Denmark has announced a €2 billion investment to strengthen its military presence in the Arctic and North Atlantic region.
Key Highlights of Denmark Initiative
- The move comes amid repeated statements by the U.S. President Donald Trump about acquiring Greenland, despite Denmark’s firm rejection
- Military Expansion: Denmark plans to enhance Arctic security with:
- Three new Arctic naval vessels.
- Two additional long-range surveillance drones.
- Improved satellite capacity.
- Diplomatic Engagement:
- PM of Denmark Frederiksen is set to meet NATO allies to reinforce unity on Greenland’s sovereignty.
- Denmark has emphasized the need for European unity on security and sovereignty issues.
- Germany has indirectly criticized Trump’s stance, stating that borders should not be altered by force.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About the Arctic Circle
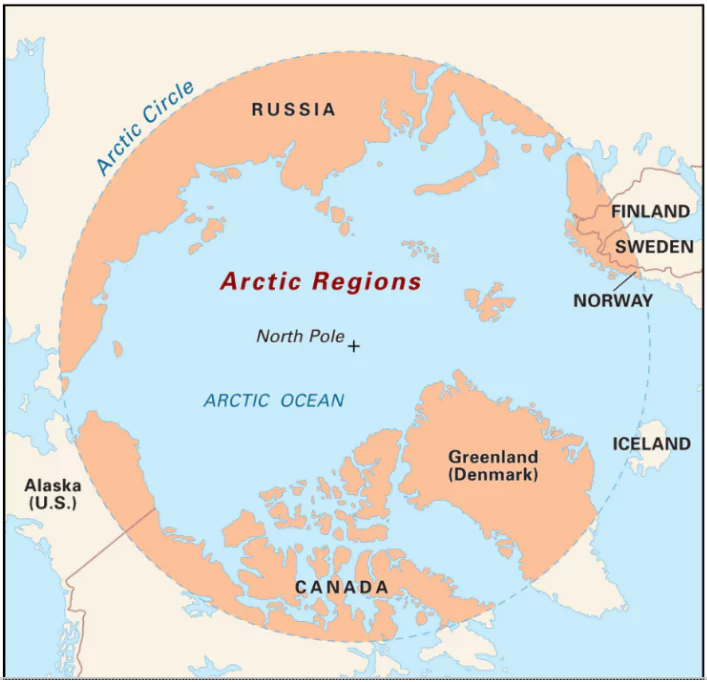
- Countries with Arctic Territory: Eight countries have sovereignty over parts of the Arctic: Canada, Denmark (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and the United States (Alaska).
- Vegetation: The region is characterized by tundra vegetation, with low shrubs, mosses, and lichens due to extreme cold and permafrost.
- Significance:
- Rich in natural resources such as oil, gas, and minerals.
- Key for global shipping routes due to melting ice, opening the Northern Sea Route.
- Crucial for climate studies as Arctic ice influences global weather patterns.
Climate Change Challenges in the Arctic
- Rising Temperatures: The Arctic is warming nearly four times faster than the global average, leading to ice melting and habitat loss.
- Sea Level Rise: Melting glaciers contribute to global sea-level rise, threatening coastal communities worldwide.
- Biodiversity Loss: Wildlife such as polar bears and Arctic foxes face survival threats due to habitat shrinkage.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Increased accessibility to Arctic resources has led to territorial disputes and military activities.
International Organizations for the Arctic
- Arctic Council: A key intergovernmental forum comprising Arctic states, Indigenous groups, and observers, focused on sustainable development and environmental protection.
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS): Governs maritime rights and territorial claims in the Arctic Ocean.
- NATO’s Arctic Strategy: Addresses security concerns and military coordination among Arctic member states.
- International Maritime Organization (IMO): Regulates Arctic shipping through the Polar Code, ensuring environmental and safety standards.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Conclusion
Denmark’s Arctic defense initiative signals its commitment to regional security while responding to growing geopolitical challenges.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 31 Jan 2025
31 Jan 2025


