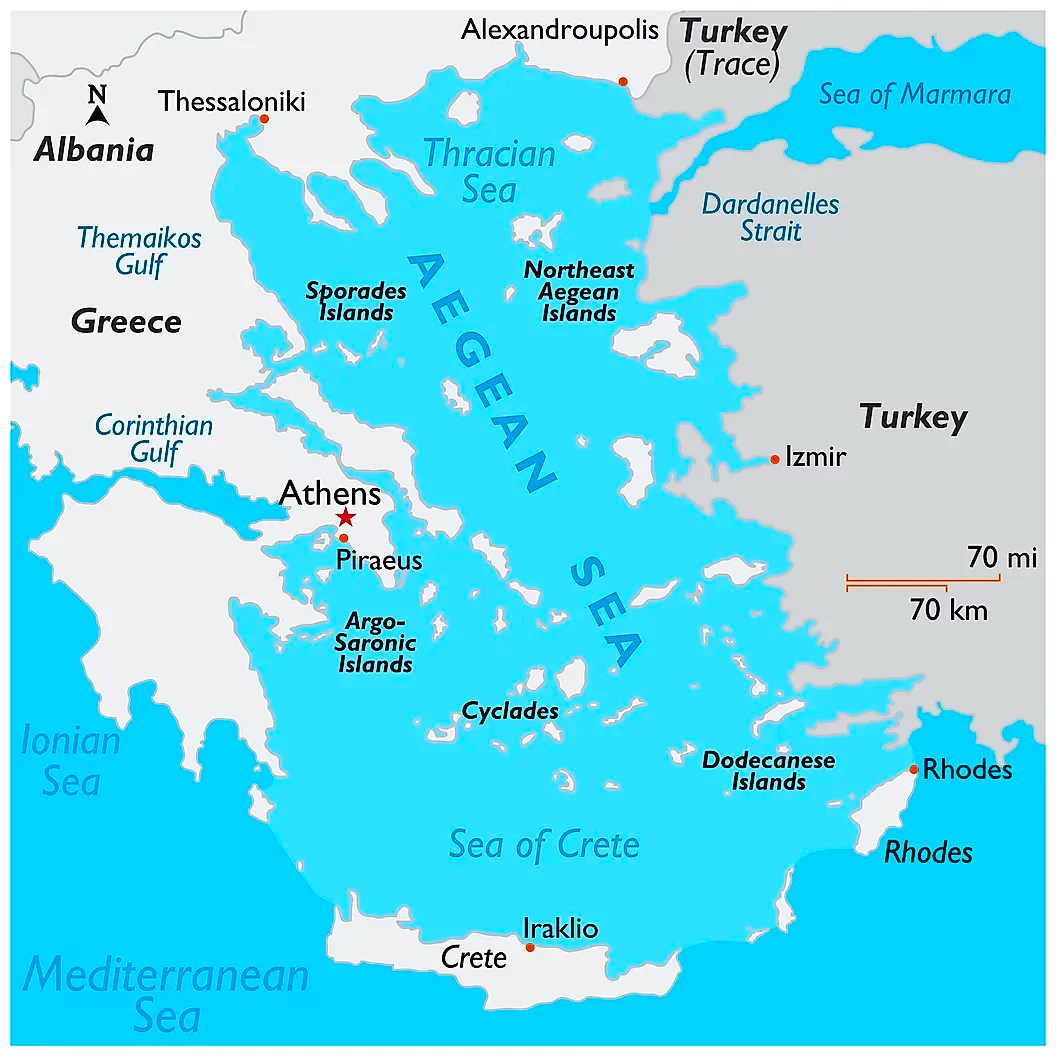
- Geographic Location of Delos: Delos is situated in the Eastern Mediterranean Basin, bordered by the Greek peninsula to the west and Anatolia (the Asian side of Turkey) to the east.
- Straits: The Bosphorus and Dardanelles Straits connect the Aegean Sea to the Black Sea and the Marmara Sea.
- Ownership of Aegean Islands: Most of the Aegean Islands are part of Greece. Turkey’s notable possessions in the Aegean Sea include Imbros (Gökçeada) and Tenedos (Bozcaada), located in the northeastern part of the sea.
- Climate: It features a Mediterranean climate similar to that of Western Turkey and Greece. The climate is classified as Hot-summer Mediterranean, with dry and hot summers and wetter, milder winters. Summers in the region are cooler compared to arid and semi-arid climates.
- The northern part of the Aegean Sea experiences a cold, semi-arid climate characterized by cooler summers.
- The weather in the Aegean basin is predominantly influenced by the Etesian wind.
![]() 22 Jun 2024
22 Jun 2024
